The Oil and Gas Industry is a complex and multifaceted sector that relies on a wide range of instruments and technologies to ensure the efficient extraction, processing, and transportation of hydrocarbons. Among these instruments, venturimeters play a crucial role in measuring and controlling fluid flow, which is a fundamental aspect of many oil and gas operations. In this article, we will explore the significance of venturimeters in the industry, their principles of operation, various types, applications, and the benefits they bring to oil and gas projects.
Table of Contents
Do not miss the detailed course 7 Modules of Piping Codes & Standards
Enrollment link
Understanding Venturimeters
Definition and Purpose
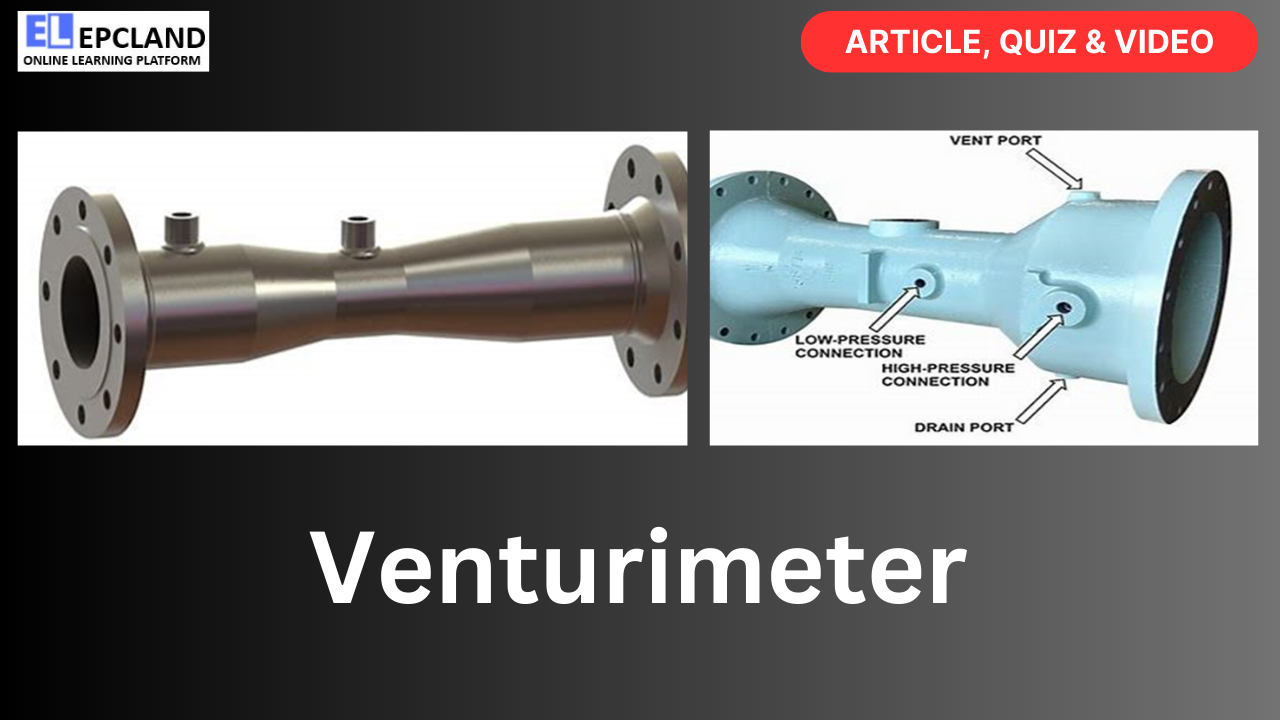
A venturimeter is a specialized flow measurement device that operates on the principle of Bernoulli’s equation. It is designed to measure the flow rate of a fluid (liquid or gas) passing through a pipeline or conduit. Venturimeters are particularly useful in the Oil and Gas Industry, where accurate flow measurement is critical for process control, safety, and economic considerations.
Principles of Operation
Venturimeters operate on the principles of fluid dynamics, specifically Bernoulli’s equation, which relates the pressure, velocity, and elevation of a fluid in a streamline. The venturimeter consists of a converging section (throat) followed by a diverging section. When fluid flows through the venturimeter, it accelerates as it enters the throat due to the narrowing of the passage. According to Bernoulli’s equation, as the fluid velocity increases, the pressure decreases. This pressure drop is measured to determine the flow rate.
Types of Venturimeters
Venturimeters come in various types, each tailored to specific applications within the Oil and Gas Industry. Some common types include:
1. Classical Venturimeter
The classical venturimeter is the standard design and consists of a converging section, throat, and diverging section. It is versatile and widely used for measuring flow rates of various fluids in pipelines and industrial processes.
2. Insertion Venturimeter
Insertion venturimeters are designed to be inserted into existing pipelines without the need for cutting or welding. They are often used for retrofitting flow measurement capabilities into an established pipeline system.
3. S-type Venturimeter
The S-type venturimeter is specially designed for applications where the fluid contains suspended solids or is prone to clogging. Its unique shape helps prevent debris from accumulating in the throat, ensuring accurate flow measurement.
4. Wet Gas Venturimeter
In the Oil and Gas Industry, natural gas often contains liquid droplets. Wet gas venturimeters are specifically designed to handle such conditions, providing accurate measurement even when both gas and liquid phases are present.
Applications of Venturimeters in Oil and Gas Industry Projects
Venturimeters find extensive use in a wide range of applications within the Oil and Gas Industry. Some of the key applications include:
1. Well Testing
In the exploration and production phase, venturimeters are used to measure the flow rates of oil, gas, and water from individual wells. This data is essential for reservoir management and optimizing production.
2. Pipeline Flow Measurement
Venturimeters are commonly employed in pipeline systems to monitor the flow of hydrocarbons, ensuring that the right quantity of oil or gas is transported safely and efficiently.
3. Refinery Operations
In petroleum refineries, venturimeters are utilized for measuring and controlling the flow of crude oil, intermediate products, and finished products through various processes such as distillation, cracking, and blending.
4. Gas Compression and Distribution
Venturimeters are used in gas compression and distribution systems to accurately measure the flow of natural gas, ensuring that it meets the demands of consumers while maintaining safety and efficiency.
5. Emissions Monitoring
For environmental compliance and safety, venturimeters play a role in measuring the flow of exhaust gases from combustion processes, helping companies adhere to emissions regulations.
6. Water Injection
In enhanced oil recovery (EOR) projects, venturimeters are employed to measure and control the injection of water or other fluids into reservoirs to improve oil recovery rates.
Advantages of Venturimeters
Venturimeters offer several advantages that make them highly suitable for use in the Oil and Gas Industry:
1. Accuracy
Venturimeters provide highly accurate flow measurements, making them ideal for critical applications where precision is paramount.
2. Minimal Pressure Loss
Compared to other flow measurement devices, venturimeters induce minimal pressure loss in the system, reducing energy consumption and operational costs.
3. Low Maintenance
Venturimeters are relatively simple in design, with no moving parts. This simplicity translates into lower maintenance requirements and longer service life.
4. Wide Range of Applications
The versatility of venturimeters allows them to be used in various applications, from well testing to emissions monitoring, making them valuable assets across the entire Oil and Gas Industry spectrum.
5. Resistance to Abrasion
In applications where the fluid may contain abrasive particles, venturimeters are less susceptible to wear and damage compared to some other flow measurement devices.
Do not miss the detailed course 7 Modules of Piping Codes & Standards
Enrollment link
Challenges and Considerations
While venturimeters offer numerous advantages, they are not without their challenges and considerations:
1. Installation and Sizing
Proper installation and sizing of venturimeters are critical to ensure accurate flow measurements. Improper installation can lead to measurement errors.
2. Cost
Venturimeters can be more expensive to install initially compared to some other flow measurement devices. However, their long-term reliability often justifies the initial investment.
3. Limited Turndown Ratio
Venturimeters may have limitations in measuring flow rates over a wide range. In applications with highly variable flow rates, other measurement devices may be more suitable.
4. Maintenance and Calibration
While venturimeters require less maintenance than some alternatives, they still need periodic inspection and calibration to ensure accurate measurements.
Conclusion
In the Oil and Gas Industry, where precise flow measurement is essential for operational efficiency, safety, and compliance, venturimeters play a vital role. Their ability to provide accurate measurements with minimal pressure loss, along with their resistance to wear and abrasion, makes them indispensable in various applications, from well testing and pipeline flow measurement to refinery operations and emissions monitoring.
As technology continues to advance, venturimeters are likely to become even more sophisticated, offering enhanced capabilities and accuracy. This, in turn, will contribute to the continued success and sustainability of the Oil and Gas Industry by ensuring that processes are optimized, resources are utilized efficiently, and environmental regulations are met.
In conclusion, venturimeters are not just measurement devices; they are essential tools that help drive the Oil and Gas Industry forward, ensuring that it operates safely, economically, and in harmony with the environment.
FAQs
- What is a venturimeter, and how does it work in the Oil and Gas Industry?
- A venturimeter is a flow measurement device that operates on Bernoulli’s principle. It measures fluid flow rates by creating a pressure drop as fluid accelerates through a constriction in a pipe or conduit. In the Oil and Gas Industry, venturimeters are used to measure and control the flow of hydrocarbons and other fluids.
- What are the key types of venturimeters used in the industry?
- There are several types of venturimeters used in the Oil and Gas Industry, including classical venturimeters, insertion venturimeters, S-type venturimeters, and wet gas venturimeters. Each type is designed for specific applications and conditions.
- Why are accurate flow measurements crucial in the Oil and Gas Industry?
- Accurate flow measurements are essential for optimizing production, ensuring safety, and meeting regulatory requirements. They help in monitoring the quantity of hydrocarbons transported, processed, or injected, which directly impacts operational efficiency and revenue.
- What are the advantages of using venturimeters in the Oil and Gas Industry?
- Venturimeters offer advantages such as high accuracy, minimal pressure loss, low maintenance, versatility in applications, and resistance to abrasion. These benefits make them valuable for various industry operations.
- What are some common applications of venturimeters in oil and gas projects?
- Venturimeters are used in well testing, pipeline flow measurement, refinery operations, gas compression and distribution, emissions monitoring, and water injection for enhanced oil recovery (EOR).
- What challenges should be considered when using venturimeters?
- Challenges include proper installation and sizing, initial cost, limited turndown ratio in some cases, and the need for periodic maintenance and calibration to ensure accurate measurements.
- How do venturimeters compare to other flow measurement devices in the industry?
- Venturimeters are known for their accuracy and low-pressure loss, but their suitability depends on specific applications. They are often compared to devices like orifice meters and electromagnetic flowmeters, with each having its advantages and limitations.
- Are venturimeters suitable for measuring flow rates in wet gas applications?
- Yes, wet gas venturimeters are specially designed to accurately measure flow rates in conditions where both gas and liquid phases are present. They are commonly used in the Oil and Gas Industry.
- Can venturimeters be retrofitted into existing pipeline systems?
- Yes, insertion venturimeters are designed for retrofitting into existing pipelines without the need for cutting or welding. They provide a convenient way to add flow measurement capabilities.
- How is the data from venturimeters utilized in oil and gas projects?
- The data collected by venturimeters is used for process control, production optimization, environmental compliance, and ensuring the safe and efficient transportation and processing of hydrocarbons. It is critical for decision-making and maintaining operational excellence.
Do not miss the detailed course 7 Modules of Piping Codes & Standards
Enrollment link
Recommended courses (Published on EPCLand)
- Basics of Piping Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Complete Course on Piping Engineering
- Material Requisitions
- Piping Material Specifications
- Valve Material Specifications
Don’t miss the published articles on following:
| Data Analysis and Technology with Link | Data Analysis and Technology with Link |
| Data Analytics | Industrial Control Networks |
| Machine Learning | The Power of Acoustic Sensors |
Related Video
Attempt Quiz
Question 1:
What is the primary purpose of a Venturimeter in the oil & gas industry?
Explanation: A Venturimeter is primarily used to measure fluid flow rate in the oil & gas industry.
Question 2:
Which principle of fluid mechanics is utilized in a Venturimeter?
Explanation: A Venturimeter operates based on Bernoulli’s principle.
Question 3:
What happens to the fluid’s velocity in the constricted portion of a Venturimeter?
Explanation: In the constricted portion of a Venturimeter, the fluid’s velocity increases.
Question 4:
What type of energy is converted in a Venturimeter to measure fluid flow?
Explanation: In a Venturimeter, kinetic energy of the fluid is converted to measure fluid flow.
Question 5:
Which of the following factors can affect the accuracy of a Venturimeter’s flow measurement?
Explanation: Fluid viscosity is one of the factors that can affect the accuracy of a Venturimeter’s flow measurement.