1. Introduction
The oil and gas industry relies on a complex network of equipment and processes to extract, transport, and refine hydrocarbon resources efficiently. Among the many components essential to this industry, Y Type Strainers play a critical role in ensuring the integrity and performance of equipment and systems. In this article, we will delve into the world of Y Type Strainers, exploring their history, basic function, main components, applications in the oil and gas sector, and the relevant codes and standards. Understanding the significance of Y Type Strainers in oil and gas projects is vital for optimizing operational efficiency and maintaining equipment longevity.
Table of Contents
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
2. Brief History
Evolution of Strainers in Industrial Applications
Strainers have been an integral part of industrial processes for centuries. Their primary purpose is to remove solid particles and impurities from liquids or gases before they enter critical equipment or systems. Early strainers were simple mesh screens or perforated plates, serving as rudimentary filtration devices. Over time, the need for more sophisticated and effective strainers became evident as industries evolved.
Introduction of Y Type Strainer in the Oil & Gas Sector
The oil and gas industry, with its demanding requirements for equipment reliability and safety, witnessed the introduction of specialized strainers. The Y Type Strainer, as its name suggests, features a Y-shaped configuration and offers several advantages over its predecessors. This innovative design enables efficient particle removal while minimizing pressure drop, making it ideal for applications in the oil and gas sector.
Key Milestones in Strainer Technology Development
The evolution of strainer technology has been marked by significant milestones. From basic mesh screens to complex, self-cleaning strainers, continuous improvement has been the norm. Y Type Strainers represent a milestone in this journey, combining efficiency, durability, and ease of maintenance. These milestones have contributed to the growth and efficiency of various industries, particularly in the context of the oil and gas sector.
3. Basic Function and Working Principle
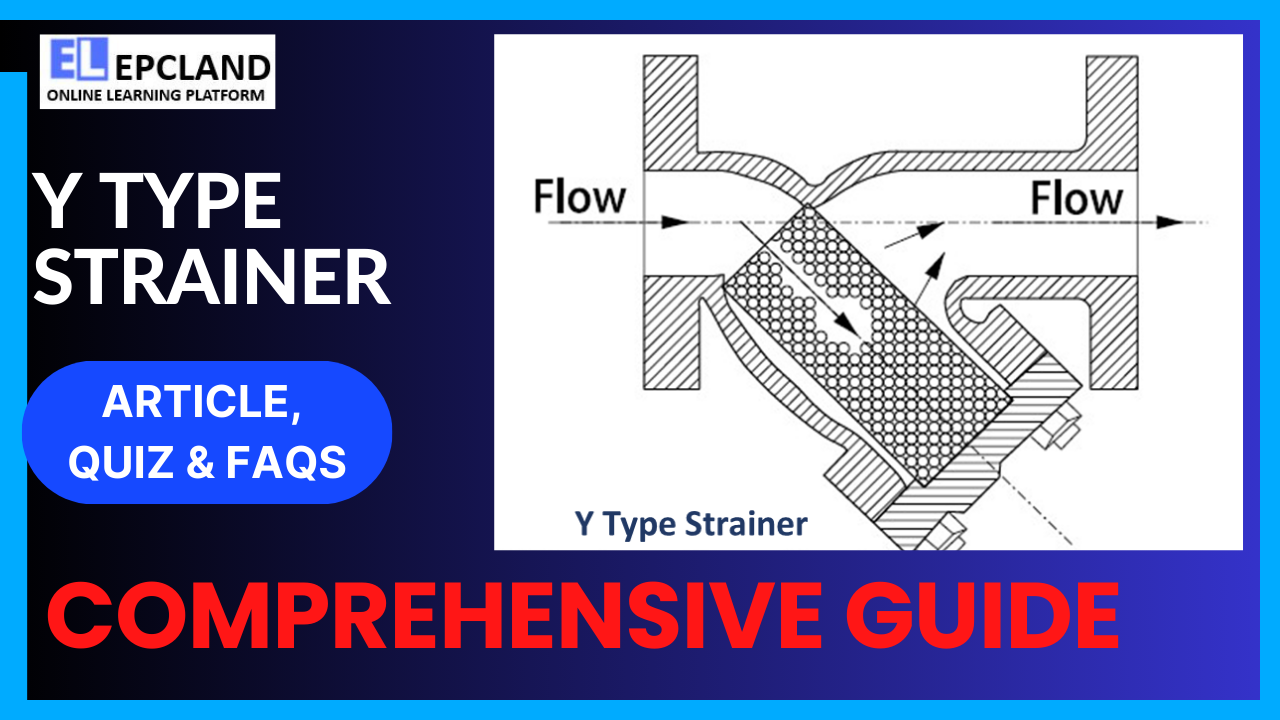
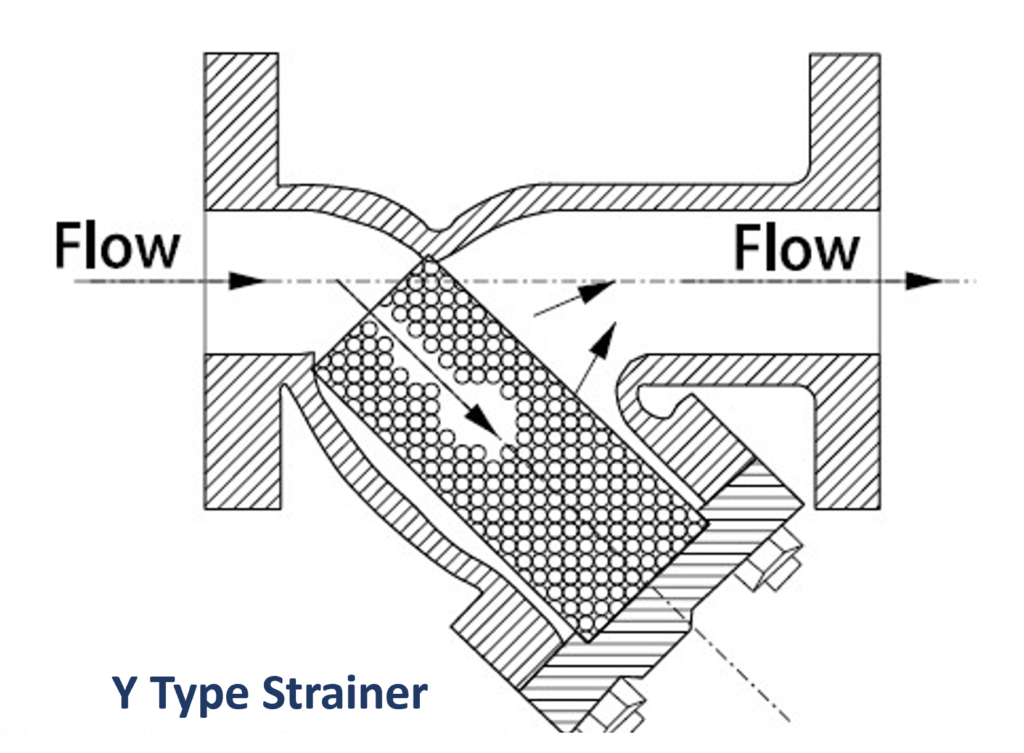
At its core, a Y Type Strainer is designed to remove unwanted particles and debris from liquids or gases, ensuring that only clean, filtered fluid enters downstream equipment. Its operation is based on a simple yet effective principle.
Explanation of the Filtration Process
When fluid flows through a Y Type Strainer, it encounters a Y-shaped chamber. The strainer’s inlet is positioned at the stem of the Y, while the filtered fluid exits through the arms of the Y. As the fluid passes through the strainer, any solid particles or impurities present in the flow are trapped by a perforated or mesh screen. This screen allows clean fluid to pass through while retaining contaminants.
Demonstration of Y Type Strainer’s Operation
The Y Type Strainer’s design ensures that debris and particles accumulate in the lower portion of the Y-shaped chamber. This accumulation can be periodically removed by closing the valve at the base of the strainer and detaching the strainer cap. This maintenance process is relatively straightforward, making Y Type Strainers a practical choice for industries where downtime must be minimized.
Comparison with Other Types of Strainers
While Y Type Strainers are highly effective for many applications, it’s essential to consider their advantages and disadvantages compared to other types of strainers. Basket strainers, duplex strainers, and T Type Strainers are among the alternatives, each with its own set of characteristics and applications. Y Type Strainers excel in situations where space is limited, and frequent maintenance is undesirable.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
4. Main Components & Its Function
A Y Type Strainer comprises several key components, each playing a crucial role in its efficient operation.
Y-Shaped Body
The Y-shaped body is the defining feature of this type of strainer. It serves as the primary chamber through which fluid flows. Its design allows for the efficient separation of particles from the fluid.
Perforated or Mesh Screen
Located within the Y-shaped body, the perforated or mesh screen is the heart of the Y Type Strainer. It captures solid particles and impurities, preventing them from entering downstream equipment.
Strainer Cap
The strainer cap covers the Y-shaped body and screen, keeping contaminants trapped inside. It is removable to facilitate maintenance and cleaning.
Inlet and Outlet
The strainer has clearly marked inlet and outlet ports. The inlet is where the unfiltered fluid enters, while the outlet delivers the filtered fluid to downstream processes.
Drain Valve
At the base of the Y Type Strainer, a drain valve is typically provided. This valve allows for the controlled release of accumulated debris and particles during maintenance.
Seals and Gaskets
Seals and gaskets ensure a tight and leak-free seal between the strainer’s components, preventing fluid from bypassing the strainer screen.
Mounting Flanges or Connections
The strainer is equipped with mounting flanges or connections that facilitate its installation into the pipeline or process system.
5. Application of Y Type Strainer in Oil & Gas Industry
Filtering Requirements in Oil & Gas Projects
The oil and gas industry is known for its rigorous requirements regarding equipment reliability and safety. Contaminants present in the fluid can lead to equipment damage, reduced efficiency, and safety hazards. Consequently, effective filtration is crucial to maintain the integrity of equipment and processes.
Specific Applications in Upstream and Downstream Processes
Y Type Strainers find extensive use in both upstream and downstream processes within the oil and gas industry:
Upstream Applications
- Wellhead Protection: Y Type Strainers are installed at wellheads to filter out sand, debris, and other particulate matter, preventing damage to pumps and other equipment.
- Pipeline Filtration: In pipelines transporting crude oil or natural gas, Y Type Strainers protect valves and meters from fouling, ensuring accurate measurements and efficient flow control.
- Produced Water Treatment: Y Type Strainers play a role in separating solids from produced water, a crucial step in environmental compliance and resource recovery.
Downstream Applications
- Refinery Processes: In refineries, Y Type Strainers are used to protect heat exchangers, compressors, and other critical equipment from fouling caused by contaminants in feedstock and process streams.
- Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) Plants: Y Type Strainers are employed to filter natural gas before it is liquefied, ensuring the purity of the final product.
- Chemical Injection Systems: Y Type Strainers are essential components in chemical injection systems, preventing clogging and damage to injection pumps.
Real-Life Examples Showcasing Successful Implementation
Several oil and gas projects have benefited significantly from the use of Y Type Strainers. For instance, a major offshore drilling operation in the Gulf of Mexico reduced maintenance downtime by 30% and extended the lifespan of their pumps by employing Y Type Strainers at key points in their fluid handling systems. Similarly, a large-scale LNG plant in Qatar achieved more efficient operations and minimized costly shutdowns by incorporating Y Type Strainers into their gas processing units.
6. Advantages & Disadvantages
Advantages:
| Advantage | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Filtration Efficiency | Y Type Strainers effectively capture solid particles, ensuring a high degree of filtration and equipment protection. |
| Reduction in Maintenance Costs | Regular maintenance of Y Type Strainers is straightforward, reducing downtime and the associated costs. |
| Prolonged Equipment Lifespan | By preventing damage from contaminants, Y Type Strainers contribute to the longevity of pumps, valves, and meters. |
| Improved Overall System Performance | Clean and filtered fluids enhance the efficiency of downstream equipment, leading to improved system performance. |
Disadvantages:
| Disadvantage | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Initial Installation Cost | The upfront cost of purchasing and installing Y Type Strainers might be higher compared to some other strainer types. |
| Possibility of Clogging | In environments with exceptionally high levels of particulate matter, Y Type Strainers can potentially clog over time. |
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
7. Codes & Standards
Relevant Codes and Standards:
| Code/Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| ASME B16.34 | Standard for valves, including strainers, providing specifications for materials, design, and testing. |
| API 598 | Standard specifying inspection and testing requirements for various types of valves, including strainers. |
| ANSI/ASME B31.3 | Code for process piping systems, ensuring compliance with pressure, temperature, and design requirements. |
It is crucial for oil and gas industry professionals to adhere to these standards to ensure the proper selection, installation, and maintenance of Y Type Strainers, guaranteeing safe and efficient operations.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, Y Type Strainers stand as indispensable guardians of equipment integrity in the oil and gas industry. Their evolution from simple screens to sophisticated, efficient filters mirrors the advancement of industrial technology. By understanding their basic functions, components, and applications, industry professionals can make informed decisions regarding their implementation. Adhering to relevant codes and standards ensures that these strainers perform optimally, contributing to the overall efficiency, safety, and longevity of oil and gas projects. As the industry continues to evolve, Y Type Strainers will undoubtedly remain a cornerstone of efficient fluid handling and filtration, ensuring the smooth flow of operations in the challenging environments of the oil and gas sector.
FAQs
- What is a Y Type Strainer and how does it differ from other types of strainers used in the oil and gas industry?
- This question addresses the fundamental definition and distinctions of Y Type Strainers, providing clarity on its unique features and advantages in comparison to other strainer types.
- What are the common challenges faced in the maintenance of Y Type Strainers in offshore oil rigs, and how can these challenges be mitigated?
- This question focuses on practical concerns, highlighting the specific issues faced in real-world applications and seeking solutions or best practices to ensure the efficient maintenance of Y Type Strainers in offshore environments.
- Can Y Type Strainers handle extreme operating conditions, such as high pressures and corrosive fluids, commonly encountered in the oil and gas industry?
- Addressing the strainer’s capabilities under extreme conditions provides valuable insights for professionals dealing with challenging industrial environments, emphasizing the strainer’s durability and reliability in demanding situations.
- Are there any advancements or innovations in Y Type Strainer technology that have been introduced recently, and how do these developments benefit the efficiency of oil and gas operations?
- This question explores the evolving landscape of strainer technology, emphasizing recent innovations that enhance its performance and efficiency. It sheds light on how these advancements contribute to improving overall operations in the oil and gas sector.
- What are the key considerations that engineers and project managers should keep in mind when selecting and installing Y Type Strainers in a new oil and gas project?
- This question is essential for decision-makers involved in project planning and execution. It delves into critical factors such as sizing, installation requirements, and compatibility, guiding professionals in making informed choices for the successful implementation of Y Type Strainers in their projects.
Recommended courses (Published on EPCLand)
- Basics of Piping Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Complete Course on Piping Engineering
- Material Requisitions
- Piping Material Specifications
- Valve Material Specifications
Don’t miss the published articles on following:
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
Attempt Quiz
Question 1:
What is the primary function of a Y Type Strainer in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Explanation: A Y Type Strainer is used to remove solid particles from fluids, ensuring the integrity of equipment and processes in the Oil & Gas Industry.
Question 2:
What is the shape of the straining element in a Y Type Strainer?
Explanation: The straining element in a Y Type Strainer is Y-shaped, allowing efficient filtration of fluids.
Question 3:
What is the main advantage of using a Y Type Strainer over other types of strainers?
Explanation: Y Type Strainers offer a larger filtration area compared to other types of strainers, allowing for efficient particle removal.
Question 4:
Where is a Y Type Strainer typically installed in a piping system?
Explanation: A Y Type Strainer is typically installed before the pump, protecting the pump and downstream components from debris.
Question 5:
What material is commonly used for the construction of Y Type Strainers in corrosive environments?
Explanation: Stainless Steel is commonly used for the construction of Y Type Strainers in corrosive environments due to its corrosion resistance properties.
Question 6:
What is the purpose of the blowdown valve in a Y Type Strainer?
Explanation: The blowdown valve in a Y Type Strainer is used to release trapped debris, ensuring continuous filtration efficiency.
Question 7:
What is the typical mesh size of the straining element in a Y Type Strainer?
Explanation: The typical mesh size of the straining element in a Y Type Strainer varies, but common sizes include 50 mesh, 100 mesh, 200 mesh, and 300 mesh.
Question 8:
What is the maximum operating pressure for most Y Type Strainers?
Explanation: The maximum operating pressure for most Y Type Strainers is 150 psi, although this can vary based on specific designs and materials.
Question 9:
What is the purpose of the drain plug in a Y Type Strainer?
Explanation: The drain plug in a Y Type Strainer is used to drain collected debris, maintaining the efficiency of the filtration process.
Question 10:
What is the typical temperature range for the operation of Y Type Strainers?
Explanation: Y Type Strainers are typically designed to operate within the temperature range of 0°C to 100°C, making them suitable for various industrial applications.