Introduction
Storage tanks play a pivotal role in various industries, enabling the safe and efficient storage of liquids and gases. Among the diverse range of tank designs, cone roof and dome roof tanks stand out as two prominent choices. These designs offer unique advantages in terms of structural integrity, suitability for specific liquids, and environmental considerations. This article delves into the features, benefits, applications, and challenges associated with cone and dome roof tanks, providing insights into their comparative analysis and highlighting real-world case studies.
Table of Contents
Do not miss the detailed course on Tank Farm Layout & Stress Analysis
Enrollment link
Check out Similar Articles on other Storage Tanks
Cone Roof Tanks: Design and Features
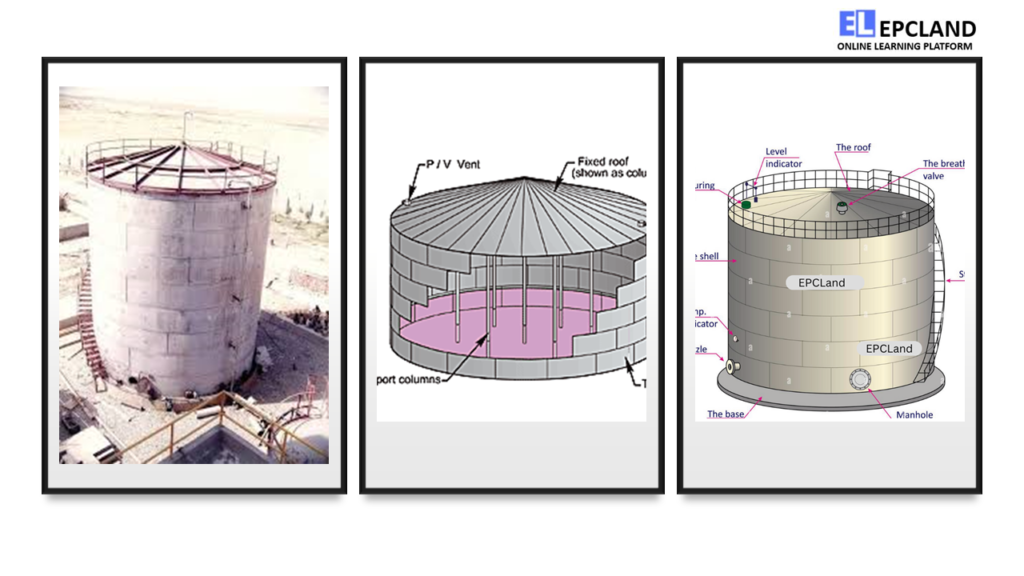
Cone roof tanks, characterized by their conical shape and single sloped roof, are a popular choice in numerous industries. The design simplicity and cost-effectiveness of cone roof tanks make them an attractive option for storage applications. The primary components of a cone roof tank include:

Tank Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Shell | Vertical cylindrical body that holds the stored liquid. |
| Cone Roof | Sloping roof that allows rainwater and debris to slide off. |
| Roof Support | Rings or columns that provide structural support to the roof. |
| Venting System | Ensures pressure regulation and prevents vacuum formation. |
| Drainage System | Collects rainwater and prevents accumulation on the roof. |
| Manway Access | Entry point for inspection, maintenance, and cleaning. |
The structural integrity of cone roof tanks is achieved through the distribution of forces along the sloped roof, minimizing the chances of buckling or collapse. Common materials used in their construction include steel and aluminum due to their strength and corrosion resistance. Venting systems and pressure relief mechanisms are essential to prevent pressure buildup caused by temperature changes or liquid expansion. Cone roof tanks are ideal for storing non-volatile liquids, making them suitable for applications such as crude oil storage and liquid fertilizer containment.
Do not miss the detailed course on Tank Farm Layout & Stress Analysis
Enrollment link
Advantages of Cone Roof Tanks
- Cost-effectiveness: Cone roof tanks are relatively simpler to construct and maintain, making them a cost-effective storage solution.
- Ease of Maintenance: The single-sloped design facilitates easy cleaning, inspection, and maintenance activities.
- Suitability for Certain Liquids: Cone roof tanks are well-suited for storing non-volatile liquids that do not emit harmful vapors.
Dome Roof Tanks: Design and Features
Dome roof tanks, distinguished by their hemispherical or elliptical dome-shaped roofs, are chosen for applications requiring high structural strength. These tanks are commonly used to store volatile liquids, industrial chemicals, and liquefied gases. The essential components of dome roof tanks are:
Tank Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Shell | Vertical cylindrical body that holds the stored liquid. |
| Dome Roof | Hemispherical or elliptical roof that offers maximum structural strength. |
| Support Structure | Robust columns that bear the load of the dome roof and liquid contents. |
| Sealable Devices | Gaskets, seals, or rim connections to minimize vapor emissions. |
| Pressure Relief | Devices that maintain safe internal pressure levels. |
| Manway Access | Entry point for inspection, maintenance, and cleaning. |
Dome roof tanks excel in distributing loads uniformly, with the curved shape inherently providing stability against external forces. Materials like stainless steel and specialized alloys are employed to ensure durability and corrosion resistance. To reduce vapor emissions, dome roof tanks are equipped with sealable devices and pressure relief mechanisms. Their structural strength makes them suitable for storing hazardous materials, volatile substances, and high-pressure liquids.
Advantages of Dome Roof Tanks
- Maximum Structural Strength: The dome-shaped roof design ensures uniform load distribution and superior strength.
- Reduced Emissions: Sealable devices minimize vapor emissions, making dome roof tanks suitable for storing volatile substances.
- Versatile Applications: Dome roof tanks can safely store hazardous materials, volatile substances, and high-pressure liquids.
Do not miss the detailed course on Tank Farm Layout & Stress Analysis
Enrollment link
Applications of Cone and Dome Roof Tanks
Both cone and dome roof tanks find extensive applications across various industries due to their unique design features. Cone roof tanks are commonly used in the petroleum, chemical, and agriculture sectors. They are preferred for storing crude oil, liquid fertilizers, and other non-volatile liquids. Dome roof tanks, on the other hand, excel in storing volatile substances, industrial chemicals, and liquefied gases. They are utilized for storing hazardous materials that require robust structural integrity.
Comparative Analysis of Cone and Dome Roof Tanks
A comparative analysis of cone and dome roof tanks reveals the strengths and weaknesses of each design, aiding in the selection process based on specific requirements.
Pros & Cons
| Aspect | Cone Roof Tanks | Dome Roof Tanks |
|---|---|---|
| Pros | – Cost-effective | – Maximum structural strength |
| – Easy maintenance and cleaning | – Reduced vapor emissions | |
| – Suitable for non-volatile liquids | – Versatile applications | |
| Cons | – Limited suitability for volatile liquids | – Higher construction costs |
| – Less suited for high-pressure storage | – Complex maintenance requirements |
Codes & Standards
Both cone and dome roof tanks are subject to industry standards and codes that ensure safety and compliance. Organizations like the American Petroleum Institute (API) provide guidelines for tank design, fabrication, inspection, and maintenance. For instance, API 650 outlines standards for welded steel tanks, including cone and dome roof designs.
Accidents in the Past & Lessons Learned
Past accidents involving storage tanks have led to valuable lessons in tank design, safety measures, and regulations. Incidents like the Buncefield fire in the UK highlighted the importance of adequate safety measures, including proper venting systems, pressure relief mechanisms, and emergency response plans.
Comparison with Each Type
Cone Roof Tanks vs. Dome Roof Tanks
| Aspect | Cone Roof Tanks | Dome Roof Tanks |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Conical shape with single sloped roof | Hemispherical or elliptical dome-shaped roof |
| Strength | Good for non-volatile liquids; less suited for high pressure | Excellent structural strength; ideal for high pressure |
| Emissions | Minimal emissions | Reduced emissions due to sealable devices |
| Maintenance | Easy maintenance and cleaning | Complex maintenance requirements due to dome shape |
| Applications | Non-volatile liquids like crude oil and liquid fertilizers | Volatile substances, hazardous materials, liquefied gases |
Future Trends and Innovations
The storage tank industry is experiencing innovations driven by advanced materials, real-time monitoring systems, and automation. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies enables remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and early fault detection. Computational modeling is being used to optimize tank designs, enhancing performance and safety.
Do not miss the detailed course on Tank Farm Layout & Stress Analysis
Enrollment link
Conclusion
Cone and dome roof tanks offer distinct advantages and cater to different storage needs in various industries. The choice between these two designs depends on factors such as the nature of the stored liquids, structural requirements, and environmental considerations. Continuous research and innovation in storage tank design, coupled with adherence to industry standards, are pivotal in ensuring the safe and efficient storage of liquids and gases. As technology advances, the role of cone and dome roof tanks in maintaining the integrity of stored materials will remain essential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are cone roof and dome roof tanks, and how do they differ in design? Cone roof tanks are characterized by their conical shape and single sloped roof, while dome roof tanks have hemispherical or elliptical dome-shaped roofs. The difference in design impacts factors like load distribution, structural strength, and suitability for different types of stored liquids.
2. What materials are commonly used for constructing cone and dome roof tanks? Cone roof tanks are often constructed using materials like steel and aluminum due to their strength and cost-effectiveness. Dome roof tanks, designed for structural integrity, commonly use stainless steel and specialized alloys for durability and corrosion resistance.
3. What are the advantages of cone and dome roof tanks? Cone roof tanks offer cost-effectiveness, easy maintenance, and suitability for non-volatile liquids. Dome roof tanks excel in structural strength, reduced emissions due to sealable devices, and versatility for storing hazardous materials and high-pressure liquids.
4. Which industries commonly use cone and dome roof tanks? Cone roof tanks find applications in the petroleum, chemical, and agriculture sectors for storing crude oil, liquid fertilizers, and non-volatile liquids. Dome roof tanks are used in industries involving volatile substances, hazardous materials, and liquefied gases.
5. How do cone and dome roof tanks comply with industry standards and regulations? Both cone and dome roof tanks adhere to industry standards outlined by organizations such as the American Petroleum Institute (API). For instance, API 650 provides guidelines for tank design, fabrication, inspection, and maintenance to ensure safety and compliance with regulations.
Recommended courses (Published on EPCLand)
- Basics of Piping Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Complete Course on Piping Engineering
- Material Requisitions
- Piping Material Specifications
- Valve Material Specifications
Don’t miss the published articles on following:
Related Video
Attempt Quiz
Question 1:
What is a key structural difference between cone and dome tanks?
Explanation: A key structural difference between cone and dome tanks is the shape of the base. Cone tanks have a conical (tapered) base, while dome tanks have a hemispherical (curved) base.
Question 2:
Which type of tank generally requires more floor space for the same storage capacity?
Explanation: A cone tank generally requires more floor space for the same storage capacity compared to a dome tank, due to the tapered shape of the cone.
Question 3:
Which type of tank is often used for bulk storage of liquids or granular materials?
Explanation: Cone tanks are often used for bulk storage of liquids or granular materials, as their conical shape helps in efficient discharge of contents.
Question 4:
Which type of tank is known for its superior structural integrity?
Explanation: Dome tanks are known for their superior structural integrity due to their curved hemispherical shape, which evenly distributes pressure and stresses.
Question 5:
Which type of tank is often preferred for applications where aesthetics are important?
Explanation: Dome tanks are often preferred for applications where aesthetics are important, as their curved shape can be visually appealing and harmonious with the surroundings.



