1. Introduction
Flexible hoses are indispensable components in the realm of oil and gas exploration, production, and transportation. These hoses serve a critical purpose, enabling the seamless transfer of fluids, gases, and even solids in various challenging environments. From offshore drilling rigs to onshore refineries, flexible hoses play a vital role in ensuring the efficiency and safety of operations. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricate world of flexible hoses in the oil and gas industry, exploring their history, functions, types, applications, and the standards that govern their usage.
Table of Contents
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
2. Brief History
The history of flexible hoses in the oil and gas industry traces back to the early days of drilling and exploration. Initially, rigid pipes were used for fluid transfer, posing significant challenges in environments where flexibility was paramount. The need for more adaptable solutions led to the development of flexible hoses. The 20th century witnessed remarkable advancements, with the introduction of innovative materials and manufacturing techniques. These developments revolutionized the industry, enabling the efficient handling of various substances across diverse applications.
3. Basic Function and Working Principle
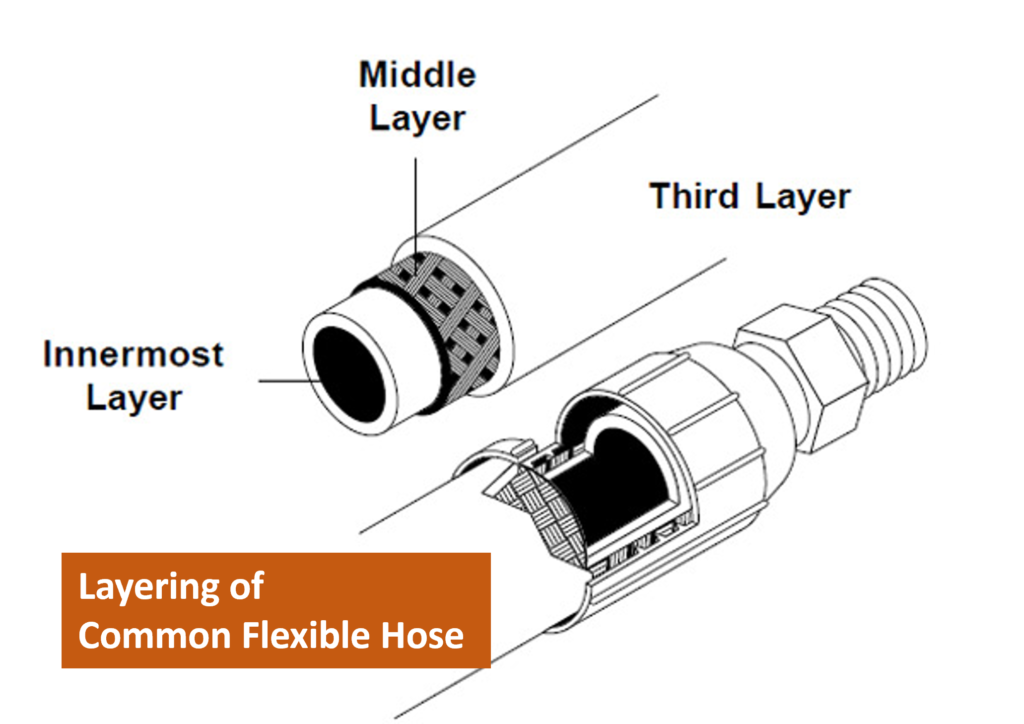
Flexible hoses are designed to handle complex operational requirements, providing a conduit for the safe transfer of liquids, gases, and slurries. Their primary function lies in their flexibility, which allows them to accommodate movements, vibrations, and bending without compromising the integrity of the fluid transport system. The working principle of flexible hoses revolves around their construction, comprising layers of materials engineered to withstand specific pressures, temperatures, and corrosive elements. The inner tube, reinforcement layers, and outer cover collectively ensure the hose’s functionality and durability.
4. Main Components & Their Functions
- Inner Tube: The inner tube is the core component, directly in contact with the transported substance. It is selected based on the nature of the fluid, ensuring compatibility and preventing chemical reactions.
- Reinforcement Layers: Reinforcement layers, typically made of high-strength materials like steel or synthetic fibers, provide structural support. These layers determine the hose’s working pressure and prevent it from collapsing or bursting under extreme conditions.
- Outer Cover: The outer cover shields the hose from environmental factors, abrasion, and damage. It enhances the hose’s longevity and protects it from wear and tear, ensuring prolonged functionality.
- Fittings and End Connections: Fittings and end connections are crucial components that enable the hose to be connected to the equipment or pipeline. Properly designed fittings ensure a secure and leak-free connection, vital for maintaining operational safety and efficiency.
5. Types of Flexible Hoses
Flexible hoses are diverse, catering to a wide array of applications in the oil and gas industry. Several types are prevalent:
- Metal Hoses: Constructed from stainless steel, these hoses are suitable for high-temperature and high-pressure applications, offering exceptional durability and resistance to corrosion.
- Composite Hoses: Composite hoses combine various materials, including thermoplastics, reinforcing fabrics, and films. They are lightweight, flexible, and resistant to chemicals, making them ideal for transferring corrosive substances.
- Rubber Hoses: Rubber hoses are versatile and find applications in both onshore and offshore projects. They are suitable for transporting oil, gas, water, and other fluids, offering flexibility and ease of handling.
- Thermoplastic Hoses: These hoses, made from thermoplastic materials, are lightweight and highly flexible. They are resistant to chemicals and abrasion, making them suitable for applications where flexibility and chemical resistance are crucial.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
6. Applications of Flexible Hoses
Flexible hoses find extensive applications in the oil and gas industry, contributing significantly to various processes:
- Offshore Drilling: Offshore drilling rigs require flexible hoses to transfer drilling mud, chemicals, and other substances between different components. The hoses accommodate the rig’s movements, ensuring uninterrupted operations.
- Hydraulic Systems: Flexible hoses are integral to hydraulic systems in heavy machinery and equipment. They facilitate the transfer of hydraulic fluids, enabling precise control and efficient power transmission.
- Chemical Transfer: Industries dealing with chemicals rely on flexible hoses to transport corrosive substances safely. The hoses’ chemical resistance properties prevent leaks and ensure the secure transfer of hazardous materials.
- Oil and Gas Transportation: Flexible hoses are essential in pipelines for the transportation of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products. They accommodate the thermal expansion and contraction of the pipelines, maintaining the integrity of the system.
7. Advantages & Disadvantages
Advantages:
| Advantages | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Flexibility | Flexible hoses can bend and twist, adapting to various configurations and movements without compromising functionality. |
| Versatility | They can handle a wide range of substances, including liquids, gases, and solids, making them versatile for diverse applications. |
| Ease of Installation | Flexible hoses are relatively easy to install and replace, reducing downtime during maintenance and repairs. |
| Shock Absorption | They absorb vibrations and shocks, protecting the connected equipment and reducing wear and tear on machinery. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Certain types of flexible hoses, such as metal and composite hoses, offer excellent resistance to corrosion, ensuring longevity and reliability. |
Disadvantages:
| Disadvantages | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Limited Lifespan | Flexible hoses have a finite lifespan and may require periodic replacement, especially in high-stress or corrosive environments. |
| Pressure and Temperature Limits | Each type of flexible hose has specific pressure and temperature limits. Exceeding these limits can lead to hose failure and potential hazards. |
| Abrasion Susceptibility | Some hoses, particularly rubber hoses, are susceptible to abrasion, which can compromise their structural integrity and functionality over time. |
| Maintenance Requirements | Regular inspection and maintenance are necessary to ensure the hoses remain in optimal condition, adding to operational costs. |
| Environmental Impact | Improper disposal of hoses can have adverse environmental effects. Recycling and proper disposal methods are essential to mitigate environmental impact. |
8. Codes & Standards
| Organization | Standard Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| American Petroleum Institute (API) | API 17K | Standard for Bonded Flexible Pipe Used in Oil and Gas Production Services |
| International Organization for Standardization (ISO) | ISO 13628-11 | Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries – Design and Operation of Subsea Production Systems – Part 11: Flexible Pipe Systems for Subsea and Marine Applications |
| American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) | ASME B31.3 | Process Piping – Code for Pressure Piping |
| European Committee for Standardization (CEN) | EN 13765 | Thermoplastic Multi-Layer (Non-Vulcanized) Hoses and Hose Assemblies for the Transfer of Hydrocarbons, Solvents, and Chemicals |
| Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) | OSHA 29 CFR 1910.106 | Standards for the Handling, Storage, and Use of Flammable and Combustible Liquids |
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
9. Conclusion
Flexible hoses are the unsung heroes of the oil and gas industry, enabling the smooth flow of fluids and gases in challenging environments. Their evolution from rigid pipes to adaptable, versatile components has significantly impacted the efficiency and safety of operations. As technology continues to advance, the industry can expect even more sophisticated and reliable flexible hose solutions. It is imperative for professionals and organizations to stay updated with the latest developments and adhere to industry standards, ensuring the seamless functioning of flexible hoses in various applications. Embracing the innovations in flexible hose technology is key to enhancing the industry’s productivity, sustainability, and safety standards.
FAQs
1. What are the key factors to consider when selecting a flexible hose for a specific oil and gas application?
Choosing the right flexible hose involves considering factors such as the type of substance being transferred, pressure and temperature requirements, environmental conditions, and regulatory compliance. Each application may have unique demands, and selecting an appropriate hose ensures optimal performance and safety.
2. How often should flexible hoses in the oil and gas industry be inspected and replaced?
Regular inspections are crucial to identifying signs of wear, abrasion, or degradation in flexible hoses. The frequency of inspections and replacements depends on factors such as the type of hose, operating conditions, and industry standards. Following manufacturer recommendations and adhering to industry standards are essential to determine the appropriate inspection intervals.
3. What safety measures should be in place when handling and installing flexible hoses in oil and gas projects?
Ensuring safety during the handling and installation of flexible hoses involves several precautions. These include proper training for personnel, using appropriate lifting equipment, verifying hose compatibility with substances being transferred, following correct installation procedures, and conducting pressure tests to identify potential leaks or weaknesses in the hose assembly.
4. How can flexible hoses contribute to environmental sustainability in the oil and gas industry?
Flexible hoses, when chosen wisely, can contribute to environmental sustainability by minimizing leaks and spillage, thus reducing the environmental impact of fluid transfer operations. Additionally, the use of certain materials in hose construction, like recyclable thermoplastics, can further enhance the industry’s eco-friendly practices.
5. What are the emerging trends and innovations in flexible hose technology for the oil and gas sector?
The oil and gas industry is witnessing continuous advancements in flexible hose technology. Some trends include the development of hoses with smart sensors for real-time monitoring, materials engineered for extreme conditions, and improvements in hose design to enhance flexibility and durability. Staying updated with these innovations is essential for industry professionals aiming to optimize their operations.
Recommended courses (Published on EPCLand)
- Basics of Piping Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Complete Course on Piping Engineering
- Material Requisitions
- Piping Material Specifications
- Valve Material Specifications
Don’t miss the published articles on following:
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
Attempt Quiz
Question 1:
What is the primary function of flexible hoses in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Explanation: Flexible hoses in the Oil & Gas Industry are used to connect rigid pipes and absorb vibration, allowing movement and flexibility in the system.
Question 2:
Which material is commonly used in the construction of flexible hoses for Oil & Gas applications?
Explanation: Stainless Steel is commonly used in the construction of flexible hoses for Oil & Gas applications due to its strength and corrosion resistance.
Question 3:
What is the purpose of corrugation in flexible hoses?
Explanation: Corrugation in flexible hoses enhances flexibility and allows movement, making them suitable for various applications in the Oil & Gas Industry.
Question 4:
What is the purpose of end fittings in flexible hoses?
Explanation: End fittings are used to connect flexible hoses to equipment or pipelines, ensuring a secure and leak-free connection in the Oil & Gas Industry.
Question 5:
What is the maximum temperature range flexible hoses in the Oil & Gas Industry are designed to handle?
Explanation: Flexible hoses in the Oil & Gas Industry are designed to handle a wide temperature range, typically from -40°C to 150°C, allowing them to be used in various operating conditions.
Question 6:
What type of fluids can flexible hoses in the Oil & Gas Industry transport?
Explanation: Flexible hoses in the Oil & Gas Industry are versatile and can transport a wide range of fluids, including oil, gas, and various chemicals.
Question 7:
What is the main advantage of using flexible hoses over rigid piping in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Explanation: The main advantage of using flexible hoses in the Oil & Gas Industry is easier installation and flexibility in movement, allowing for adaptability in various situations.
Question 8:
Which industry standard is commonly followed in the manufacturing of flexible hoses for Oil & Gas applications?
Explanation: API 17J is a commonly followed industry standard for the manufacturing of flexible hoses used in Oil & Gas applications.
Question 9:
What is the purpose of the outer protective layer in flexible hoses?
Explanation: The outer protective layer in flexible hoses protects against abrasion, chemicals, and weather, ensuring the hose’s durability and safety in various conditions.
Question 10:
What is the typical lifespan of high-quality flexible hoses in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Explanation: High-quality flexible hoses in the Oil & Gas Industry typically have a lifespan ranging from 15 to 20 years when properly maintained and used under appropriate conditions.



