Radiographic Testing, often abbreviated as RT, is a crucial method within the realm of Non-Destructive Testing (NDT). It plays a significant role in ensuring the structural integrity and safety of various materials and components. This article delves into the intricacies of Radiographic Testing, its applications, benefits, and the technology behind it.
Table of Contents
Understanding Radiographic Testing
Radiographic Testing is a non-invasive inspection technique used to examine the internal structures of materials and components. It employs X-rays or gamma rays to create images that reveal hidden defects, such as cracks, voids, inclusions, or other irregularities, without causing any damage to the tested object. This method is commonly used in industries like manufacturing, construction, aerospace, and more.
The Process
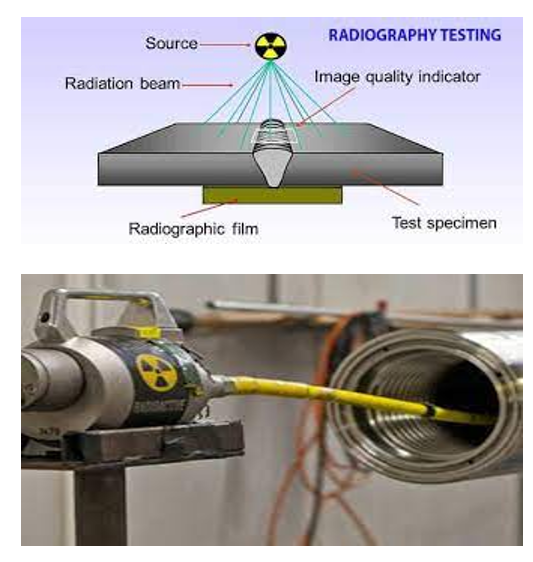
1. Source Selection
The process begins with the selection of an appropriate radiation source. X-ray machines or gamma ray sources are chosen based on the material and thickness of the object under inspection. The energy level of the radiation is critical to ensure optimal results.
2. Exposure and Image Formation
The selected radiation source emits rays that pass through the object. The interaction between the rays and the object’s internal structures results in varying levels of absorption. A detector placed on the opposite side captures the transmitted radiation, creating an image that highlights the object’s internal features.
3. Image Interpretation
Skilled radiographers analyze the obtained radiographic images to identify any indications of defects or irregularities. They use their expertise to distinguish between acceptable anomalies, such as weld seams, and potential defects that may compromise the object’s integrity.
Applications of Radiographic Testing
Radiographic Testing finds extensive applications across multiple industries:
Industrial Manufacturing
In manufacturing, RT is used to inspect welds, castings, and forged components. It helps detect defects like porosity, cracks, or incomplete penetration that might compromise the structural integrity of the final product.
Aerospace Industry
Aircraft components, such as turbine blades and engine parts, undergo RT to ensure they meet stringent safety standards. RT helps identify hidden defects that could lead to catastrophic failures in flight.
Pipeline Inspection
RT is essential in inspecting pipelines for oil, gas, or water transport. It identifies corrosion, weld defects, and other anomalies that could result in leaks or environmental hazards.
Benefits of Radiographic Testing
- Accuracy: RT provides high-resolution images that allow for accurate defect detection and characterization.
- Versatility: It can be applied to a wide range of materials, including metals, ceramics, composites, and plastics.
- Non-Destructive: As a non-invasive method, RT does not damage the tested object, making it suitable for critical components.
- Early Detection: RT helps identify defects in their early stages, preventing costly failures and ensuring safety.
Technology Advancements
Recent technological advancements have enhanced the efficiency and accuracy of Radiographic Testing. Digital radiography (DR) and computed tomography (CT) are two notable innovations. DR eliminates the need for chemical processing, allowing for faster image analysis. CT generates 3D images, providing a comprehensive view of complex structures.
Pros and Cons of Radiographic Testing (RT):
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Accurate defect detection and characterization | Exposure to radiation for operators |
| Versatility – applicable to various materials | Limited sensitivity to surface defects |
| Non-destructive – minimal damage to objects | Costly equipment and training requirements |
| Early detection of defects | Environmental considerations for disposal |
| Applicable to thick and dense materials | Limited suitability for radiation-sensitive objects |
| Enhances safety and reliability | Image interpretation expertise required |
| Technology advancements (DR, CT) | Interpretation subjectivity |
| Prevents costly failures and accidents | Radiographic contrast variability |
| Complements quality control during fabrication | Inspection time can be longer |
| Well-established method with industry standards | Accessibility challenges for certain objects |
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: Is Radiographic Testing safe for operators and the environment?
A1: Yes, RT is safe when conducted by trained professionals following safety protocols. Proper shielding and distance ensure minimal exposure to radiation.
Q2: How does RT compare to other NDT methods?
A2: RT offers unique advantages, including the ability to inspect thick and dense materials. However, it might not be suitable for objects that are sensitive to radiation.
Q3: Can RT detect all types of defects?
A3: RT is highly effective in detecting volumetric defects like cracks and porosity. However, surface defects might require additional testing methods.
Q4: What qualifications are required for RT technicians?
A4: RT technicians should undergo formal training and certification to operate radiation sources and interpret results accurately.
Q5: Can RT be used during the fabrication of critical components?
A5: Absolutely. RT is often employed during fabrication to ensure components meet quality standards before being put into service.
Conclusion
Radiographic Testing (RT) is an indispensable tool for maintaining the safety and reliability of critical structures and components. Its non-destructive nature, accuracy, and versatility make it a preferred choice across various industries. As technology continues to advance, RT’s capabilities are only expected to improve, contributing to safer and more efficient manufacturing processes worldwide.
Recommended courses (Published on EPCLand)
- Basics of Piping Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Complete Course on Piping Engineering
- Material Requisitions
- Piping Material Specifications
- Valve Material Specifications
Don’t miss the published articles on following:
Related Video
Attempt Quiz
Question 1:
What is Radiographic Testing (RT) in Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)?
Explanation: Radiographic Testing (RT) is a non-destructive testing method that uses X-rays or gamma rays to create images of the internal structures of materials, helping to detect defects or irregularities.
Question 2:
What type of defects can Radiographic Testing (RT) detect?
Explanation: Radiographic Testing (RT) is capable of detecting various types of internal defects within materials, including voids, inclusions, cracks, and more.
Question 3:
Which of the following materials is commonly inspected using Radiographic Testing (RT)?
Explanation: Radiographic Testing (RT) is commonly used to inspect metallic materials, including various types of metals, alloys, and welds.
Question 4:
Which type of radiation is used in Radiographic Testing (RT)?
Explanation: Radiographic Testing (RT) utilizes X-rays or gamma rays, which are forms of ionizing radiation, to create images of the internal structures of materials.
Question 5:
What safety precautions are important when performing Radiographic Testing (RT)?
Explanation: Safety precautions in Radiographic Testing (RT) include using proper shielding, maintaining a safe distance from radiation sources, and implementing radiation monitoring to minimize the risk of radiation exposure to personnel and the public.



