1. Introduction
Butterfly valves, despite their unassuming name, play a pivotal role in various industries by regulating fluid flow within pipelines. Unlike traditional globe valves, butterfly valves are compact, cost-effective, and versatile. This article delves into the intricacies of butterfly valves, from their historical origins to their modern applications, exploring the fundamental principles behind their operation and dissecting their components.
Table of Contents
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
2. Brief History
Origins and Early Designs
The concept of regulating fluid flow dates back to ancient civilizations. Early valve designs were rudimentary, often using simple mechanisms like gates and levers. The butterfly valve, as we recognize it today, has roots in the 18th century. Inventors and engineers refined the design, leading to the creation of the modern butterfly valve.
Evolution Over Centuries
Throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, butterfly valves underwent significant improvements in materials and design. The advent of industrialization spurred innovation, resulting in valves capable of handling diverse fluids and operating conditions. These advancements paved the way for the widespread adoption of butterfly valves across industries.
3. Basic Function and Working Principle
At its core, a butterfly valve controls the flow of fluids by rotating a disc, known as the “butterfly,” within the pipeline. The position of the disc determines the flow rate. When the disc is parallel to the flow, the valve is fully open, allowing maximum flow. Conversely, closing the valve involves perpendicular alignment, stopping the flow entirely.
How Butterfly Valves Regulate Flow
The control mechanism of butterfly valves is swift and efficient. When the operator turns the valve handle or actuator, the disc inside the valve rotates. This rotation either allows fluid to pass through or obstructs the flow, depending on the desired flow rate. The simplicity of this process contributes to the valve’s rapid operation, making it ideal for applications where quick response times are crucial.
Role in Controlling Pressure
Butterfly valves excel in regulating pressure within pipelines. By adjusting the disc’s angle, the valve can maintain consistent pressure levels, preventing surges that could damage sensitive equipment or compromise the integrity of the system. This ability to manage pressure makes butterfly valves indispensable in critical industries such as water treatment and oil refining.
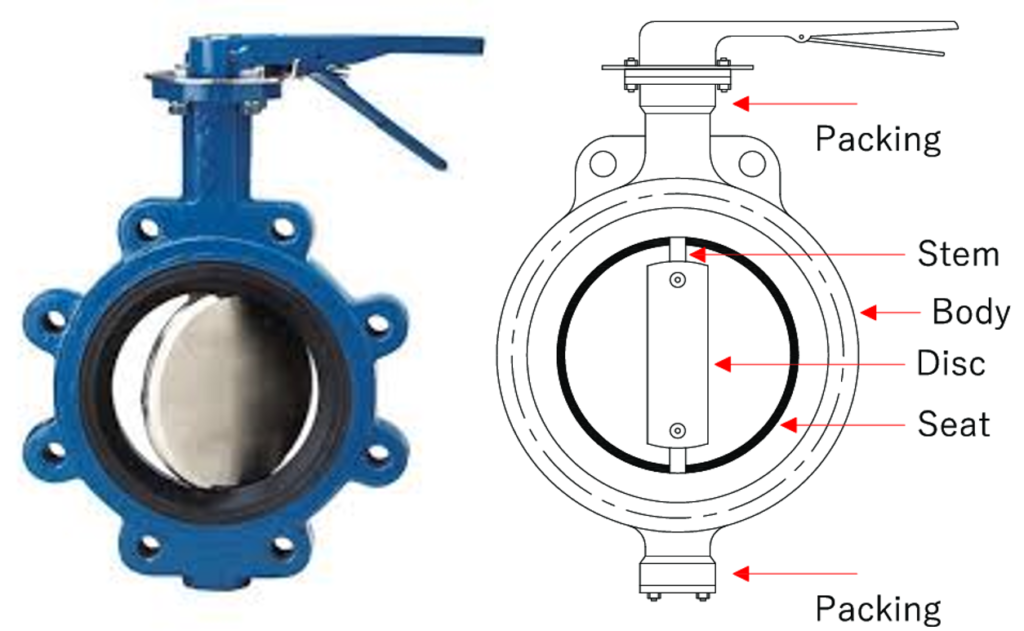
4. Main Components
Butterfly valves consist of several essential components, each playing a vital role in the valve’s operation and longevity.
Valve Body
The valve body serves as the primary structure, housing other components. It provides stability and support to withstand the pressure and flow within the pipeline. The material of the valve body varies based on the intended application, with options including stainless steel, cast iron, and PVC for corrosive or sanitary environments.
Disc
The disc, resembling a butterfly hence the name, is the central component responsible for controlling the flow. It can be made from metal or composite materials. The shape and size of the disc significantly influence the valve’s performance, allowing engineers to tailor valves for specific applications, whether low-pressure water systems or high-temperature industrial processes.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
Stem
The stem connects the operator (usually a handle or actuator) to the disc. When the operator is turned, the stem transfers this motion to the disc, causing it to rotate within the valve body. It’s essential for the stem to be durable and corrosion-resistant to ensure seamless operation over the valve’s lifespan.
Actuator
In automated systems, an actuator provides the necessary force to turn the stem and control the disc’s position. Actuators can be pneumatic, hydraulic, electric, or manual. Pneumatic and electric actuators are particularly common in industrial settings due to their precision and reliability, allowing for remote operation and integration into complex control systems.
Seals and Bearings
Seals and bearings are critical for ensuring the valve’s tight closure and smooth operation. Seals prevent leakage around the valve disc, maintaining the integrity of the pipeline. Bearings reduce friction between moving parts, enabling effortless rotation of the disc. Proper maintenance and selection of high-quality seals and bearings are crucial to preventing operational issues and extending the valve’s lifespan.
5. Types of Butterfly Valves
Butterfly valves come in various types, each tailored to specific applications and operating conditions.
Centric vs. Eccentric Designs
Centric butterfly valves have the stem centered in the middle of the disc, offering a symmetrical flow pattern. Eccentric butterfly valves, on the other hand, have the stem offset, allowing a more efficient flow around the disc. The choice between centric and eccentric designs depends on factors such as pressure, flow rate, and the nature of the fluid being transported.
High-Performance Butterfly Valves
High-performance butterfly valves are designed to handle demanding applications that require tight shutoff and precise control. These valves often feature enhanced sealing mechanisms and materials capable of withstanding extreme temperatures and corrosive substances. Industries such as chemical processing and power generation rely on high-performance butterfly valves to ensure safety and efficiency.
Triple Offset Butterfly Valves
Triple offset butterfly valves are engineered to provide reliable shutoff in high-temperature, high-pressure, and abrasive media environments. Unlike traditional butterfly valves, triple offset valves feature a conical seating design, which reduces wear and extends their lifespan. These valves are commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, where the integrity of the system is paramount.
Wafer, Lug, and Flanged Butterfly Valves
Butterfly valves can be classified based on their connection methods. Wafer butterfly valves are lightweight and fit between two flanges, making them suitable for applications with limited space. Lug butterfly valves have threaded inserts on both sides, allowing them to be bolted into a pipeline. Flanged butterfly valves have flanges on both ends, providing a sturdy connection and ease of installation. The choice of connection type depends on the specific requirements of the application and the surrounding infrastructure.
6. Applications of Butterfly Valves
Butterfly valves find extensive use across diverse industries due to their versatility and reliability.
Water Treatment Plants
In water treatment facilities, butterfly valves regulate the flow of water, chemicals, and sludge. Their quick operation and tight shutoff capabilities are essential for controlling the various processes involved in water purification and distribution. Butterfly valves also play a role in wastewater treatment, ensuring efficient drainage and preventing backflow.
HVAC Systems
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems utilize butterfly valves to control the flow of air and water. These valves modulate the supply of hot or cold water to maintain optimal temperatures within buildings. Their compact design and ability to handle large flow rates make them ideal for HVAC applications, where space constraints and energy efficiency are paramount.
Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas sector, butterfly valves are employed in pipelines to regulate the flow of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products. These valves are crucial for isolating sections of the pipeline during maintenance or emergencies. Their ability to handle high pressures and temperatures makes them indispensable in the extraction, transportation, and processing of hydrocarbons.
Food and Beverage Processing
Butterfly valves are widely used in the food and beverage industry to control the flow of liquids and gases during processing. Stainless steel butterfly valves are preferred in sanitary applications due to their resistance to corrosion and ability to maintain hygienic conditions. These valves are employed in processes such as brewing, dairy production, and beverage bottling, ensuring product quality and safety.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
Pharmaceuticals
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, butterfly valves are utilized for precise control of fluids and gases in various stages of production. These valves are designed to meet stringent sanitary and quality standards to prevent contamination and ensure product purity. Butterfly valves play a vital role in pharmaceutical formulations, where accuracy and consistency are paramount for producing high-quality medications.
7. Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Quick Operation: Rapid response to changes in flow | Limited to Certain Pressure Ranges |
| Lower Pressure Drop: Minimizes energy loss | Limited to Clean, Non-Abrasive Media |
| Compact Design: Requires less space in pipelines | Not Suitable for High-Temperature Fluids |
| Cost-Effective: Economical choice for many setups | Limited in Size for Large Pipelines |
| Low Maintenance: Fewer moving parts, easy upkeep | Limited to Bi-Directional Applications |
8. Associated Codes & Standards
| Industry | Relevant Codes & Standards |
|---|---|
| Water Industry | AWWA C504, BS EN 593, ISO 5752 |
| Oil and Gas Industry | API 609, API 598, API 594 |
| HVAC Systems | ASHRAE Standard 111, SMACNA |
| Food and Beverage Processing | FDA Regulations, 3-A Sanitary Standards |
| Pharmaceutical Industry | ISPE Baseline Guides, cGMP Regulations, FDA Guidelines for CFR |
9. Conclusion
In conclusion, butterfly valves have become indispensable components in various industries, owing to their efficient operation, diverse applications, and adaptability to different operating conditions. From water treatment plants to pharmaceutical manufacturing, these valves play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth and reliable flow of fluids and gases.
As technology continues to advance, butterfly valves are likely to undergo further innovations, enhancing their performance and expanding their applications. Engineers and researchers are constantly exploring new materials, designs, and control mechanisms to meet the evolving needs of industries around the world.
Understanding the fundamental principles and applications of butterfly valves is essential for engineers, technicians, and decision-makers involved in fluid control systems. By leveraging the advantages of butterfly valves and being aware of their limitations, industries can optimize their processes, improve efficiency, and ensure the safety and reliability of their systems.
FAQs
1. What distinguishes a butterfly valve from other types of valves?
Butterfly valves are unique due to their compact design and rapid operation. Unlike globe valves, they use a rotating disc to control the flow of fluids. This design allows for quick opening and closing, making them ideal for applications where swift response times are crucial.
2. How do butterfly valves handle different types of fluids, including corrosive or abrasive substances?
Butterfly valves can be constructed from a variety of materials, including stainless steel, which offers excellent resistance to corrosion. For abrasive substances, valves with special coatings or liners are used to prevent damage to the disc and ensure a longer lifespan. The choice of materials depends on the specific characteristics of the fluid being handled.
3. What factors influence the selection of a specific type of butterfly valve, such as wafer, lug, or flanged design?
The selection of a butterfly valve type depends on the application’s requirements and the surrounding infrastructure. Wafer valves are lightweight and fit between flanges, making them suitable for space-constrained environments. Lug valves are bolted into the pipeline and offer secure connection, while flanged valves provide a robust connection, ensuring stability and ease of installation.
4. What are the key maintenance considerations for butterfly valves?
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of butterfly valves. This includes inspecting seals and bearings for signs of wear, checking the disc for any damage, and lubricating moving parts as necessary. Additionally, it’s crucial to monitor the valve’s operation for any signs of leakage or irregularities, addressing issues promptly to prevent costly downtime and repairs.
5. How are butterfly valves integrated into automated systems, and what are the advantages of automation?
Butterfly valves can be integrated into automated systems using various types of actuators, such as pneumatic, hydraulic, or electric. Automation allows for precise control of the valve remotely, enabling consistent and accurate regulation of fluid flow. Advantages of automation include improved efficiency, reduced human intervention, and the ability to integrate valves into complex industrial processes, enhancing overall system performance and reliability.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
Recommended courses (Published on EPCLand)
- Basics of Piping Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Complete Course on Piping Engineering
- Material Requisitions
- Piping Material Specifications
- Valve Material Specifications
Don’t miss the published articles on following:
Attempt Quiz
Question 1:
What is a butterfly valve primarily used for?
Explanation: Butterfly valves are primarily used for regulating fluid flow in pipes.
Question 2:
Which of the following best describes the operation of a butterfly valve?
Explanation: Butterfly valves operate by rotating around a disc to control flow.
Question 3:
What is the disc in a butterfly valve typically made of?
Explanation: The disc in a butterfly valve is typically made of metal.
Question 4:
Which of the following applications is NOT suitable for a butterfly valve?
Explanation: Butterfly valves are not typically used in high-pressure steam systems.
Question 5:
What is the advantage of a butterfly valve over a ball valve?
Explanation: Butterfly valves generally have less pressure drop compared to ball valves.
Question 6:
What kind of actuator is commonly used to automate butterfly valves?
Explanation: Pneumatic actuators are commonly used to automate butterfly valves.
Question 7:
What is the main advantage of a double-offset butterfly valve?
Explanation: Double-offset butterfly valves provide tighter sealing compared to other types.
Question 8:
Which material is commonly used for the construction of butterfly valve discs?
Explanation: Stainless steel is commonly used for the construction of butterfly valve discs.
Question 9:
Which factor is important when selecting a butterfly valve for high-temperature applications?
Explanation: The material and design of the disc are crucial when selecting a butterfly valve for high-temperature applications.
Question 10:
What is the typical range of motion for a butterfly valve?
Explanation: Butterfly valves typically have a range of motion of 90 degrees.



