1. Introduction
In the intricate web of industries where the flow of fluids is fundamental, ensuring safety, efficiency, and reliability is paramount. One of the key components contributing to this equilibrium is the Double Block & Bleed Valve (DBBV). This valve system plays a pivotal role in various sectors, including oil and gas, petrochemical, water treatment, and aviation. In this article, we delve into the depths of DBBV, exploring its evolution, fundamental functions, applications, and the standards governing its usage.
Table of Contents
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
2. Brief History
The roots of Double Block & Bleed Valve technology can be traced back to the early developments in fluid control mechanisms. As industries burgeoned and the need for safer fluid handling systems became apparent, engineers and scientists embarked on a journey to create a valve that not only controlled the flow of fluids effectively but also minimized the risks associated with leakage and contamination. Over the years, these efforts led to the birth of the Double Block & Bleed Valve as we know it today. Significant milestones in its development have reshaped industries’ approach to fluid control, ensuring a safer and more efficient operational landscape.
3. Basic Function and Working Principle
At its core, a Double Block & Bleed Valve is designed to provide two separate isolation seals in a single valve body, offering a compact solution for critical applications. The fundamental principle behind its operation lies in the arrangement of internal components. When the valve is in the closed position, it provides a double block, meaning it seals against pressure from both ends, isolating the downstream and upstream fluids effectively. Additionally, the bleed function allows for controlled venting or draining of the cavity between the seals, ensuring there is no residual pressure, which is crucial during maintenance or integrity checks.
4. Main Components & Their Functions
A typical Double Block & Bleed Valve comprises several essential components, each serving a specific function to maintain its integrity and functionality.
- Ball: The spherical ball within the valve body acts as the primary mechanism to block the fluid flow when the valve is in the closed position.
- Body: The outer casing of the valve that houses all internal components, providing structural support and stability.
- Seats: The seats are the sealing surfaces against which the ball comes into contact, ensuring a tight seal.
- Actuators: Actuators, such as levers, gears, or motors, facilitate the movement of the ball, allowing the valve to be opened or closed as required.
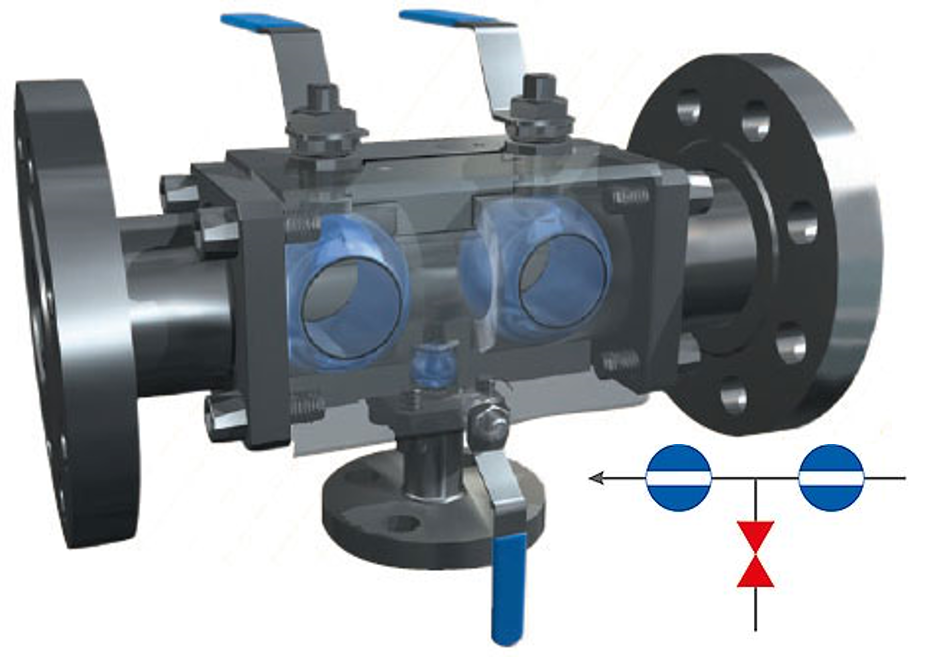
5. Applications of Double Block & Bleed Valve
5.1 Oil and Gas Industry: Offshore and Onshore Applications
In the oil and gas sector, where volatile and pressurized fluids are commonplace, the Double Block & Bleed Valve finds extensive use. Offshore drilling platforms and onshore refineries rely on these valves to isolate sections of pipelines, facilitating maintenance activities and ensuring safety during emergencies.
5.2 Petrochemical Industry: Chemical Processing and Storage
In chemical plants and storage facilities, the DBBV plays a crucial role in managing various corrosive and hazardous chemicals. By providing a reliable means of isolation, these valves prevent accidents and environmental contamination, ensuring the integrity of the entire system.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
5.3 Water Treatment: Control and Isolation of Fluids in Treatment Processes
Water treatment plants utilize Double Block & Bleed Valves to regulate the flow of water and chemicals during different stages of the treatment process. These valves offer precise control, preventing cross-contamination and ensuring the purity of treated water.
5.4 Aviation: Aircraft Fuel Systems and Maintenance Procedures
Aircraft fuel systems demand a high level of safety and reliability. Double Block & Bleed Valves are integrated into these systems to isolate fuel lines during maintenance, repair, and emergency situations. By effectively blocking and bleeding the fuel flow, these valves prevent spillage and enhance the overall safety of aviation operations.
6. Advantages & Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Safety: DBBV provides dual isolation, reducing the risk of leaks and accidents. | Initial Cost Higher: DBBV systems can be more expensive to install initially. |
| Space and Weight Efficiency: Combining two functions in one valve saves space and reduces weight in the system. | Complex Installation: Installation and maintenance require skilled technicians due to the valve’s complexity. |
| Minimized Leakage: Tight seals reduce the chances of leakage, enhancing system efficiency. | Regular Maintenance Required: Routine maintenance is necessary to ensure the valves continue to function optimally. |
| Simultaneous Block and Bleed: The valve can block fluid flow while bleeding off trapped pressure. | Limited in High-Pressure Systems: DBBV may have limitations in extremely high-pressure applications. |
| Reduced Risk of Cross-Contamination: Isolating fluids ensures there is no cross-contamination between different media. | Limited Availability in Some Sizes: DBBV may not be readily available in all sizes, requiring customization in certain cases. |
7. Double Block & Bleed Valve vs Double Isolation Valve
| Aspect | Double Block & Bleed Valve (DBBV) | Double Isolation Valve (DIV) |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Functionality | Provides two separate isolation seals in one valve. | Uses two separate valves for isolation, one upstream and one downstream of the system. |
| Number of Valves | One valve system. | Two separate valves are required. |
| Space and Weight | More compact design, saving space and reducing weight. | Requires additional space and can be heavier due to two valves. |
| Complexity | Complex internal structure due to combined functions. | Simpler internal design as it consists of two individual valves. |
| Maintenance | May require more intricate maintenance due to complexity. | Easier maintenance as each valve can be serviced separately. |
| Installation Cost | Initial cost can be higher due to the complexity of design. | Initial cost might be lower as it involves standard valves. |
| Safety | Enhanced safety due to double isolation capability. | High safety, but slight risk during maintenance if both valves fail to close properly. |
| Flexibility | Can be customized for specific applications. | Limited customization options due to standard valve configurations. |
| Applications | Suitable for critical applications requiring high safety. | Commonly used in various applications where dual isolation is necessary. |
| Availability | Readily available in standard and customized configurations. | Widely available as standard valves in different sizes and materials. |
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
8. Codes & Standards
| Codes | Standards |
|---|---|
| API 6D: Pipeline Valves | API 6FA: Fire Test for Valves |
| ASME B16.34: Valves-Flanged, Threaded | ASME B31.3: Chemical Plant Piping |
| ANSI B16.5: Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings | NACE MR0175/ISO 15156: Materials for Use in H2S-Containing Environments |
| API 598: Valve Inspection and Testing | ISO 5208: Industrial Valves – Pressure Testing of Valves |
9. Conclusion
The Double Block & Bleed Valve stands as a testament to human ingenuity in ensuring the safety and efficiency of fluid systems across diverse industries. Its evolution from simple valve designs to sophisticated systems reflects the continuous efforts of engineers and scientists to enhance industrial practices. By providing dual isolation capabilities and controlled bleeding, these valves have become indispensable in critical applications, where safety and reliability are non-negotiable.
As industries progress, the demand for more advanced and reliable fluid control solutions will only increase. Innovations in materials, manufacturing techniques, and automation are likely to shape the future of Double Block & Bleed Valve technology. Embracing these advancements will not only enhance safety standards but also contribute to the overall efficiency and sustainability of various industrial processes.
FAQs
1. What is the primary purpose of a Double Block & Bleed Valve (DBBV)?
A Double Block & Bleed Valve is designed to provide two separate isolation seals in a single valve body. Its primary purpose is to offer a compact solution for critical applications, ensuring the simultaneous blockage and bleeding of fluids, enhancing safety and efficiency in fluid systems.
2. How does a Double Block & Bleed Valve differ from traditional isolation valves?
Unlike traditional isolation valves, a Double Block & Bleed Valve combines the functions of two separate valves into one. It offers dual isolation in a single unit, reducing space requirements and providing a more efficient solution for critical applications where safety and reliability are paramount.
3. Where are Double Block & Bleed Valves commonly used in industrial applications?
Double Block & Bleed Valves are extensively used in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemical, water treatment, and aviation. They are employed in applications where fluid control, safety, and prevention of cross-contamination are crucial. Common uses include offshore and onshore oil drilling, chemical processing plants, water treatment facilities, and aircraft fuel systems.
4. What are the key advantages of using Double Block & Bleed Valves?
Some key advantages of Double Block & Bleed Valves include enhanced safety through dual isolation, space and weight efficiency due to the combination of functions, minimized leakage, simultaneous block and bleed capabilities, and reduced risk of cross-contamination between different fluids in the system.
5. Are there any specific industry standards and regulations governing the use of Double Block & Bleed Valves?
Yes, there are industry standards and regulations that govern the design, manufacturing, and testing of Double Block & Bleed Valves. Standards such as API 6D for pipeline valves, API 6FA for fire testing, and ASME B16.34 for valve specifications provide guidelines ensuring the quality and performance of these valves in various applications. Compliance with these standards is essential to meet safety requirements and industry best practices.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
Recommended courses (Published on EPCLand)
- Basics of Piping Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Complete Course on Piping Engineering
- Material Requisitions
- Piping Material Specifications
- Valve Material Specifications
Don’t miss the published articles on following:
Attempt Quiz
Question 1:
What is the primary purpose of a Double Block & Bleed Valve?
Explanation: A Double Block & Bleed Valve is designed to isolate and bleed a line simultaneously.
Question 2:
Which of the following is a common application of Double Block & Bleed Valves?
Explanation: Double Block & Bleed Valves are commonly used in oil and gas pipelines.
Question 3:
What is the purpose of the “bleed” function in a Double Block & Bleed Valve?
Explanation: The “bleed” function in a Double Block & Bleed Valve is used to release trapped fluid or pressure.
Question 4:
Which industry commonly uses Double Block & Bleed Valves for safety?
Explanation: The oil and gas industry commonly uses Double Block & Bleed Valves for safety purposes.
Question 5:
What is the typical configuration of a Double Block & Bleed Valve?
Explanation: A typical configuration of a Double Block & Bleed Valve consists of two inlet valves and one outlet valve.
Question 6:
Which material is commonly used for making Double Block & Bleed Valves?
Explanation: Stainless steel is commonly used for making Double Block & Bleed Valves due to its durability and corrosion resistance.
Question 7:
Which of the following statements about Double Block & Bleed Valves is correct?
Explanation: Double Block & Bleed Valves provide positive isolation in critical applications.
Question 8:
What is the function of the “double block” feature in a Double Block & Bleed Valve?
Explanation: The “double block” feature in a Double Block & Bleed Valve is designed to completely seal off the flow path.
Question 9:
Why is the “bleed” valve necessary in a Double Block & Bleed Valve?
Explanation: The “bleed” valve in a Double Block & Bleed Valve is necessary to relieve excess pressure and drain the line.
Question 10:
Which industry standards are commonly followed in the design of Double Block & Bleed Valves?
Explanation: Double Block & Bleed Valves are commonly designed following American Petroleum Institute (API) standards.



