When it comes to ensuring the structural integrity of pipes in various industries, non-destructive testing, specially Dye Penetration test, play a pivotal role. One such method is the dye penetration test, commonly known as dye penetrant inspection or DPI. This technique allows inspectors to identify surface-breaking defects, such as cracks and discontinuities, in pipes without causing any damage. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the principles, procedure, benefits, and applications of the dye penetration test on pipes.
Table of Contents
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
By EPCLand.com
Understanding the Dye Penetration Test
The Basics of Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
Non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques are essential tools used to evaluate the properties of materials and components without causing any permanent alteration or damage. These methods are crucial in industries where safety, reliability, and structural integrity are paramount. NDT helps detect flaws, defects, and irregularities that might compromise the functionality of materials, ensuring that they meet quality standards.
Introducing the Dye Penetration Test
The dye penetration test is a widely used NDT method that focuses on identifying surface-breaking defects. It’s particularly effective for detecting flaws that are open to the surface, such as cracks, porosity, and leaks. This technique involves the application of a liquid dye penetrant followed by a developer, which brings out the penetrant from the defect. The penetrant highlights the defect, making it visible for inspection.
Principles of Operation
The foundation of this inspection method lies in the principle of capillary action, wherein a fluid with low surface tension has the ability to infiltrate fractures on a clean and dry surface. The application of penetrant to the test component can be achieved through various means such as dipping, spraying, or brushing. Following an appropriate penetration period, the excess penetrant is removed, and a developer is subsequently applied. The developer serves the purpose of coaxing the penetrant out of any flaw, rendering an initially invisible indication discernible to the inspector. The inspection itself takes place under either ultraviolet or white light, contingent on the nature of the dye employed—either fluorescent or nonfluorescent.
Utilized Materials
Penetrants are categorized into sensitivity levels:
- Visible Penetrants: Predominantly red in hue, these possess the lowest sensitivity level.
- Fluorescent Penetrants: Comprising two or more dyes that fluoresce upon exposure to ultraviolet (UV-A) radiation, these dyes emit a vivid yellow-green light against a dark backdrop in a dimly lit environment. This material exhibits heightened sensitivity to defects.
Dye Penetration Inspection Kit
The choice of inspection sensitivity level hinges on factors such as the testing environment, specimen surface finish, and defect size to be scrutinized. Furthermore, it’s imperative to ensure that the test chemicals are compatible with the sample, preventing permanent staining or degradation during examination.
The requisite kit for this testing can be as straightforward as a trio of aerosol cans often bundled by kit providers. Additionally, a supply of lint-free cloths and ample visible light is necessary. More advanced iterations of the kit encompass stationary systems equipped with dedicated application, wash, and development stations. Though more intricate and costly, these advanced kits offer heightened sensitivity and facilitate greater sample throughput.
The Dye Penetration Process: Step by Step
Preparing the Surface
Before the dye penetration test can begin, the surface of the pipe must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants that could interfere with the results. This step ensures that the penetrant can flow into any existing defects effectively.
Applying the Penetrant
The liquid penetrant is then applied to the surface of the pipe. The penetrant has a low viscosity, which allows it to seep into even the smallest surface discontinuities. It’s left on the surface for a specific period, known as the penetration time, during which it is drawn into any cracks or defects.
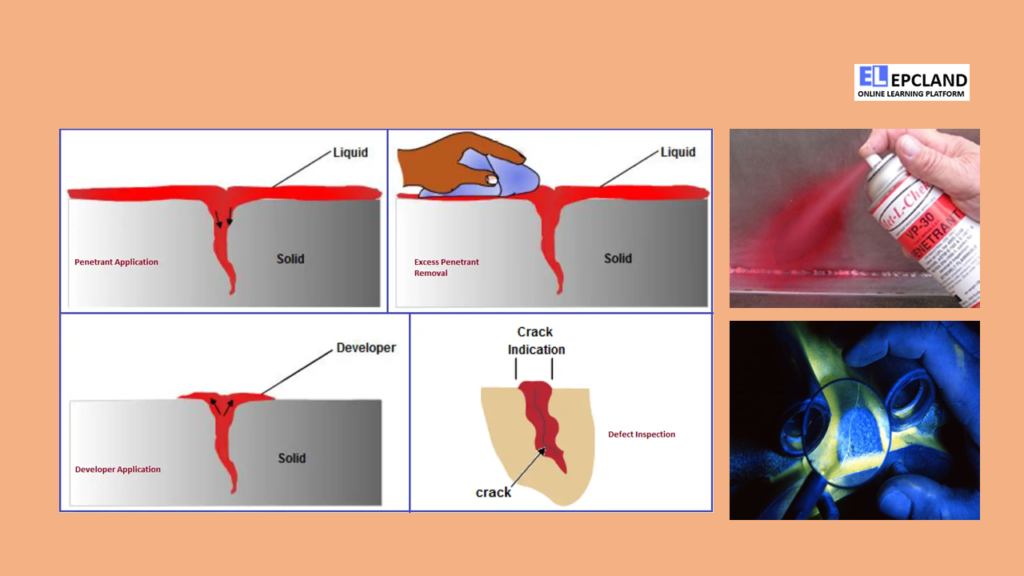
Removing Excess Penetrant
After the penetration time has elapsed, the excess penetrant is carefully removed from the surface of the pipe. This step prevents false indications caused by excess penetrant obscuring the defect.
Applying the Developer
The developer is applied to the surface after the excess penetrant has been removed. The developer acts as an absorbent, drawing the penetrant out of any defects and creating a visible indication on the surface.
Inspection and Interpretation
The inspector carefully examines the surface for any indications of defects. The indications appear as visible lines or spots where the dye has been drawn out of defects. The size, shape, and location of these indications provide valuable information about the nature and severity of the defects.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
By EPCLand.com
Benefits of Dye Penetration Testing
Sensitivity to Surface Defects
Dye penetration testing is highly sensitive to surface defects, making it an excellent choice for identifying cracks, pores, laps, and other irregularities that may be present on the outer layer of the pipe.
Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to other NDT methods, dye penetration testing is relatively cost-effective. The materials required for the test are readily available and don’t require specialized equipment.
Quick Results
Dye penetration testing provides rapid results, allowing inspectors to identify defects promptly. This quick turnaround time is particularly beneficial in industries where minimizing downtime is crucial.
Versatility
The dye penetration test can be used on various materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. This versatility makes it applicable across a wide range of industries.
Simplicity
The procedure for conducting a dye penetration test is relatively straightforward, making it accessible for both experienced professionals and those new to NDT techniques.
Applications of Dye Penetration Testing
Weld Inspections
Welded joints are critical components in many industries, and their integrity is paramount. Dye penetration testing can effectively detect defects in welds, ensuring that the joints are free from cracks and imperfections.
Manufacturing Quality Control
In manufacturing processes where pipes are fabricated, dye penetration testing can be employed to check for any defects that may have occurred during production.
Maintenance and Inspection
Dye penetration testing is valuable for routine maintenance and inspections of pipes in industries such as oil and gas, aerospace, automotive, and more. It helps identify potential issues before they lead to catastrophic failures.
Infrastructure Assessment
In industries involving infrastructure, such as water distribution and sewage systems, dye penetration testing can be used to evaluate the condition of pipes and identify defects that could impact their functionality.
FAQs
Q1: Is dye penetration testing suitable for all types of materials? A1: Dye penetration testing can be used on a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites.
Q2: How does dye penetration testing differ from other NDT methods? A2: Dye penetration testing focuses on surface defects and is particularly effective for identifying cracks and pores on the outer layer of materials.
Q3: Can dye penetration testing identify defects beneath the surface? A3: No, dye penetration testing is designed to detect surface-breaking defects. For defects beneath the surface, other NDT methods like radiographic testing or ultrasonic testing may be more appropriate.
Q4: How is excess penetrant removed before applying the developer? A4: Excess penetrant can be removed through methods such as wiping, water rinsing, or solvent cleaning, depending on the specific requirements of the test.
Q5: Is dye penetration testing a reliable method for identifying defects? A5: Yes, dye penetration testing is a reliable method for identifying surface defects, provided that the procedure is performed correctly and by trained inspectors.
In conclusion, the dye penetration test is a valuable non-destructive testing method that plays a crucial role in ensuring the structural integrity of pipes in various industries. By effectively detecting surface-breaking defects, this technique helps prevent failures and ensures that materials meet quality standards. From weld inspections to manufacturing quality control and infrastructure assessment, dye penetration testing has a wide range of applications that contribute to safer and more reliable operations.
Recommended courses (Published on EPCLand)
- Basics of Piping Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Complete Course on Piping Engineering
- Material Requisitions
- Piping Material Specifications
- Valve Material Specifications
Don’t miss the published articles on following:
Related Video
Attempt Quiz
Question 1:
What is the purpose of a Dye Penetration Test on pipes?
Explanation: The Dye Penetration Test is used to detect surface-breaking defects and discontinuities, such as cracks, porosity, and other imperfections, in the surface of pipes and other materials.
Question 2:
What is the basic principle behind the Dye Penetration Test?
Explanation: The basic principle of the Dye Penetration Test involves applying a liquid dye to the surface of the material, allowing it to penetrate any surface defects. Excess dye is removed, and the dye that remains in the defects is made visible under ultraviolet (UV) light.
Question 3:
Which type of defects can the Dye Penetration Test effectively detect?
Explanation: The Dye Penetration Test is most effective at detecting surface cracks, fissures, and other surface-breaking defects. It may not be suitable for detecting internal defects or corrosion.
Question 4:
Which step is typically performed after applying the dye during the test?
Explanation: After applying the dye to the surface, the next step typically involves cleaning the surface with a solvent or cleaner to remove excess dye. This helps to ensure that only the dye within defects remains visible under UV light.
Question 5:
Which industries commonly use the Dye Penetration Test for quality control?
Explanation: The Dye Penetration Test is commonly used in industries such as aerospace, manufacturing, and other engineering fields to ensure the quality and integrity of materials and components.



