Introduction
In the world of oil and gas, where extreme temperatures, high pressures, and corrosive environments are commonplace, ensuring the integrity of pipelines and equipment is paramount. One critical component that plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of these systems is the insulation gasket. Insulation gaskets are specialized sealing devices that find extensive use in the oil and gas industry, contributing to safety, efficiency, and environmental protection.
Table of Contents
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
Brief History
Insulation gaskets have a rich history, evolving alongside the oil and gas industry’s growth. Early pipeline systems used basic gaskets for sealing purposes, but the need for enhanced insulation and corrosion resistance led to the development of more advanced solutions. Over the years, materials, designs, and manufacturing processes have significantly improved, resulting in the insulation gaskets we rely on today.
Basic Function and Working Principle
The Role of Insulation Gaskets
Insulation gaskets serve a dual purpose in oil and gas applications. They are primarily designed to provide a reliable seal between flange connections, preventing leakage of hazardous fluids. Simultaneously, these gaskets act as electrical insulators, ensuring the integrity of cathodic protection systems used to mitigate corrosion in pipelines and equipment.

Working Principle
The working principle of insulation gaskets is relatively straightforward. When placed between two flange surfaces, the gasket material, typically a dielectric material like rubber or non-conductive composites, creates an electrical barrier. This barrier prevents the flow of electric current between the flanges, maintaining the effectiveness of cathodic protection systems.
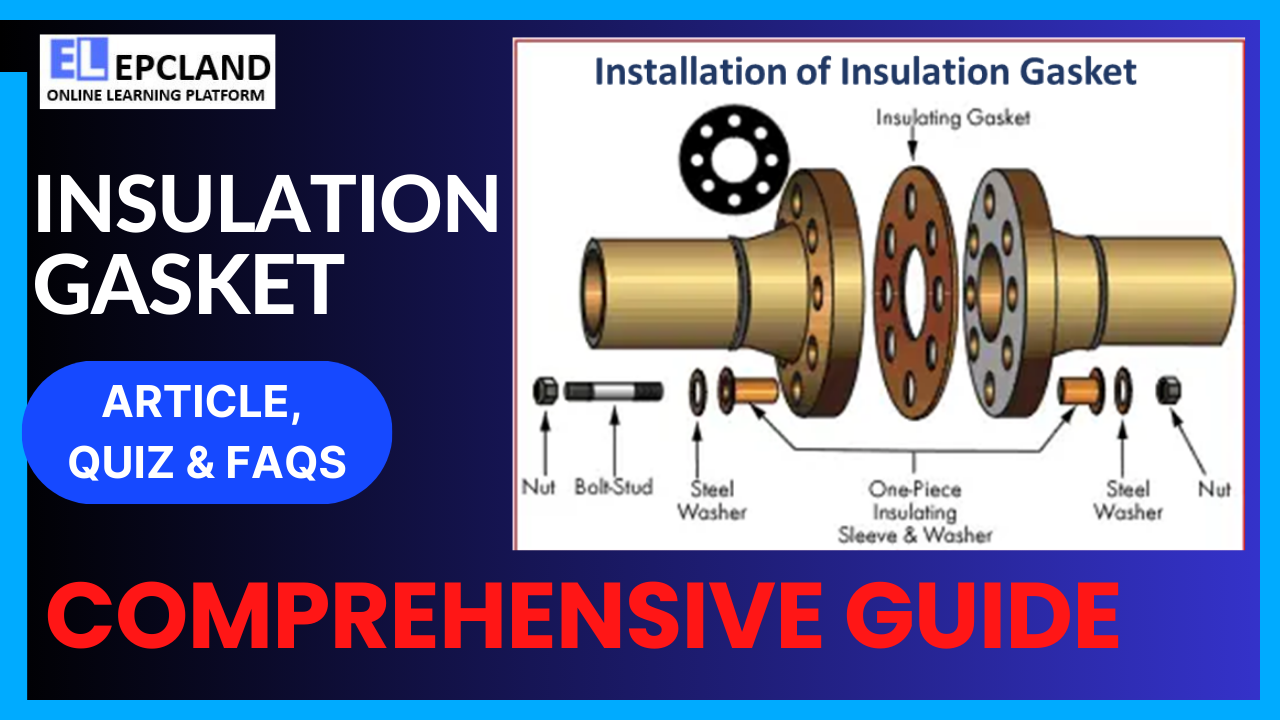
Parts and Functions of Insulation Gaskets
Insulation gaskets are complex sealing devices, comprising several key components that work together to ensure both effective sealing and electrical isolation in critical applications within the oil and gas industry. Understanding these components and their functions is essential for appreciating how insulation gaskets contribute to the integrity of pipelines and equipment. Here’s a breakdown of the main parts and their functions:
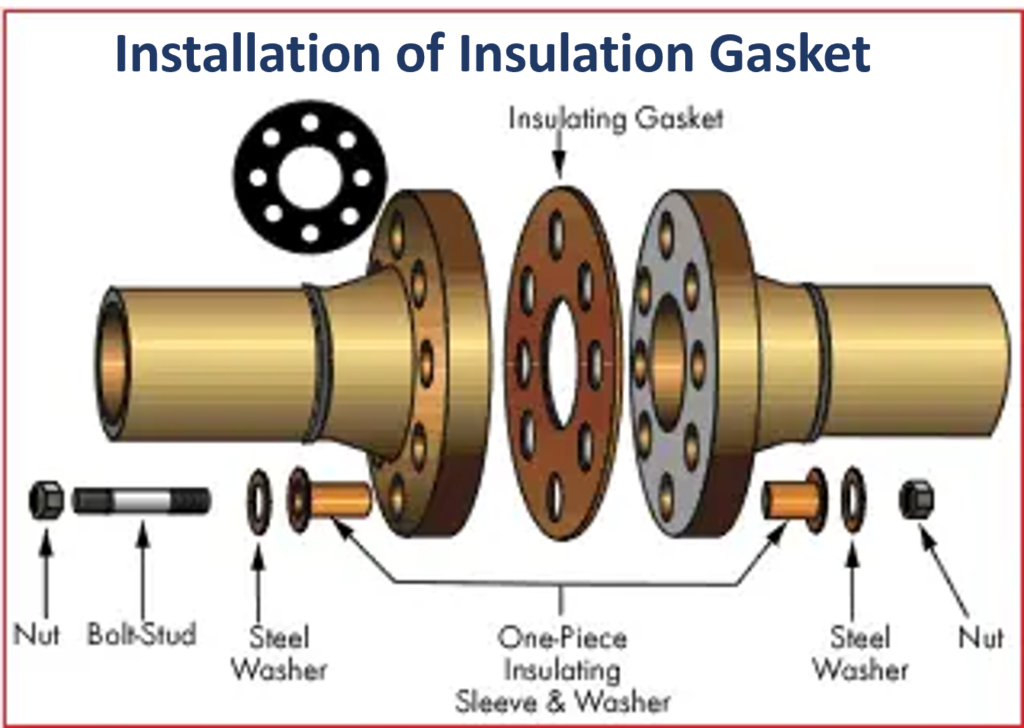
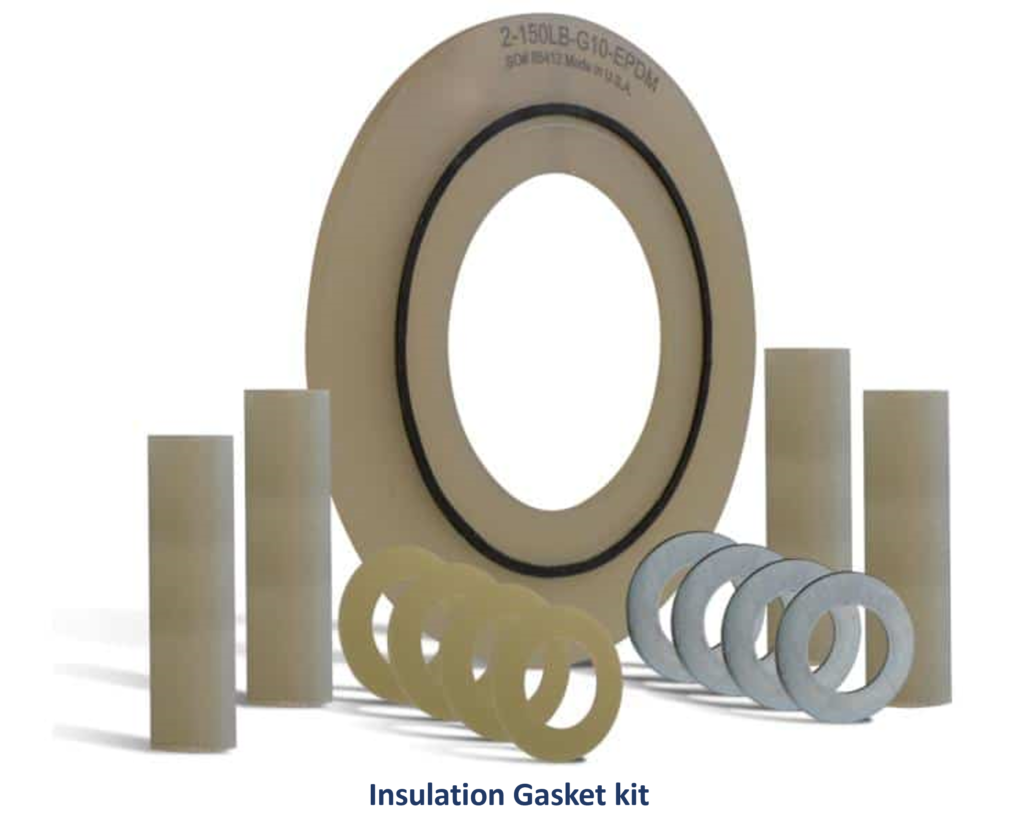
1. Gasket Material
Function: The gasket material is the heart of the insulation gasket. It forms the primary barrier between the two flange surfaces and plays a crucial role in preventing fluid leakage and providing electrical insulation.
Materials: Gasket materials can vary and include rubber, non-conductive composites, and other dielectric materials. The choice of material depends on the application’s requirements, such as temperature, pressure, and chemical compatibility.
2. Outer Ring
Function: The outer ring is typically made of a rigid material, such as stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant alloys. Its primary function is to provide structural support to the gasket and prevent deformation or damage during installation and operation.
3. Inner Ring
Function: The inner ring is also constructed from a durable material, often stainless steel or a similar alloy. Its primary role is to support the inner portion of the gasket, ensuring proper alignment and preventing deformation. It also helps maintain electrical insulation.
4. Sealing Element
Function: The sealing element is the part of the gasket that directly contacts the flange faces to create a seal. It deforms under pressure to fill any irregularities or imperfections in the flange surfaces, ensuring a tight and secure seal. The sealing element is typically made from the same material as the gasket body.
5. Bolt Holes
Function: Bolt holes are strategically located in the gasket to align with the holes in the flanges. They facilitate the secure attachment of the gasket between the flanges using bolts. Proper alignment and spacing of these holes are crucial for a reliable seal.
6. Electrical Isolation Inserts
Function: In certain insulation gaskets, especially those designed for cathodic protection applications, electrical isolation inserts may be included. These inserts are typically made of non-conductive materials and are placed strategically within the gasket to ensure the electrical isolation of the flanges.
7. Flange Faces
Function: While not a part of the insulation gasket itself, the condition of the flange faces is critical to the gasket’s performance. Flange faces should be smooth, clean, and free from defects to ensure proper sealing and electrical isolation.
8. Bolts and Nuts
Function: Bolts and nuts are used to secure the two flanges together, compressing the insulation gasket between them. The pressure applied by the bolts is essential for creating a tight seal and ensuring electrical isolation.
9. Compression and Torque Control
Function: Proper compression and torque control during the installation process are essential for achieving the desired sealing and electrical isolation properties. Over-tightening can damage the gasket, while insufficient torque may result in leaks.
10. Anti-Stick Coating (Optional)
Function: In some cases, an anti-stick coating may be applied to one or both sides of the gasket. This coating reduces the risk of the gasket sticking to the flange faces during installation and facilitates easier removal and reinstallation if maintenance is required.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
Types of Insulation Gaskets
Insulation gaskets are not one-size-fits-all; they come in various types, each designed to meet specific sealing and electrical insulation requirements. Understanding the different types of insulation gaskets is essential for selecting the most suitable option for a particular application. Here, we explore the common types:
1. Full-Face Insulation Gaskets
Full-face insulation gaskets are among the most commonly used types in the oil and gas industry. As the name suggests, these gaskets cover the entire surface area of the flanges. This comprehensive coverage ensures complete sealing and electrical isolation of the flange connection. Here are some key features and applications of full-face insulation gaskets:
Features:
- Complete Coverage: Full-face gaskets extend across the entire flange face, providing a secure seal and complete electrical isolation.
Applications:
- Critical Sealing: Full-face insulation gaskets are used in applications where a reliable and secure seal is of utmost importance to prevent leakage of hazardous fluids.
- Cathodic Protection: They are essential in systems where maintaining the effectiveness of cathodic protection is vital for corrosion prevention.
2. Raised Face Insulation Gaskets
Raised face insulation gaskets are specifically designed to fit the raised surface, known as the raised face, of flanges. This type of gasket is suitable for applications where the flange design includes a raised surface. Here are the key features and applications of raised face insulation gaskets:
Features:
- Precise Fit: Raised face gaskets are engineered to match the raised face profile of the flange, ensuring a snug fit.
- Effective Sealing: They provide effective sealing and electrical isolation while accommodating raised face flanges.
Applications:
- Raised Face Flanges: Raised face insulation gaskets are used in applications with raised face flanges, ensuring a tight seal and electrical insulation.
3. Ring Type Joint (RTJ) Insulation Gaskets
Ring Type Joint (RTJ) insulation gaskets are favored for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. They are specially designed to work with ring-type joint flanges, known for their robust sealing and insulating properties. Here’s a closer look at RTJ insulation gaskets:
Features:
- High Pressure and Temperature Resistance: RTJ gaskets are capable of withstanding extreme pressure and temperature conditions.
- Secure Sealing: They create a reliable seal and maintain electrical isolation in challenging environments.
Applications:
- High-Pressure Pipelines: RTJ insulation gaskets are used in applications where maintaining a secure seal under extreme pressure is crucial.
- High-Temperature Environments: They are suitable for applications involving high temperatures, such as in steam systems or high-temperature pipelines.
4. Low-Pressure Insulation Gaskets
In contrast to the high-pressure capabilities of RTJ insulation gaskets, there are also low-pressure insulation gaskets designed for applications with lower pressure requirements. These gaskets are typically used in situations where the sealing and insulation demands are not as extreme as high-pressure scenarios.
Features:
- Cost-Efficiency: Low-pressure insulation gaskets are often more cost-effective than their high-pressure counterparts.
- Suitable for Less Demanding Environments: They are used in applications where lower pressure and temperature resistance are acceptable.
Applications:
- General Sealing: Low-pressure insulation gaskets are employed in various standard sealing applications where high-pressure sealing is unnecessary.
Applications of Insulation Gaskets
Insulation gaskets are indispensable in a wide range of oil and gas industry applications:
1. Pipeline Systems
Insulation gaskets are used to seal pipeline flange connections, preventing leakage of hydrocarbons and ensuring electrical isolation. This is crucial for both transporting and storing oil and gas products.
2. Offshore Platforms
Offshore oil and gas platforms rely on insulation gaskets to maintain the integrity of subsea pipelines and connections. They protect against the corrosive effects of saltwater and ensure cathodic protection.
3. Refineries and Petrochemical Plants
In refineries and petrochemical plants, insulation gaskets are used in various equipment and vessels to prevent leaks and protect against the corrosive nature of chemicals and gases.
4. Natural Gas Compression Stations
Natural gas compression stations utilize insulation gaskets to seal flanges and maintain the safety and efficiency of gas compression and transmission processes.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
Advantages & Disadvantages
Advantages of Using Insulation Gaskets
Insulation gaskets offer several advantages:
1. Leakage Prevention
They provide an effective seal that prevents the leakage of hazardous fluids, enhancing safety and environmental protection.
2. Corrosion Mitigation
Insulation gaskets maintain the integrity of cathodic protection systems, reducing the risk of corrosion in pipelines and equipment.
3. Versatility
They are suitable for various types of flange connections, making them versatile and adaptable to different applications.
4. Longevity
Insulation gaskets are designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, ensuring long-term reliability.
Disadvantages and Considerations
While insulation gaskets offer numerous benefits, there are some considerations:
1. Material Selection
Choosing the right gasket material is crucial to ensure compatibility with the specific application’s requirements.
2. Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and regular maintenance are essential to maximize the performance and lifespan of insulation gaskets.
3. Cost
High-quality insulation gaskets can be relatively expensive, but their long-term benefits often outweigh the initial investment.
Associated Codes & Standards
Ensuring compliance with industry-specific codes and standards is vital when using insulation gaskets. Some relevant standards include:
1. API 6FB
API 6FB outlines the requirements for fire test methods for sealing and isolation devices.
2. NACE MR0175/ISO 15156
NACE MR0175/ISO 15156 specifies materials for use in sour oilfield equipment and provides guidelines for material selection.
3. ASME B16.5
ASME B16.5 covers the dimensions and tolerances of pipe flanges and flanged fittings, ensuring compatibility with insulation gaskets.
Conclusion
Insulation gaskets are unsung heroes in the oil and gas industry, playing a crucial role in maintaining safety, preventing leaks, and preserving the environment. Their evolution over time has resulted in sophisticated solutions that continue to meet the industry’s demanding needs. Whether in pipelines, offshore platforms, or refineries, insulation gaskets are a critical component that ensures the oil and gas industry functions safely and efficiently. Understanding their importance and selecting the right insulation gaskets for specific applications is essential for the continued success of oil and gas projects.
FAQs
- What is the primary purpose of insulation gaskets in the oil and gas industry?Insulation gaskets serve a dual purpose: they provide a reliable seal between flange connections to prevent fluid leakage, and they offer electrical insulation to protect against corrosion through cathodic protection systems.
- What are the key factors to consider when selecting the right insulation gasket for a specific oil and gas application?When selecting insulation gaskets, factors such as temperature, pressure, chemical compatibility, and flange type must be considered. The choice of gasket material and type should align with these application-specific requirements.
- Are there any industry standards or codes that govern the use of insulation gaskets in the oil and gas sector?Yes, there are industry-specific standards and codes, such as API 6FB and NACE MR0175/ISO 15156, that provide guidelines for the selection, installation, and performance testing of insulation gaskets in oil and gas applications.
- What maintenance procedures are recommended to ensure the longevity and performance of insulation gaskets?Proper installation, regular inspection, and torque control are essential maintenance procedures for insulation gaskets. Regular checks for wear, damage, or deterioration can help prevent leaks and ensure continued electrical insulation.
- Can insulation gaskets be used in both onshore and offshore oil and gas applications?Yes, insulation gaskets are versatile and suitable for use in both onshore and offshore applications. They are crucial for maintaining the integrity of subsea pipelines and equipment in offshore platforms, as well as in various equipment within onshore refineries and petrochemical plants.
Recommended courses (Published on EPCLand)
- Basics of Piping Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Complete Course on Piping Engineering
- Material Requisitions
- Piping Material Specifications
- Valve Material Specifications
Don’t miss the published articles on following:
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
Attempt Quiz
Question 1:
What is the primary purpose of Insulation Gaskets in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Explanation: Insulation Gaskets are used to provide electrical insulation between pipeline sections, preventing the flow of electrical current.
Question 2:
What materials are commonly used in the construction of Insulation Gaskets?
Explanation: Insulation Gaskets are commonly constructed from non-conductive materials like neoprene, phenolic, and PTFE to provide electrical insulation.
Question 3:
Where are Insulation Gaskets typically installed in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Explanation: Insulation Gaskets are typically installed at pipeline joints and flanges to provide electrical insulation and prevent galvanic corrosion.
Question 4:
What is the function of an Insulation Gasket in preventing galvanic corrosion?
Explanation: An Insulation Gasket’s function in preventing galvanic corrosion is to separate dissimilar metals in contact, reducing the risk of corrosion.
Question 5:
What is the main advantage of using Insulation Gaskets in pipelines?
Explanation: The main advantage of using Insulation Gaskets in pipelines is the prevention of electrical arcing and corrosion, ensuring safety and integrity.
Question 6:
What is the maximum operating temperature range for Insulation Gaskets?
Explanation: The maximum operating temperature range for Insulation Gaskets typically falls within -40°C to 150°C, allowing them to function effectively in various conditions.
Question 7:
What type of flange connection are Insulation Gaskets commonly used with?
Explanation: Insulation Gaskets are commonly used with raised face flanges in pipeline applications.
Question 8:
What is the typical thickness range of Insulation Gaskets?
Explanation: The typical thickness range of Insulation Gaskets falls within 3-6 mm, providing adequate insulation while maintaining flexibility.
Question 9:
What is the purpose of the outer protective layer on some Insulation Gaskets?
Explanation: The outer protective layer on some Insulation Gaskets is used to protect against moisture, chemicals, and weather, enhancing their durability.
Question 10:
What is the typical lifespan of high-quality Insulation Gaskets in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Explanation: High-quality Insulation Gaskets in the Oil & Gas Industry typically have a lifespan ranging from 15 to 20 years when properly maintained and used under appropriate conditions.