1. Gather Mechanical Specifications
What is the first step in the process of heat exchanger piping?
Explanation: The first step in the heat exchanger piping process is to gather the mechanical specifications of the heat exchanger.
2. Analyze P&ID
What does P&ID stand for, and why is it important in heat exchanger piping?
Explanation: P&ID stands for Piping and Instrumentation Diagram, and it is important in heat exchanger piping to identify connections and arrangements around the heat exchanger.
3. Note Process Requirements
What details should be noted when considering process requirements in heat exchanger piping?
Explanation: When considering process requirements in heat exchanger piping, one should note special process or functional requirements and arrangement details.
4. Verify Nozzle Schedule
Why is it important to verify the nozzle schedule against the P&ID in heat exchanger piping?
Explanation: Verifying the nozzle schedule against the P&ID in heat exchanger piping is important to ensure accurate positioning on the equipment.
5. Sketch Relative Location and Level
Why is creating a sketch depicting the relative location and level of the heat exchanger important in piping?
Explanation: Creating a sketch of the relative location and level of the heat exchanger is important to determine required tube cleaning space and maintenance space.
6. Locate Control Valve Stations
What is the purpose of identifying the locations of control valve stations in heat exchanger piping?
Explanation: Identifying the locations of control valve stations in heat exchanger piping is important to ensure instrument accessibility and maintain valve accessibility.
7. Designate Flanged Joint Locations
Why is it crucial to determine the placement of flanged joints in heat exchanger piping?
Explanation: Determining the placement of flanged joints in heat exchanger piping is crucial to facilitate heat exchanger replacement or maintenance.
Short Article on Steps to Do Heat Exchanger Piping
Steps to Do Heat Exchanger Piping
- Gather Mechanical Specifications: Collect the mechanical specifications of the heat exchanger.
- Analyze P&ID: Study the P&ID (Piping and Instrumentation Diagram) around the heat exchanger to identify its connections to other equipment, such as columns or reactors.
- Note Process Requirements: Take note of any special process or functional requirements, along with specific arrangement details, such as level or height differences relative to other connected equipment like pumps.
- Verify Nozzle Schedule: Review the nozzle schedule, including its position on the equipment, and verify it against the P&ID.
- Sketch Relative Location and Level: Create a sketch depicting the relative location and level of the heat exchanger. Determine the required tube cleaning space for shell and tube heat exchangers, as well as the maintenance space for tube bundle removal.
- Locate Control Valve Stations: Identify the locations of control valve stations for both shell-side and tube-side fluids.
- Designate Flanged Joint Locations: Determine the placement of flanged joints to facilitate heat exchanger replacement or maintenance.
- Consider Stream Directionality: As a general rule, cooled streams should flow downwards, while heated streams should flow upwards. This arrangement is mandatory when there is a phase change, desirable when streams are liquid, but not crucial for gases, vapors, or situations without superheating or supercooling.
- Prevent Piping Interference: Ensure that piping does not obstruct heat exchanger removal, either horizontally for bundle pulling or vertically for complete exchanger removal.
- Ensure Instrument Accessibility: Verify that locally mounted instruments, such as pressure indicators (PIs), temperature indicators (TIs), sight glasses, and level indicators, are visible from access aisles, and that valves are accessible from the aisles.
- Mark Piping Supports: Indicate the locations and arrangements of piping supports on the piping study.
- Maintain Valve Accessibility: Ensure adequate accessibility for operating all valves. Verify that clearances meet the recommended minimum requirements.
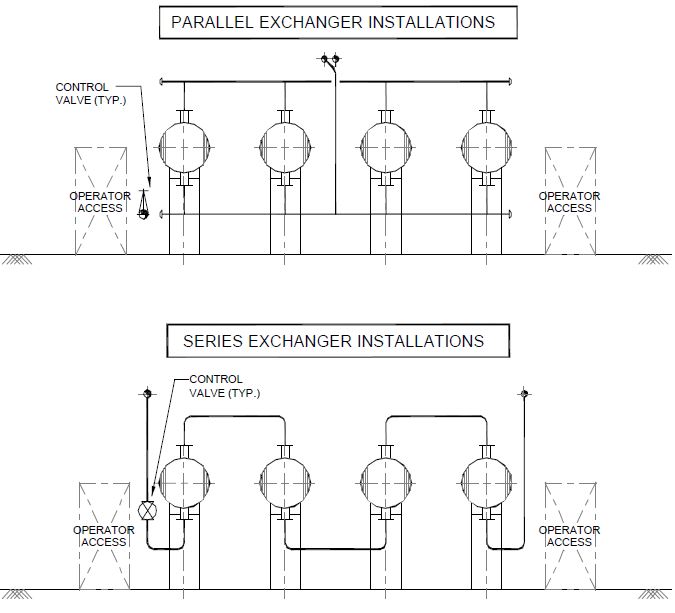
Table of Contents
Don’t miss the Course on Effective Isometrics Management: Check Now
Enrollment Link
Recommended courses (Published on EPCLand)
- Complete Course on Piping Engineering
- Basics of Piping Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Material Requisitions
- Piping Material Specifications
- Valve Material Specifications
- Plant Design & Layouts-OISD 118
- Isometric Management
Library of Technical Articles
Don’t miss out the collection of 15+ articles on following topics:
- Basics of Oil and Gas Industry
- Valves
- Testing
- Tank
- Piping Bulk Items
- Pipe
- Metallurgy
- Piping Materials
- Layout
- Instrumentation
- Heat Exchanger
- Type of Contracts
- Codes and Standards
- ASTM Standards
- Articles on Piping Specialty Items
Video details of Complete Course on Piping Engineering
Why Enroll in the EPCLand
Proven Track Record– PTR
Activities & Achievements before launching EPCLand
- Published more than 50+ short courses
- 3000+ Enrolments
- More than 3,500,00 Minutes of watch hours in the last 2 years
- 4000+ Students in 100+ Countries
- Rating of 4+ out of 5
- 1000+ YouTube Videos
- 8K+ Subscribers
What Students will Learn
- Codes & Standards of the Energy Sector
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Stress Analysis
Interesting facts
- All the published courses have been developed by Industry Experts with more than 2 decades of experience
- Content is based on Practical experience and real-time problems.
- Content is designed and organized in such a manner that it can be easily grabbed.
- Complete website, Blogs and Quiz sections are Planned, Designed and published by myself (About me: Atul Singla)
- Complete flexibility of Time & Location, Students can access the content from anywhere & anytime
- Moreover, once enrolled, the content can be access as many times as you want, which helps in understand the fundamentals in a better way.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our courses are meticulously crafted by industry experts with over two decades of hands-on experience. The content is rooted in practical knowledge, addressing real-time problems. The material is thoughtfully designed and organized for easy comprehension. Every aspect, from the website to blogs and quizzes, has been planned, designed, and executed by Atul Singla, ensuring a comprehensive and seamless learning experience. With the flexibility of accessing the content at any time and from any location, students have the freedom to learn on their terms. Furthermore, enrollment grants unlimited access, allowing learners to revisit the material as often as needed, fostering a deep understanding of the fundamentals.