1. Introduction
In the intricate web of machinery that is the oil and gas industry, every component plays a crucial role. Among these, the T Type Strainer stands out as a sentinel, guarding the equipment against impurities that could potentially jeopardize the entire system. This article delves deep into the intricacies of T Type Strainers, exploring their evolution, functions, applications, advantages, and the standards that govern their usage in the oil and gas sector.
Table of Contents
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
2. Brief History
T Type Strainers, although seemingly mundane, have a rich history. They have evolved significantly from their humble beginnings. Initially conceived as simple filters, they have transformed into sophisticated instruments that are integral to the smooth functioning of the oil and gas industry. The journey from their inception to the present day is a testament to human ingenuity and the industry’s relentless pursuit of efficiency and reliability.
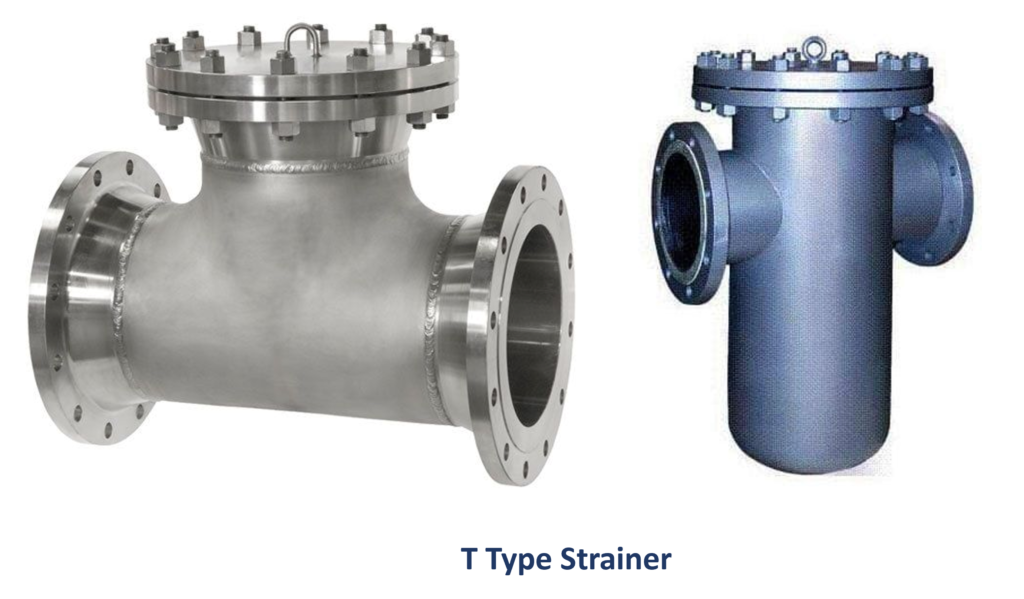
3. Basic Function and Working Principle
At its core, a T Type Strainer is designed to remove impurities from fluids, ensuring that the machinery downstream operates with optimal efficiency. The working principle is elegant in its simplicity. Fluid passes through the strainer body, where a mesh or perforated screen captures contaminants. Cleaned fluid continues its journey, while the impurities are trapped for later disposal. This fundamental process lies at the heart of the strainer’s functionality and is vital in maintaining the integrity of the oil and gas equipment.
4. Main Components & Their Functions
T Type Strainers are ingeniously designed filtration devices, consisting of several essential components, each serving a specific function to ensure the efficient removal of impurities from fluids. Understanding the roles of these components is pivotal in appreciating the strainer’s overall effectiveness and reliability.
4.1 Body
The body of the T Type Strainer serves as the primary structure that houses the filtration element and provides the necessary framework for other components. It is typically made of durable materials such as cast iron, carbon steel, stainless steel, or exotic alloys, depending on the specific application and the nature of the fluids being filtered. The body is engineered to withstand high pressures and temperatures commonly encountered in the oil and gas industry, ensuring the strainer’s longevity and robustness.
4.2 Filtration Element
At the heart of the T Type Strainer is the filtration element, which can take the form of a perforated sheet or a mesh screen. This element is strategically positioned within the body to capture particles and impurities present in the fluid. The perforated sheet or screen is meticulously designed with precise hole sizes, allowing the passage of desired fluids while effectively trapping contaminants. The choice of the filtration element depends on the nature and size of the impurities to be removed, ensuring optimal filtration efficiency.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
4.3 Cap, Gasket, and Bolts
The cap of the T Type Strainer serves as the top cover, tightly securing the filtration element within the body. It is fastened in place by gaskets and bolts. The gasket, usually made of rubber or other resilient materials, forms a tight seal between the body and the cap. This seal is critical in preventing fluid leakage, ensuring that all the fluid passes through the filtration element, enhancing the strainer’s efficiency. High-quality bolts, often made of stainless steel, are used to fasten the cap securely, maintaining the integrity of the seal under varying pressure conditions.
4.4 Drain Plug
A drain plug is a small yet crucial component located at the bottom of the T Type Strainer. It serves as an access point for removing accumulated impurities and debris from the strainer. Periodically, when the strainer traps a substantial amount of contaminants, the drain plug is opened. This allows for easy disposal of the collected impurities, ensuring the strainer continues to function optimally. The presence of a drain plug simplifies maintenance procedures, making the strainer user-friendly and efficient in real-world applications.
4.5 Connection Ports
T Type Strainers are equipped with connection ports that facilitate the integration of the strainer into the pipeline system. These ports are strategically positioned on the body and are designed to match standard pipe sizes and configurations. Proper alignment and secure connections are vital to prevent leaks and maintain the structural integrity of the pipeline. The placement and sizing of these ports are carefully considered during the strainer’s design phase, ensuring seamless integration into the existing infrastructure.
4.5 Basket Support
In some T Type Strainers, especially those designed for heavy-duty applications in the oil and gas industry, a basket support is included. This component provides additional reinforcement to the filtration element, preventing it from collapsing under high differential pressures. The basket support ensures the longevity of the filtration element, prolonging its lifespan and maintaining consistent filtration performance over time. This feature is particularly important in applications where the strainer is subjected to fluctuating pressure conditions.
Understanding the intricate synergy of these components highlights the engineering precision behind T Type Strainers. Each part plays a vital role, ensuring the effective removal of impurities and guaranteeing the smooth operation of machinery in the oil and gas industry. Engineers and operators rely on the meticulous design and robust construction of these components to safeguard their equipment, making T Type Strainers indispensable in the complex and demanding landscape of the oil and gas sector.
5. Applications in the Oil & Gas Industry
T-Type strainers, also known as basket strainers, are widely used in various industries to remove unwanted solid particles from liquid or gas pipelines. Their design features a basket-shaped straining element that captures debris, preventing it from damaging downstream equipment or processes. Here are the detailed applications of T-Type strainers in different industries:
5.1. Chemical Industry:
In the chemical industry, T-Type strainers are used to filter out impurities from various chemicals and solvents. These impurities could otherwise contaminate the end products or damage sensitive equipment like pumps and valves. Strainers protect processes such as polymer production, where maintaining purity is critical.
5.2. Petroleum Industry:
T-Type strainers play a vital role in the petroleum industry. They are employed in pipelines to remove rust, scale, and other contaminants from crude oil, refined products, and natural gas. Clean fuel is essential for the efficient operation of engines and turbines, making strainers indispensable in refineries and petrochemical plants.
5.3. Water Treatment Plants:
Municipal water treatment plants use T-Type strainers to remove debris such as leaves, sticks, and large particles from raw water sources before the water undergoes further treatment processes. This ensures the protection of pumps, valves, and other sensitive equipment within the water treatment facility.
5.4. Power Generation:
In power plants, especially those using steam turbines, T-Type strainers are installed in pipelines to protect the turbines from foreign particles that could damage the blades. They also find application in cooling water systems where large debris needs to be filtered out to prevent clogging of pipes and heat exchangers.
5.5. Food and Beverage Industry:
T-Type strainers are used in the food and beverage industry to filter liquids like fruit juices, sauces, and dairy products. Maintaining product purity is crucial in this industry, and strainers help remove unwanted particles and ensure that the final products meet quality standards.
5.6. Pharmaceutical Industry:
Pharmaceutical manufacturing processes require high levels of purity. T-Type strainers are utilized to filter pharmaceutical solutions and suspensions, ensuring that medicines are free from particulate contaminants. They are also used in water systems within pharmaceutical facilities to maintain the quality of purified water used in drug formulations.
5.7. Pulp and Paper Industry:
In the pulp and paper industry, T-Type strainers are used to filter out bark, wood chips, and other debris from process water and pulp slurries. Clean water is essential in papermaking processes to maintain the quality of the paper and to prevent damage to pumps and nozzles.
5.8. Agriculture and Irrigation:
Farm irrigation systems often incorporate T-Type strainers to filter water from rivers, lakes, or wells before it reaches the irrigation equipment. Strainers prevent clogging of sprinklers and drippers due to sand, algae, or other particulate matter present in the water.
5.9. HVAC Systems:
T-Type strainers are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to protect pumps, cooling towers, and other components from debris present in the circulating water. Clean water ensures the efficient operation of HVAC equipment and prolongs their lifespan.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
6. Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of T Type Strainers
T Type Strainers offer several advantages. They efficiently remove contaminants, ensuring the purity of the fluid. Maintenance is relatively straightforward, with periodic cleaning being the primary requirement. Moreover, these strainers are cost-effective, providing a robust solution at a reasonable price point. Their durability and reliability further enhance their appeal, making them a preferred choice in the oil and gas sector.
Disadvantages of T Type Strainers
However, T Type Strainers have limitations. Their filtration capacity is finite, and they can clog if not maintained regularly. This susceptibility to clogging necessitates vigilant monitoring, which, if neglected, could lead to operational issues. Recognizing these limitations is essential in making informed decisions regarding their usage in specific applications.
7. Codes and Standards of T Type Strainers
Adherence to industry standards is paramount in ensuring the quality and safety of equipment. T Type Strainers are no exception. International standards, such as those set by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the American Petroleum Institute (API), dictate the design, manufacturing, and testing requirements for these strainers. Compliance with these standards not only guarantees the strainer’s performance but also promotes interoperability and compatibility within the industry.
8. Future Trends and Innovations
As technology continues to advance, T Type Strainers are also undergoing significant innovations. Enhanced materials, improved filtration techniques, and automation are shaping the future of these essential components. Nanotechnology, for instance, offers the possibility of even finer filtration, paving the way for strainers that can capture particles at the molecular level. These advancements are not only increasing the efficiency of T Type Strainers but also expanding their applicability to new frontiers within the oil and gas industry.
9. Conclusion
In conclusion, T Type Strainers are the unsung heroes of the oil and gas industry, ensuring the purity and integrity of fluids that drive our world. From their historical roots to their modern applications, these strainers have come a long way, evolving with the industry’s changing needs. While they have limitations, their advantages far outweigh the disadvantages, making them indispensable in various operational contexts.
As the industry continues to innovate, T Type Strainers will likely undergo further enhancements, becoming even more efficient and reliable. Their adherence to stringent codes and standards guarantees their quality, providing peace of mind to engineers and operators alike. As we move into an era of increased technological sophistication, these unassuming components will continue to play a vital role, silently safeguarding the intricate machinery that powers our global energy needs.
FAQs
Q1: What is the primary purpose of a T Type Strainer in the oil and gas industry?
A1: T Type Strainers are specifically designed filtration devices used in the oil and gas industry to remove impurities, such as debris, particles, and contaminants, from fluids. By capturing these impurities, T Type Strainers ensure the integrity and efficiency of equipment by preventing potential damage and clogging, ultimately ensuring the smooth operation of pipelines, pumps, and other essential machinery.
Q2: How often should T Type Strainers be inspected and maintained in industrial applications?
A2: The frequency of inspections and maintenance for T Type Strainers depends on the specific operating conditions, the nature of the fluids being filtered, and the level of impurities present. Generally, regular visual inspections are recommended, and maintenance intervals can vary from monthly to quarterly. However, in environments where there are higher chances of impurities, more frequent checks and cleaning might be necessary to prevent clogging and maintain optimal filtration efficiency.
Q3: Can T Type Strainers be customized for specific applications in the oil and gas industry?
A3: Yes, T Type Strainers can be customized to meet the unique requirements of different applications within the oil and gas industry. Engineers can modify aspects such as the material of construction, filtration element type, mesh size, pressure and temperature ratings, and connection sizes to tailor the strainer for specific fluids, pressures, and environmental conditions. Customization ensures that the strainers effectively address the challenges posed by diverse operational settings.
Q4: What is the significance of compliance with industry standards for T Type Strainers?
A4: Compliance with industry standards, such as those set by organizations like ASME and API, is crucial for T Type Strainers. These standards define the manufacturing, testing, and performance criteria that ensure the strainers meet quality and safety requirements. Adherence to these standards not only guarantees the reliability and efficiency of the strainers but also promotes consistency and compatibility across various components used in the oil and gas industry.
Q5: Are T Type Strainers suitable for both onshore and offshore oil and gas operations?
A5: Yes, T Type Strainers are versatile and find applications in both onshore and offshore oil and gas operations. Their robust construction, corrosion-resistant materials, and adaptability to various environmental conditions make them suitable for offshore platforms, subsea installations, as well as onshore facilities. Whether in pipelines, drilling operations, or refining processes, T Type Strainers are designed to withstand challenging conditions and are widely used in diverse settings within the oil and gas industry.
Recommended courses (Published on EPCLand)
- Basics of Piping Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Complete Course on Piping Engineering
- Material Requisitions
- Piping Material Specifications
- Valve Material Specifications
Don’t miss the published articles on following:
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
Attempt Quiz
Question 1:
What is the primary function of a T Type Strainer in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Explanation: A T Type Strainer is used to remove solid particles from the fluid in the Oil & Gas Industry.
Question 2:
What is the typical design of a T Type Strainer?
Explanation: T Type Strainers are typically T-shaped in design.
Question 3:
What is the material commonly used for making T Type Strainers?
Explanation: Stainless Steel is commonly used for making T Type Strainers due to its corrosion resistance properties.
Question 4:
What is the purpose of the mesh in a T Type Strainer?
Explanation: The mesh in a T Type Strainer is used to remove debris and contaminants from the fluid.
Question 5:
Where in the pipeline system is a T Type Strainer typically installed?
Explanation: A T Type Strainer is typically installed at the beginning of the pipeline to filter out contaminants before the fluid enters the system.
Question 6:
What is the main advantage of using a T Type Strainer in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Explanation: The main advantage of using a T Type Strainer is reduced maintenance and prevention of equipment damage by removing particles from the fluid.
Question 7:
What is the proper way to clean a T Type Strainer?
Explanation: The proper way to clean a T Type Strainer is to flush it with clean water or air to remove accumulated debris.
Question 8:
What size particles can a T Type Strainer typically remove?
Explanation: A T Type Strainer can typically remove both large and small particles from the fluid.
Question 9:
What is the impact of a clogged T Type Strainer on the system?
Explanation: A clogged T Type Strainer can decrease flow rate and potentially damage equipment due to restricted fluid flow.
Question 10:
Which industry besides Oil & Gas commonly uses T Type Strainers?
Explanation: Besides Oil & Gas, the Food & Beverage industry commonly uses T Type Strainers for filtration purposes.



