Introduction to Fixed Roof Tanks
Fixed roof tanks are vital components of industries such as oil and gas, chemicals, petrochemicals, and more. These storage vessels play a crucial role in storing and maintaining the integrity of liquids and gases. Understanding their design, operational considerations, and safety measures is essential for ensuring efficient and secure storage.
Table of Contents
Do not miss the detailed course on Tank Farm Layout & Stress Analysis
Enrollment link
Check out Similar Articles on other Storage Tanks
Definition and Purpose of Fixed Roof Tanks
Fixed roof tanks, as the name suggests, have a stationary roof that remains in a fixed position regardless of the tank’s liquid level. They are designed to store various substances, including liquids and gases, while preventing contamination, evaporation, and leakage. These tanks are essential for industries that require large-scale storage of materials to meet production demands.
Importance in Various Industries
Industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, petrochemicals, and others rely on fixed roof tanks to store raw materials, intermediate products, and end products. These tanks ensure a steady supply of materials, enabling continuous production processes. Additionally, they serve as buffers for market fluctuations, allowing industries to manage inventory effectively.
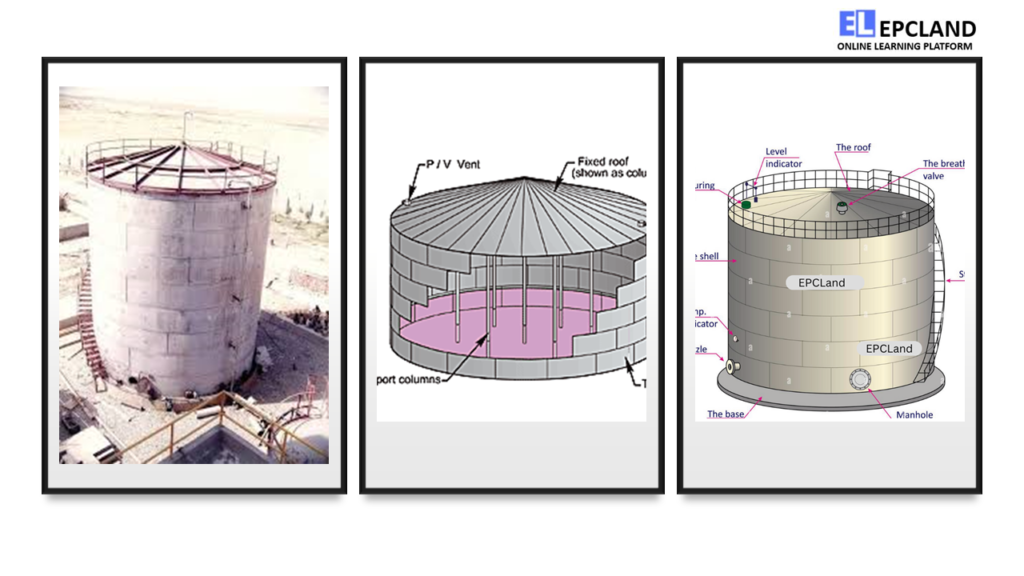
Brief Overview of Key Components
Fixed roof tanks consist of several critical components:
- Shell: The outer cylindrical structure that holds the tank’s contents.
- Roof Types: Various roof designs, such as cone roofs, dome roofs, and floating roofs.
- Seals: Sealing systems prevent vapor emissions, maintaining product integrity and safety.
- Vents: Ventilation systems ensure pressure and temperature regulation within the tank.
- Access Points: Nozzles, manholes, and hatches for maintenance and inspections.
| Component | Description and Function |
|---|---|
| Shell | Outer cylindrical structure holding the tank’s contents |
| Roof Types | Various designs: cone roofs, dome roofs, floating roofs |
| Seals | Prevent vapor emissions, maintain product integrity |
| Vents | Regulate pressure and temperature within the tank |
| Access Points | Nozzles, manholes, hatches for maintenance and inspection |
| Foundation | Supports the tank and distributes loads to the ground |
| Bottom Design | Prevents leaks and provides structural integrity |
| Roof Support | Structures supporting the roof, e.g., rafters, columns |
| Roof Fittings | Components integrated into the roof, e.g., vents, nozzles |
Do not miss the detailed course on Tank Farm Layout & Stress Analysis
Enrollment link
Types of Fixed Roof Tanks
Fixed roof tanks come in different configurations to suit specific industry needs.
| Tank Type | Description and Design Features | Advantages | Disadvantages | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cone Roof Tanks | Sloped roof resembling an inverted cone | Structural stability, resistance to forces | Complex construction, limited storage capacity | Crude oil, chemicals, refineries |
| Dome Roof Tanks | Curved roof resembling a dome | Effective sealing, minimal rainwater | Specialized construction, cost-intensive | Chemicals, bulk liquid storage |
| Floating Roof Tanks | Roof moves vertically, compensating for liquid | Reduced vapor emissions, adaptable to levels | Maintenance challenges, complex construction | Gasoline, volatile chemicals |
Cone Roof Tanks
Cone roof tanks feature a sloped roof that resembles an inverted cone. These tanks are known for their durability and suitability for storing volatile liquids.
Description and Design Features
Cone roof tanks consist of a steel shell with a cone-shaped roof that directs rainwater and snowmelt away from the tank’s center. The roof’s slope prevents the accumulation of flammable vapors and reduces the risk of fire.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of cone roof tanks include their structural stability and resistance to wind and seismic forces. However, they can be more challenging to construct due to their intricate design.
Applications and Industries
Cone roof tanks find applications in the storage of crude oil, refined petroleum products, and various chemicals. Industries such as oil refineries and chemical processing plants benefit from their design.
Dome Roof Tanks
Dome roof tanks are recognized for their curved roof, resembling the shape of a dome. These tanks offer effective sealing and protection against external elements.
Description and Design Features
Dome roof tanks are constructed with a curved roof that provides a self-supporting structure. This design minimizes the risk of rainwater accumulation and eliminates the need for internal support columns.
Pros and Cons
The seamless design of dome roof tanks ensures better sealing and reduced emissions. However, their construction requires specialized equipment and expertise.
Industries That Commonly Use Dome Roof Tanks
Dome roof tanks are commonly used in the storage of liquids that require stringent vapor emission control. Industries like chemical manufacturing and bulk liquid storage benefit from their airtight design.
Do not miss the detailed course on Tank Farm Layout & Stress Analysis
Enrollment link
Floating Roof Tanks
Floating roof tanks differ from fixed roof tanks as they have a roof that can move vertically along the tank’s inner shell. This movement compensates for changes in liquid levels and reduces vapor space.
Comparison with Fixed Roof Tanks
Floating roof tanks are particularly useful for substances that emit hazardous vapors, as the floating roof maintains a tight seal, minimizing emissions. This distinguishes them from fixed roof tanks, where emissions control may be less efficient.
Internal and External Floating Roofs
There are two main types of floating roofs: internal and external. Internal floating roofs are inside the liquid, while external floating roofs rest on top of the liquid’s surface.
Use Cases and Benefits
Floating roof tanks are used for storing materials with high vapor pressure, such as gasoline and volatile chemicals. Their ability to minimize vapor emissions enhances safety and environmental compliance.

Codes & Standards
| Code/Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| API 650: Welded Steel Tanks for Oil Storage | Provides requirements for the design, fabrication, and erection of welded steel tanks for various storage purposes, including fixed roof tanks. |
| API 620: Design and Construction of Large, Welded, Low-Pressure Storage Tanks | Focuses on the design and construction of larger, low-pressure storage tanks, including those with fixed roofs. |
| API 653: Tank Inspection, Repair, Alteration, and Reconstruction | Focuses on the inspection, repair, alteration, and reconstruction of existing tanks, ensuring their continued integrity and safety. |
| ASME BPVC Section VIII: Rules for Construction of Pressure Vessels | Provides guidelines for designing and constructing pressure vessels, including some types of fixed roof tanks. |
| AWWA D100: Welded Carbon Steel Tanks for Water Storage | Specifically covers the design and construction of welded carbon steel tanks for water storage, providing relevant insights for similar tanks. |
| NFPA 30: Flammable and Combustible Liquids Code | Offers guidelines for the safe storage and handling of flammable and combustible liquids, influencing tank design and operation. |
| EN 14015: Specification for the Design and Manufacture of Site Built, Vertical, Cylindrical, Flat-bottomed, Above Ground, Welded, Steel Tanks for the Storage of Liquids at Ambient Temperature and Above | A European standard providing specifications for above-ground vertical cylindrical welded steel tanks. |
Do not miss the detailed course on Tank Farm Layout & Stress Analysis
Enrollment link
Pros & Cons of Fixed Roof Tanks
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Design Stability | – Structural stability against external forces | – Limited storage capacity (cone roof tanks) |
| – Suitable for volatile substances (cone roof) | – Complex construction (cone roof tanks) | |
| – Minimal rainwater accumulation (dome roof) | – Specialized construction (dome roof tanks) | |
| – Effective sealing against emissions (dome roof) | – Higher cost (dome roof tanks) | |
| – Reduced vapor emissions (floating roof) | – Maintenance challenges (floating roof tanks) | |
| – Adaptable to varying liquid levels (floating) | – Complex construction (floating roof tanks) | |
| Environmental Control | – Better sealing, reduced emissions (dome roof) | – Risk of emissions (cone roof tanks) |
| – Airtight design (dome roof) | – Exposure to external elements (dome roof tanks) | |
| – Emissions control (floating roof) | – Emissions during roof movement (floating roof) | |
| Maintenance & Inspection | – Relatively simple access (cone and dome) | – Inspection limitations (cone roof tanks) |
| – Proper ventilation (all types) | – Potential for corrosion (all types) | |
| – Regular maintenance prevents issues | – Sealing maintenance (all types) | |
| Safety & Fire Prevention | – Minimal fire risk (dome roof) | – Fire risk (cone roof tanks) |
| – Fire protection systems (all types) | – Firefighting challenges (dome roof tanks) | |
| – Vapor emission control (all types) | – Vapor emissions (cone roof tanks) | |
| Applications | – Suitable for crude oil, chemicals (cone) | – Limited storage for some substances (cone roof) |
| – Chemicals, bulk storage (dome roof) | – Specialized use cases (dome roof tanks) | |
| – Gasoline, volatile chemicals (floating roof) | – Limited applications (floating roof tanks) |
Design and Construction of Fixed Roof Tanks
Designing and constructing fixed roof tanks involves several critical considerations to ensure their safety and longevity.
Tank Shell Design
Selecting the appropriate materials for the tank shell is crucial to prevent corrosion and ensure structural integrity.
Material Selection and Considerations
Materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloys are commonly used for tank shells. The choice depends on factors such as the stored substance’s corrosiveness, operating temperature, and budget.
Thickness Calculations and Standards
Tank shell thickness calculations adhere to industry standards such as API 650. These calculations ensure the shell can withstand internal and external forces without failure.
Corrosion Prevention and Coatings
Corrosion protection is vital to extend the tank’s lifespan. Coatings, cathodic protection, and regular inspections help prevent corrosion-related issues.
Roof Design
The design of the tank’s roof impacts its structural stability and operational efficiency.
Factors Influencing Roof Type Selection
Factors like the stored substance, climate, and local regulations influence the choice between cone, dome, and floating roofs.
Roof Support Structures
Roof support structures, such as rafters and columns, provide stability to the roof and distribute loads to the tank’s shell.
Roof Fittings
Fittings like vents, nozzles, and access hatches are integrated into the roof design. These components ensure proper ventilation and facilitate maintenance.
Do not miss the detailed course on Tank Farm Layout & Stress Analysis
Enrollment link
Sealing Systems
Sealing systems play a critical role in preventing vapor emissions and maintaining product quality.
Primary and Secondary Seals
Primary seals prevent vapor leakage between the roof and the shell. Secondary seals act as a backup, enhancing the overall sealing integrity.
Emission Control and Environmental Considerations
Effective seals reduce emissions and environmental impact. Proper maintenance of seals is essential to ensure compliance with emission regulations.
Maintenance and Inspection of Seals
Regular maintenance and inspections of seals are necessary to identify wear and tear and ensure their functionality.
Foundation and Bottom Design
A strong foundation and bottom design are essential for stability and preventing leaks.
Foundation Types and Requirements
Foundations can be concrete or steel. Proper soil analysis is critical to determine the foundation’s type and design.
Tank Bottom Design and Materials
Tank bottoms are subjected to internal and external forces. Materials like concrete, steel, and coatings are chosen based on the stored substance.
Leakage Prevention Measures
Preventing leaks is paramount. Tank bottoms are equipped with leak detection systems and secondary containment for added safety.
Operational Considerations
Efficient operation of fixed roof tanks involves safe filling, emptying, and maintaining proper pressure and temperature.
Filling and Emptying Fixed Roof Tanks
Proper procedures for filling and emptying tanks are crucial to prevent overfilling and ensure efficient operations.
Overfill Prevention Mechanisms
Overfill prevention mechanisms, such as level sensors and alarms, prevent spills and maintain safe operations.
Pumping and Draining Procedures
Pumping and draining substances from the tank require proper equipment and adherence to safety protocols.
Safety Measures During Filling and Emptying Operations
Safety measures, such as grounding and bonding, ensure static electricity does not ignite flammable vapors during filling and emptying.
Venting and Pressure Control
Ventilation and pressure control systems are essential to maintain safe pressure levels within the tank.
Importance of Venting
Venting prevents the build-up of excessive pressure or vacuum inside the tank, which can lead to structural failure.
Pressure Relief Devices and Settings
Pressure relief devices, such as pressure vacuum valves, release excess pressure to protect the tank from over-pressurization.
Ventilation Requirements to Prevent Toxic Atmospheres
Adequate ventilation prevents the accumulation of toxic or flammable atmospheres within the tank.
Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance and inspections are crucial for ensuring the tank’s integrity and preventing leaks.
Regular Inspection Schedules
Scheduled inspections identify signs of corrosion, leaks, and other issues that could compromise the tank’s integrity.
Corrosion Monitoring and Prevention
Corrosion monitoring involves techniques like ultrasonic testing and visual inspections to detect and mitigate corrosion.
Repair and Maintenance Practices
Timely repairs and maintenance ensure the tank’s longevity. This includes welding repairs, coating maintenance, and addressing any structural issues.
Do not miss the detailed course on Tank Farm Layout & Stress Analysis
Enrollment link
Safety and Environmental Concerns
Safety and environmental considerations are paramount when dealing with fixed roof tanks.
Fire Hazards and Prevention
Fixed roof tanks are susceptible to fires, necessitating robust fire protection systems.
Fire Protection Systems for Fixed Roof Tanks
Fire protection systems include firewater pumps, foam systems, and fire suppression agents to control and extinguish fires.
Firefighting Strategies and Equipment
Effective firefighting strategies involve training personnel, having appropriate firefighting equipment, and conducting drills.
Mitigation of Fire-Related Risks
Preventive measures like lightning protection systems and static electricity control reduce the risk of fire incidents.
Vapor Emissions and Air Quality
Vapor emissions control is essential to maintain air quality and comply with environmental regulations.
Control of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
VOCs contribute to air pollution and smog formation. Effective control mechanisms like vapor recovery units reduce VOC emissions.
Regulations and Compliance Standards
Regulatory bodies set emission limits and standards that industries must adhere to, necessitating efficient vapor emission control.
Strategies for Reducing Emissions
Emission reduction strategies include optimizing seals, implementing vapor recovery systems, and minimizing the exposure of stored substances to air.
Environmental Impact and Risk Management
The potential environmental impact of tank failures underscores the importance of risk management.
Potential Consequences of Tank Failures
Tank failures can result in product spills, fires, and environmental contamination, leading to legal, financial, and reputational consequences.
Spill Containment and Response Plans
Effective spill containment measures, such as berms and dikes, along with well-practiced response plans, mitigate the consequences of spills.
Community and Environmental Engagement
Engaging with the community and maintaining transparency about safety measures foster trust and collaboration in preventing environmental incidents.
Historical Accidents and Their Causes
| Accident | Date | Location | Tank Type | Causes and Contributing Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buncefield Fire | Dec 2005 | Hemel Hempstead, UK | Storage tanks | Overfilling during a delivery operation led to a vapor cloud explosion. |
| Exxon Valdez Oil Spill | Mar 1989 | Prince William Sound, Alaska | Oil storage tanks | Struck a reef due to navigational error, causing a massive oil spill. |
| Texas City Refinery Explosion | Mar 2005 | Texas City, USA | Storage tanks | Overfilling of a tank led to a catastrophic explosion and fire. |
| Jaipur Oil Depot Fire | Oct 2009 | Jaipur, India | Storage tanks | Vapors ignited due to leakage during tank filling, causing a major fire. |
| Hertfordshire Oil Storage Terminal Fire | Dec 2005 | Hemel Hempstead, UK | Storage tanks | Explosions resulted from a vapor cloud caused by a fuel leak. |
Successful Implementations and Innovations
Innovative designs and practices have enhanced the safety and efficiency of fixed roof tanks.
Improved Designs for Enhanced Safety and Efficiency
Advancements in materials, seals, and coatings have improved the structural integrity and emissions control of fixed roof tanks.
Industry-Specific Adaptations and Success Stories
Industries like chemicals and petrochemicals have implemented customized tank designs and emission control strategies to meet their unique needs.
Do not miss the detailed course on Tank Farm Layout & Stress Analysis
Enrollment link
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of fixed roof tanks holds promise with technological advancements and sustainability efforts.
Technological Advances in Tank Design
Technologies like automation, remote monitoring, and advanced simulations enhance tank safety, maintenance, and operations.
Automation and Remote Monitoring
Automated systems and remote monitoring allow real-time data collection, improving predictive maintenance and reducing human intervention.
Advanced Materials and Coatings
Development of materials with enhanced corrosion resistance and longevity improves the lifespan of tanks and reduces maintenance costs.
Sustainable Practices in Fixed Roof Tanks
Sustainability efforts bring environmental and economic benefits to fixed roof tank operations.
Renewable Energy Integration
Incorporating renewable energy sources like solar power reduces the environmental impact of tank operations.
Circular Economy Principles Applied to Tank Management
Efforts to recycle materials, minimize waste, and extend the life of tank components align with circular economy principles.
Conclusion
Fixed roof tanks are integral to various industries, providing secure storage for liquids and gases. Their diverse designs, operational considerations, and safety measures ensure a balance between efficiency, environmental responsibility, and safety. As industries continue to evolve, these tanks will embrace innovation and sustainability to meet the demands of a changing world while upholding the highest standards of safety and environmental stewardship.
FAQs
- What is the purpose of a fixed roof tank?Fixed roof tanks are designed to store various substances, such as liquids and gases, while preventing contamination, evaporation, and leakage. They play a vital role in industries like oil and gas, chemicals, and petrochemicals by providing secure storage for raw materials, intermediate products, and end products.
- How do fixed roof tanks differ from floating roof tanks?Fixed roof tanks have a stationary roof that remains in place regardless of the liquid level inside the tank. On the other hand, floating roof tanks have a roof that can move vertically along the tank’s inner shell, adjusting to changes in liquid level. Floating roof tanks are often used for substances that emit hazardous vapors, as the floating roof helps minimize emissions.
- What are the advantages of dome roof tanks?Dome roof tanks have a curved roof resembling a dome. They offer effective sealing, preventing vapor emissions and protecting the tank’s contents from external elements. The seamless design eliminates the need for internal support columns, making them ideal for storing substances that require stringent vapor emission control.
- Why is proper maintenance crucial for fixed roof tanks?Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the structural integrity of fixed roof tanks. Regular inspections help identify issues like corrosion, leaks, and wear and tear on seals. Addressing these concerns promptly extends the tank’s lifespan and reduces the risk of environmental incidents, ensuring safe and efficient operations.
- What standards govern the design of fixed roof tanks?The design and construction of fixed roof tanks are regulated by various standards. Common standards include API 650 (Welded Steel Tanks for Oil Storage) and API 620 (Design and Construction of Large, Welded, Low-Pressure Storage Tanks). These standards provide guidelines for material selection, design calculations, safety measures, and more, ensuring tanks are constructed to industry best practices.
Recommended courses (Published on EPCLand)
- Basics of Piping Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Complete Course on Piping Engineering
- Material Requisitions
- Piping Material Specifications
- Valve Material Specifications
Don’t miss the published articles on following:
Recommended Video
Attempt Quiz
Question 1:
What is a fixed roof tank?
Explanation: A fixed roof tank is a type of storage tank with a roof that does not move with the liquid level inside the tank. It can be used for various liquids, including petroleum products and chemicals.
Question 2:
What is the primary purpose of a floating roof in a fixed roof tank?
Explanation: A floating roof is often used in fixed roof tanks to minimize vapor emissions to the atmosphere by adjusting its position based on the liquid level, thus reducing the vapor space above the liquid.
Question 3:
Which of the following is a common type of fixed roof design?
Explanation: A common type of fixed roof design is the Cone Roof, which has a sloped shape resembling an inverted cone. It provides structural support and sheds rainwater.
Question 4:
What is “rim space” in the context of fixed roof tanks?
Explanation: “Rim space” refers to the space between the roof and the tank wall in a fixed roof tank. It’s important for ventilation and to accommodate thermal expansion of the roof.
Question 5:
What is a common material used for the construction of fixed roof tanks?
Explanation: Stainless steel is a common material used for the construction of fixed roof tanks due to its corrosion resistance and durability, making it suitable for storing various liquids, including corrosive chemicals and petroleum products.