1. Introduction
Filtration plays a pivotal role in the smooth operation of oil and gas industry projects. The efficient removal of impurities from fluids ensures the longevity of equipment and maintains the quality of the end products. One of the indispensable tools in this filtration process is the Cone Strainer. In this article, we will delve into the significance of Cone Strainers in the oil and gas sector, exploring their history, functionality, components, applications, and the standards that govern their use.
Table of Contents
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
2. Brief History
The evolution of filtration technology in industrial applications traces a fascinating journey. From rudimentary sieves to intricate strainers, the need for cleaner fluids led to the development of Cone Strainers. In the context of the oil and gas industry, Cone Strainers found their niche due to their ability to handle high flow rates and large particulate matter, a crucial requirement in this sector.
3. Basic Function and Working Principle
Cone strainers are fundamental components in industrial pipelines, especially in the oil and gas sector, where the need for efficient filtration is paramount. Understanding their basic function and working principle is crucial to appreciating their significance in ensuring the integrity of fluid systems.
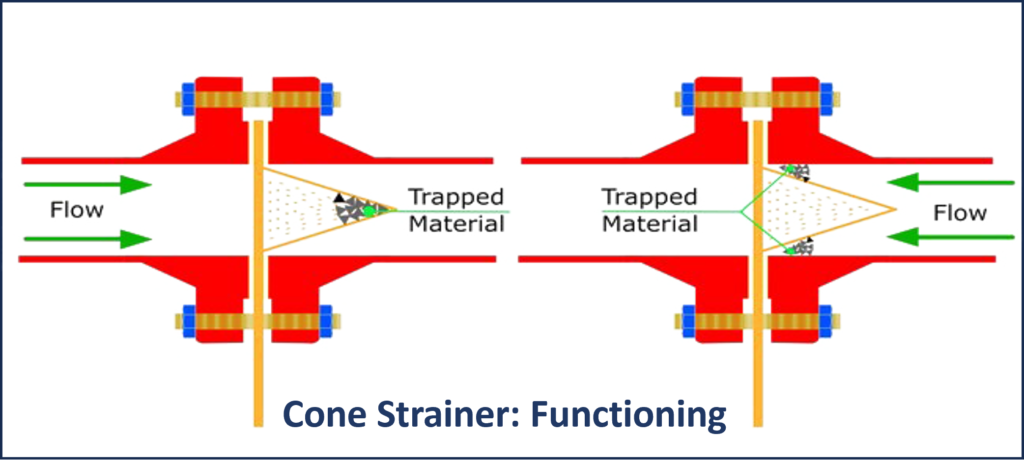
Basic Function of Cone Strainers
The primary function of a cone strainer is to filter out impurities and solid particles from fluids flowing through pipelines. In the context of the oil and gas industry, these impurities can range from debris and sand to rust particles and scale. The cone strainer acts as a protective barrier, preventing these contaminants from entering sensitive equipment downstream, such as pumps, valves, and meters.
Working Principle of Cone Strainers
Cone strainers operate on a simple yet highly effective principle. The strainer consists of a conical-shaped screen, often made from stainless steel due to its corrosion resistance and durability. This conical screen is placed inside a housing, forming the core of the strainer assembly.
When fluid flows through the pipeline, it encounters the cone strainer. The pressure of the flowing fluid drives it through the conical screen. Here, the strategically designed gaps and perforations in the screen allow the fluid to pass through, while capturing larger particles. As the fluid passes through the narrowing gap towards the apex of the cone, particles that are larger than the gaps in the screen are trapped on the inner surface of the cone.
The trapped particles accumulate on the inside of the cone, forming a filter cake. Over time, as more particles are captured, this filter cake becomes an increasingly effective filtration layer. Meanwhile, the filtered fluid, now free from larger contaminants, continues its journey through the pipeline. The conical shape is particularly efficient because it maximizes the filtration area while ensuring a gradual decrease in pressure, preventing clogging and maintaining a consistent flow rate.
Importance of the Working Principle
The working principle of cone strainers is crucial for several reasons:
- Efficient Filtration: The conical shape allows for a larger filtration area, ensuring that a substantial volume of fluid can be filtered without impeding the flow rate significantly.
- Preventing Equipment Damage: By capturing particles before they reach sensitive components like pumps and valves, cone strainers prevent wear and damage, extending the lifespan of expensive equipment.
- Maintaining Process Integrity: In the oil and gas industry, maintaining the purity and integrity of fluids is essential for product quality and safety. Cone strainers play a pivotal role in achieving these objectives.
- Reducing Maintenance Downtime: Regular maintenance, such as cleaning or replacing the strainer, is easier and less frequent because the captured particles are confined to the easily accessible conical surface.
- Versatility: Cone strainers can handle various types of fluids, including corrosive and viscous substances, making them versatile for different applications within the industry.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
Main Components & Its Function
Cone strainers, though seemingly simple, are comprised of several key components, each with a specific function that collectively ensures efficient filtration in the oil and gas industry.
Conical Screen
The conical screen is the central component of a cone strainer, and its design is critical to the strainer’s effectiveness. Usually made of stainless steel or other durable materials, the conical shape allows for a larger filtration area compared to flat screens. The conical screen’s primary function is to capture solid particles present in the fluid flowing through the strainer. As the fluid passes through the conical screen, contaminants are trapped on the inner surface, preventing them from progressing further downstream. The screen’s precision in mesh size ensures that only particles larger than the specified diameter are filtered out, allowing smaller particles and the desired fluid to pass through.
Housing
The housing, also known as the body or casing, serves as the protective enclosure for the conical screen. Typically made from materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, or exotic alloys, the housing provides structural integrity to the strainer. It guards the delicate conical screen against physical damage and ensures that the strainer can withstand high-pressure environments without deformation. Additionally, the housing features inlet and outlet connections, allowing seamless integration into pipelines. The connections are designed to match standard pipe sizes, ensuring compatibility with various industrial systems.
Support Structure
Inside the housing, the conical screen is supported by a robust structure. This support system maintains the screen’s shape and prevents it from collapsing under high flow rates or pressure differentials. The support structure is strategically designed to avoid any interference with the filtration process. It ensures that the conical screen remains stable, allowing for consistent and reliable filtration over extended periods of operation.
Drain Port
Many cone strainers feature a drain port located at the bottom of the housing. The drain port serves a crucial function during maintenance and cleaning procedures. When the strainer needs to be cleaned or inspected, opening the drain port allows the residual fluid and captured contaminants to be safely drained out of the system. This feature simplifies maintenance activities, reducing downtime and ensuring efficient cleaning of the strainer. Drain ports are typically equipped with threaded connections, allowing easy attachment of drainage mechanisms or hoses for fluid disposal.
Installation Accessories
Cone strainers are often equipped with additional components to facilitate their installation and operation. These may include mounting brackets, gaskets, bolts, and nuts. Mounting brackets provide support for the strainer, ensuring it remains stable and securely attached to the pipeline. Gaskets create a tight seal between the strainer and the pipeline connections, preventing fluid leakage. Bolts and nuts secure the housing, conical screen, and support structure together, forming a cohesive unit. Proper installation accessories are essential for the reliable and leak-free operation of cone strainers within industrial systems.
4. Application of Cone Strainer in Oil & Gas Industry
In the oil and gas industry, where large volumes of fluids are processed daily, Cone Strainers find extensive application. These strainers are commonly used in upstream processes, where raw crude oil is transported and refined. They also play a vital role in downstream processes, ensuring the purity of end products such as refined fuels and lubricants. Additionally, Cone Strainers are deployed in gas processing units, where natural gas is purified before distribution.
Real-life Examples
An illustrative example of Cone Strainers’ effectiveness can be observed in offshore drilling platforms. These platforms operate in harsh marine environments, where the ingress of seawater or debris can severely damage equipment. Cone Strainers, strategically placed in the pipelines, prevent such contaminants from entering sensitive machinery, thereby enhancing the platform’s operational reliability.
5. Advantages & Disadvantages
Advantages:
- High Filtration Efficiency: Cone Strainers effectively capture large particles, ensuring the purity of processed fluids.
- Low Pressure Drops: The well-designed conical screen minimizes pressure drops, optimizing the flow of fluids.
- Durability: Constructed from robust materials, Cone Strainers are highly durable and can withstand challenging operational conditions.
- Easy Maintenance: Cleaning and maintaining Cone Strainers are relatively straightforward, reducing downtime during maintenance activities.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Filtration for Small Particles: Cone Strainers are designed primarily for capturing large particles, making them less effective for filtering out smaller contaminants.
- Initial Installation Cost: While Cone Strainers offer long-term cost benefits, the initial investment might be higher than other filtration options.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
6. Codes & Standards
International Standards Governing Cone Strainers:
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| API 598 | Valve Inspection and Testing |
| ASME B16.34 | Valves – Flanged, Threaded, and Welding End |
| ASTM A351/A351M | Standard Specification for Castings, Austenitic, for Pressure-Containing Parts |
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, Cone Strainers stand as indispensable guardians in the oil and gas industry, ensuring the purity and efficiency of industrial processes. Their evolution from basic filtration tools to sophisticated components mirrors the industry’s progress. As technology advances, Cone Strainers continue to play a vital role in safeguarding equipment, enhancing efficiency, and contributing to the sector’s growth.
8. Future Trends
Looking ahead, the future of Cone Strainers in the oil and gas industry is promising. Research and development efforts are focused on improving their filtration capabilities, making them more versatile in handling a broader range of contaminants. Additionally, advancements in materials and manufacturing processes will likely result in more cost-effective and durable Cone Strainers, further benefiting the industry.
FAQs
1. What distinguishes Cone Strainers from other types of filtration systems commonly used in the oil and gas industry?
Cone Strainers stand out due to their conical-shaped filtering element, allowing them to efficiently capture large particles while minimizing pressure drops. This design feature makes them ideal for applications where high flow rates and large particulate matter are prevalent, setting them apart from other filtration systems.
2. How frequently do Cone Strainers require maintenance, and what are the typical maintenance procedures involved?
The frequency of maintenance for Cone Strainers depends on the specific operational conditions and the type of contaminants being filtered. Generally, regular inspections are necessary to ensure optimal performance. Maintenance procedures often include removing the strainer, cleaning the conical screen thoroughly, and inspecting the housing for any signs of wear or damage. Regular maintenance ensures the strainer operates at peak efficiency.
3. Can Cone Strainers handle corrosive fluids commonly found in the oil and gas industry?
Yes, Cone Strainers can be manufactured using materials like stainless steel, which is highly resistant to corrosion. Depending on the specific corrosive properties of the fluids being processed, material selection can be customized to withstand harsh chemical environments. Proper material selection is crucial to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of Cone Strainers in handling corrosive fluids.
4. What role do Cone Strainers play in preventing equipment damage in offshore drilling platforms?
In offshore drilling platforms, Cone Strainers serve as the first line of defense against seawater and debris ingress. Placed strategically in pipelines, these strainers prevent contaminants from entering sensitive machinery, such as pumps and valves. By ensuring that only clean fluids reach critical equipment, Cone Strainers significantly contribute to preventing damage and downtime in offshore drilling operations.
5. Are Cone Strainers compatible with various pipeline sizes, and what considerations are necessary for proper installation?
Cone Strainers are available in a range of sizes to accommodate different pipeline diameters commonly found in the oil and gas industry. Proper sizing is essential to maintain the desired flow rates while effectively capturing contaminants. During installation, factors such as flow direction, orientation, and location in the pipeline system must be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance. Consulting with engineers or experts familiar with the specific application is advisable to guarantee correct installation and operation of Cone Strainers.
Recommended courses (Published on EPCLand)
- Basics of Piping Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Complete Course on Piping Engineering
- Material Requisitions
- Piping Material Specifications
- Valve Material Specifications
Don’t miss the published articles on following:
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
Attempt Quiz
Question 1:
What is the primary purpose of a Cone Type Strainer in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Explanation: A Cone Type Strainer is used to filter contaminants from fluid pipelines in the Oil & Gas Industry.
Question 2:
What is the typical shape of a Cone Type Strainer?
Explanation: A Cone Type Strainer typically has a conical shape.
Question 3:
Which of the following materials is commonly used for making Cone Type Strainers?
Explanation: Stainless Steel is commonly used for making Cone Type Strainers due to its corrosion resistance properties.
Question 4:
What is the main function of a Cone Type Strainer in a pipeline system?
Explanation: The main function of a Cone Type Strainer is to prevent damage to downstream equipment by removing solid particles from the fluid.
Question 5:
Which industry commonly uses Cone Type Strainers for filtration purposes?
Explanation: Cone Type Strainers are commonly used in the Oil & Gas industry for filtration purposes.
Question 6:
What is the typical mesh size used in Cone Type Strainers?
Explanation: Cone Type Strainers typically have mesh sizes ranging from 100 to 1000 microns.
Question 7:
Which flow characteristic is important for Cone Type Strainers?
Explanation: Cone Type Strainers work best in applications with Laminar Flow, where the fluid flows smoothly in parallel layers.
Question 8:
What is the advantage of using a Cone Type Strainer over other types of strainers?
Explanation: Cone Type Strainers typically offer lower pressure drop compared to other types of strainers, leading to less energy loss in the system.
Question 9:
What is the function of the tapered shape in Cone Type Strainers?
Explanation: The tapered shape of Cone Type Strainers enhances filtration efficiency by trapping particles effectively as the fluid passes through the conical structure.
Question 10:
Which industry regulation or standard often governs the design and use of Cone Type Strainers in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Explanation: The design and use of Cone Type Strainers in the Oil & Gas Industry are often governed by standards such as ASME B31.3.



