1. Introduction
In the intricate web of the oil and gas industry, where precision and reliability are paramount, even the smallest particles can cause significant damage. This is where strainers come into play, serving as unsung heroes in the machinery’s smooth operation. Strainers are devices designed to remove unwanted solids from liquids or gases by passing the fluid through a filter, allowing the clean fluid to pass while trapping the debris. In the context of the oil and gas sector, strainers are indispensable components, ensuring the longevity and efficiency of various equipment.
Table of Contents
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
2. Brief History
The journey of strainers in the oil and gas industry has been marked by continuous innovation and adaptation to the sector’s evolving needs. In the early days, rudimentary filters made of woven fabrics were used to strain impurities. However, as technology advanced and the demands of the industry became more sophisticated, strainers underwent significant enhancements. The integration of durable materials and advanced engineering techniques paved the way for the development of highly efficient strainers we see today.
3. Basic Function and Working Principle
Strainers operate on a simple yet crucial principle: capturing solid particles present in fluids before they can harm sensitive equipment or disrupt processes. The basic working mechanism involves the fluid passing through a perforated barrier or mesh, which captures particles above a certain size. This filtration process ensures that only clean, particle-free fluid continues its journey through the system, safeguarding pumps, valves, and other critical components from damage.
4. Main Components & Their Functions
4.1 Housing The housing of a strainer encases the filtering elements and ensures proper alignment. It also provides structural support and protects the internal components from external damage, maintaining the integrity of the filtration system.
4.2 Screens Screens, typically made of stainless steel, are the heart of the strainer. They come in various mesh sizes, allowing the customization of filtration based on the specific requirements of the application. Finer meshes capture smaller particles, making them ideal for applications demanding high precision.
4.3 Gaskets Gaskets create a seal between the housing and the cover, preventing leakages. They play a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the strainer, ensuring that the fluid passes through the designated filtration path.
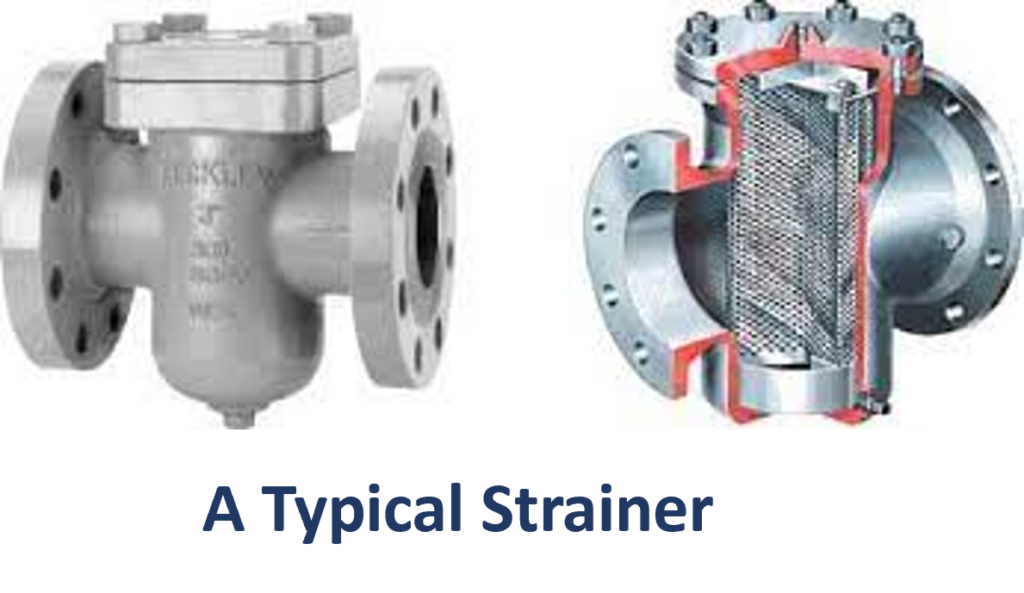
5. Types of Strainers
5.1 Y-Type Strainers Y-type strainers, characterized by their shape resembling the letter “Y,” are commonly used in applications where space is limited. They are highly efficient and easy to clean, making them suitable for processes where downtime needs to be minimized.
5.2 Simplex Strainers Simplex strainers are the most basic type, consisting of a single chamber with a removable cap for easy maintenance. They are ideal for applications where the flow can be temporarily shut down for strainer cleaning or replacement.
5.3 Duplex Strainers Duplex strainers are designed with two chambers, allowing continuous operation. When one chamber becomes clogged, the flow can be redirected to the other chamber, ensuring uninterrupted operation. This design is particularly beneficial for critical applications that require constant fluid flow.
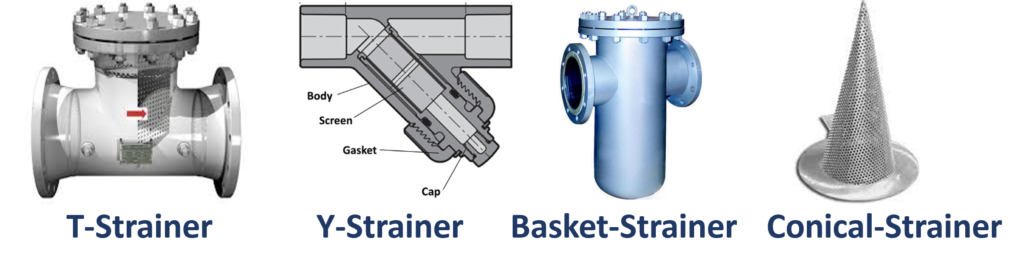
6. Applications of Strainers
6.1 Exploration and Drilling Operations In the upstream sector, strainers are utilized in drilling operations to filter drilling fluids, preventing abrasive particles from damaging pumps and drilling equipment. They also play a crucial role in protecting sensitive instruments used for geological analysis.
6.2 Refining Processes Within refineries, strainers are integral components in various processes, including distillation and cracking. They ensure that impurities are removed from crude oil and its derivatives, enhancing the quality of the final products.
6.3 Pipeline Systems Strainers are installed in pipeline systems to capture debris and contaminants, preventing blockages and maintaining the efficiency of fluid transportation. They are particularly important in pipelines carrying natural gas and petroleum products over long distances.
6.4 Offshore Platforms Offshore platforms, exposed to harsh environmental conditions, rely on strainers to safeguard critical components such as pumps and compressors. The robust construction of offshore strainers ensures they can withstand corrosive marine environments.
6.5 Other Specialized Applications Strainers find applications in various other specialized areas within the oil and gas industry, such as liquefied natural gas (LNG) processing, petrochemical plants, and power generation facilities. In each case, they contribute to the smooth operation of equipment and processes.
7. Advantages & Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Efficient particle removal | Potential pressure drop across the strainer |
| Protects equipment from damage | Regular maintenance required |
| Ensures process efficiency | Initial installation costs |
| Customizable for specific needs | Limited capacity for large particles |
| Durable and corrosion-resistant | Ineffective against dissolved impurities |
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
8. Codes & Standards of Strainers
Strainers in the oil and gas industry must adhere to specific codes and standards to ensure their quality and performance. Some of the key standards include:
- API 598: Valve Inspection and Testing
- ASME B16.34: Valves – Flanged, Threaded, and Welding End
- ASME B31.3: Process Piping
- ISO 9001: Quality Management Systems
Compliance with these standards not only guarantees the reliability of strainers but also ensures the safety of operations and personnel involved in the industry.
9. Conclusion
In the intricate world of the oil and gas industry, where precision is non-negotiable and efficiency is paramount, strainers stand as guardians, protecting vital components from harm’s way. Their evolution from simple filters to complex, highly efficient devices mirrors the industry’s progress. As technology advances, strainers continue to adapt, ensuring seamless operations in exploration, refining, transportation, and various specialized applications.
Understanding the nuances of strainers, from their basic components to their diverse applications, is essential for engineers and professionals in the oil and gas sector. By selecting the right type of strainer, adhering to industry standards, and conducting regular maintenance, operators can ensure optimal performance, minimize downtime, and prolong the lifespan of critical equipment.
In the ever-changing landscape of the oil and gas industry, one thing remains constant: the indispensable role of strainers in maintaining the industry’s heartbeat. As the sector moves forward, strainers will undoubtedly continue to evolve, becoming even more efficient, durable, and essential in ensuring the industry’s smooth operation.
FAQs
1. What is the primary purpose of using strainers in the oil and gas industry?
Strainers in the oil and gas industry serve as filtration devices, designed to remove solid particles and debris from fluids and gases. Their primary purpose is to protect sensitive equipment such as pumps, valves, and compressors from damage caused by these particles, ensuring smooth and efficient operation of the machinery.
2. What are the different types of strainers commonly used in the oil and gas sector, and how do they differ in their applications?
There are several types of strainers utilized in the oil and gas industry, including Y-type strainers, simplex strainers, and duplex strainers. Y-type strainers are suitable for applications with limited space, simplex strainers have a single chamber and are ideal for processes that can be temporarily shut down for maintenance, while duplex strainers have two chambers, allowing continuous operation by redirecting flow when one chamber is being cleaned.
3. How do strainers contribute to the efficiency and safety of oil and gas exploration, refining, and transportation processes?
Strainers play a crucial role in various sectors of the oil and gas industry. In exploration, they protect drilling equipment from abrasive particles, ensuring efficient drilling operations. In refineries, they enhance the quality of final products by removing impurities from crude oil derivatives. In transportation, strainers prevent blockages in pipelines, ensuring the uninterrupted flow of natural gas and petroleum products.
4. What are the key factors to consider when selecting a strainer for a specific oil and gas application?
When selecting a strainer for a particular oil and gas application, factors such as the type of fluid or gas, flow rate, pressure, temperature, and particle size must be carefully considered. The compatibility of materials with the substances being processed, as well as the maintenance requirements and downtime implications, also play a significant role in the selection process.
5. What are the maintenance requirements for strainers, and how can operators ensure their optimal performance over time?
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the optimal performance of strainers. This includes periodic inspection of the screens for clogs or damages, cleaning or replacing screens as needed, and checking gaskets and seals for leaks. Additionally, operators should adhere to recommended cleaning schedules and follow manufacturer guidelines to ensure the strainers continue to function effectively and contribute to the overall efficiency and safety of oil and gas operations.
Recommended courses (Published on EPCLand)
- Basics of Piping Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Complete Course on Piping Engineering
- Material Requisitions
- Piping Material Specifications
- Valve Material Specifications
Don’t miss the published articles on following:
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
Attempt Quiz
Question 1:
What is the primary function of a strainer in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Explanation: Strainers in the Oil & Gas Industry are used to filter liquids and gases, removing contaminants to ensure smooth operations.
Question 2:
Which of the following materials is commonly used to construct strainers?
Explanation: Stainless Steel is a common material used in the construction of strainers due to its corrosion resistance and durability.
Question 3:
What is the purpose of a Y-strainer?
Explanation: A Y-strainer is designed to remove solid particles from liquid or gas pipelines, ensuring the integrity of downstream equipment.
Question 4:
What is the typical mesh size of strainers used for fine filtration?
Explanation: Strainers used for fine filtration typically have mesh sizes ranging from 10 to 100 microns, ensuring the removal of tiny particles.
Question 5:
Which of the following is a type of strainer used specifically for gas applications?
Explanation: Cone Strainers are often used in gas applications for effective filtration.
Question 6:
What is the primary advantage of using a duplex strainer?
Explanation: Duplex strainers allow continuous operation during cleaning because they consist of two separate strainer baskets, ensuring uninterrupted filtration.
Question 7:
What is the purpose of a temporary strainer?
Explanation: Temporary strainers are used for temporary protection of equipment during system startup, ensuring that initial debris doesn’t damage sensitive components.
Question 8:
Which of the following is a common location for installing strainers in a pipeline?
Explanation: Strainers can be installed at various points in a pipeline, including the beginning, middle, or end, based on specific operational requirements.
Question 9:
What is the purpose of a conical strainer?
Explanation: Conical strainers are used to remove large particles from liquids, ensuring the protection of downstream equipment.
Question 10:
Which factor is crucial when selecting a strainer for a specific application?
Explanation: When selecting a strainer, material compatibility, flow rate requirements, and particle size considerations are crucial for ensuring effective filtration in specific applications.



