Introduction
In the realm of quality assurance and materials evaluation, non-destructive testing (NDT) emerges as a pivotal technique. This article aims to elucidate the significance, methodologies, advantages, and applications of non-destructive testing. Whether you’re a professional in the field or a curious learner, this comprehensive guide with a minimum of 3000 words will offer insights into NDT’s multifaceted aspects.
Table of Contents
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
By EPCLand.com
Understanding Non-Destructive Testing
Non-destructive testing, often referred to as NDT or NDE (Non-Destructive Evaluation), encompasses an array of techniques to assess the integrity and properties of materials, components, and structures without causing any permanent alteration or damage.
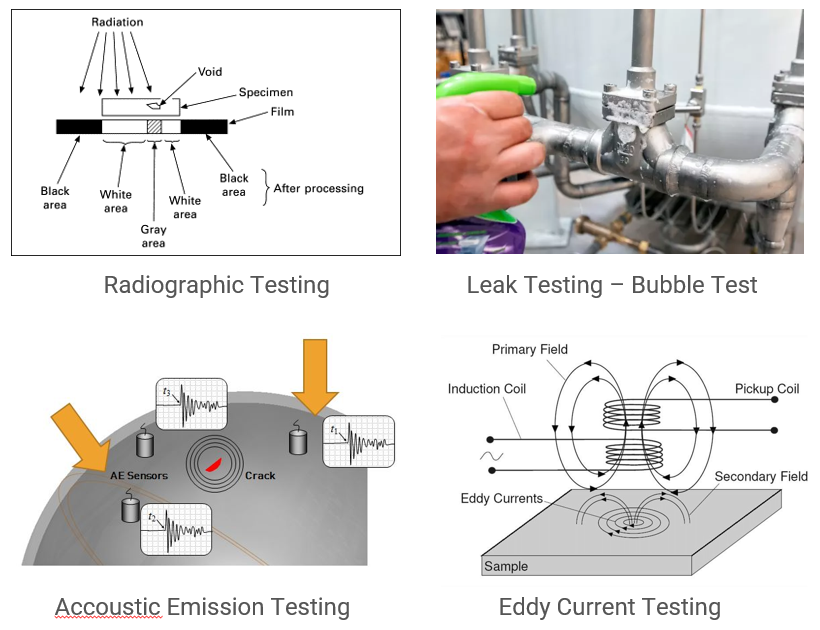
Methods of Non-Destructive Testing
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT)UT employs high-frequency sound waves to penetrate materials, detecting internal flaws such as cracks, voids, and material thickness variations. The echo patterns produced offer insights into a material’s condition.
- Radiographic Testing (RT)RT employs X-rays or gamma rays to produce images of a material’s internal structure. This method is particularly effective for detecting hidden defects in welds and castings.
- Magnetic Particle Testing (MT)MT is primarily used for ferromagnetic materials. By inducing a magnetic field and applying ferrous particles, this method can identify surface and near-surface defects like cracks and discontinuities.
- Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT)PT involves applying a liquid dye to the surface of a material. The dye penetrates surface-breaking defects, and excess dye is removed before applying a developer that makes the defects visible.
- Eddy Current Testing (ET)ET uses electromagnetic induction to identify surface and subsurface flaws, including cracks and conductivity variations. It’s commonly applied in industries like aerospace and automotive.
Benefits of Non-Destructive Testing
- Cost-Efficiency: NDT eliminates the need for destructive testing, which can be expensive due to material replacement costs. NDT minimizes downtime and saves resources.
- Enhanced Safety: By assessing materials without causing damage, NDT contributes to the overall safety of structures and components.
- Quality Assurance: NDT ensures the reliability and performance of products, reducing the likelihood of unexpected failures.
- Non-Intrusive: NDT techniques allow for assessment without dismantling or altering the structure, making it applicable to a wide range of scenarios.
Applications of Non-Destructive Testing
- Aerospace Industry: NDT is integral in examining aircraft components for defects that could compromise safety. UT and X-ray testing are commonly used to inspect critical parts.
- Welding and Fabrication: Weld joints can be prone to defects. NDT methods like radiography and ultrasonic testing validate the integrity of welds in various industries.
- Oil and Gas Sector: NDT ensures the reliability of pipelines, storage tanks, and pressure vessels, thereby preventing hazardous leaks.
- Automotive Sector: NDT guarantees the quality of automotive components, including engines, transmissions, and chassis, ensuring optimal performance.
- Construction Industry: NDT verifies the structural soundness of buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure, promoting public safety.
Challenges in Non-Destructive Testing
While NDT offers numerous advantages, it also faces challenges:
- Complexity: Some NDT methods require skilled technicians to interpret results accurately.
- Material Limitations: Certain materials may impede the penetration of waves or rays, affecting the effectiveness of NDT.
- Surface Conditions: Surface roughness or coatings can influence the accuracy of results.
Future Trends in Non-Destructive Testing
- Automation: The integration of robotics and AI could lead to automated NDT processes, enhancing efficiency and consistency.
- Advanced Imaging: Emerging imaging technologies may offer higher resolution and better defect visualization.
- Data Integration: NDT data can be integrated into digital systems, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
By EPCLand.com
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
FAQ 1 (Font Size: H3): What is the purpose of non-destructive testing?
Non-destructive testing aims to assess the integrity and properties of materials, components, and structures without causing any permanent damage. It ensures quality, safety, and performance.
FAQ 2 (Font Size: H3): How does ultrasonic testing work?
Ultrasonic testing involves sending high-frequency sound waves into a material. Echoes produced by internal flaws are analyzed to determine the material’s condition.
FAQ 3 (Font Size: H3): Is NDT only used in industrial settings?
No, NDT has applications in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, construction, and even the medical field.
FAQ 4 (Font Size: H3): Can NDT methods identify all types of defects?
No, different NDT methods excel at detecting specific types of defects. The choice of method depends on the material, the defect, and the depth at which it’s located.
FAQ 5 (Font Size: H3): Is NDT a replacement for destructive testing?
NDT is not a replacement but rather a complementary approach to destructive testing. It offers a non-intrusive way to assess materials and structures, reducing the need for destructive methods.
Conclusion
Non-destructive testing has transformed the way industries ensure quality, safety, and reliability. With its diverse methodologies, undeniable benefits, and a wide range of applications, NDT continues to play a vital role in maintaining the integrity of structures and components. As technology advances, we can anticipate further improvements in NDT processes, leading to safer, more efficient industries.
Recommended courses (Published on EPCLand)
- Basics of Piping Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Complete Course on Piping Engineering
- Material Requisitions
- Piping Material Specifications
- Valve Material Specifications
Don’t miss the published articles on following:
Related Video
Attempt Quiz
Question 1:
What is the primary purpose of Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)?
Explanation: The primary purpose of NDT is to identify and evaluate manufacturing defects, discontinuities, or irregularities in materials and structures without causing damage to them.
Question 2:
Which of the following NDT methods uses sound waves to inspect materials?
Explanation: Ultrasonic Testing (UT) uses sound waves to inspect materials and detect defects such as cracks, voids, and internal inclusions.
Question 3:
Which NDT method involves applying a magnetic field to a ferromagnetic material?
Explanation: Magnetic Particle Testing (MT) involves applying a magnetic field and ferromagnetic particles to detect surface and near-surface defects in ferromagnetic materials.
Question 4:
What is the primary advantage of Radiographic Testing (RT) in NDT?
Explanation: Radiographic Testing (RT) is advantageous for its ability to detect internal defects in materials and provide detailed images of the internal structure.
Question 5:
Which NDT method involves applying a liquid to the surface of a material to detect surface defects?
Explanation: Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT) involves applying a liquid dye or penetrant to the surface of a material to detect surface defects that may not be visible to the naked eye.



