I. Introduction
In the complex world of oil and gas extraction and processing, precision and control are paramount. One critical component that plays a crucial role in maintaining this control is the Chemical Injection Quill. This article explores the significance of Chemical Injection Quills in the oil and gas industry, shedding light on their history, basic functionality, types, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and the codes and standards that govern their usage.
Table of Contents
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
II. Brief History
The use of Chemical Injection Quills traces its roots back to the mid-20th century when the oil and gas industry started to embrace chemical additives for enhanced production and safety. Before the advent of quills, injecting chemicals into pipelines and process streams was a challenging and imprecise task. The need for a more controlled and efficient method led to the development of the Chemical Injection Quill.
III. Basic Function and Working Principle
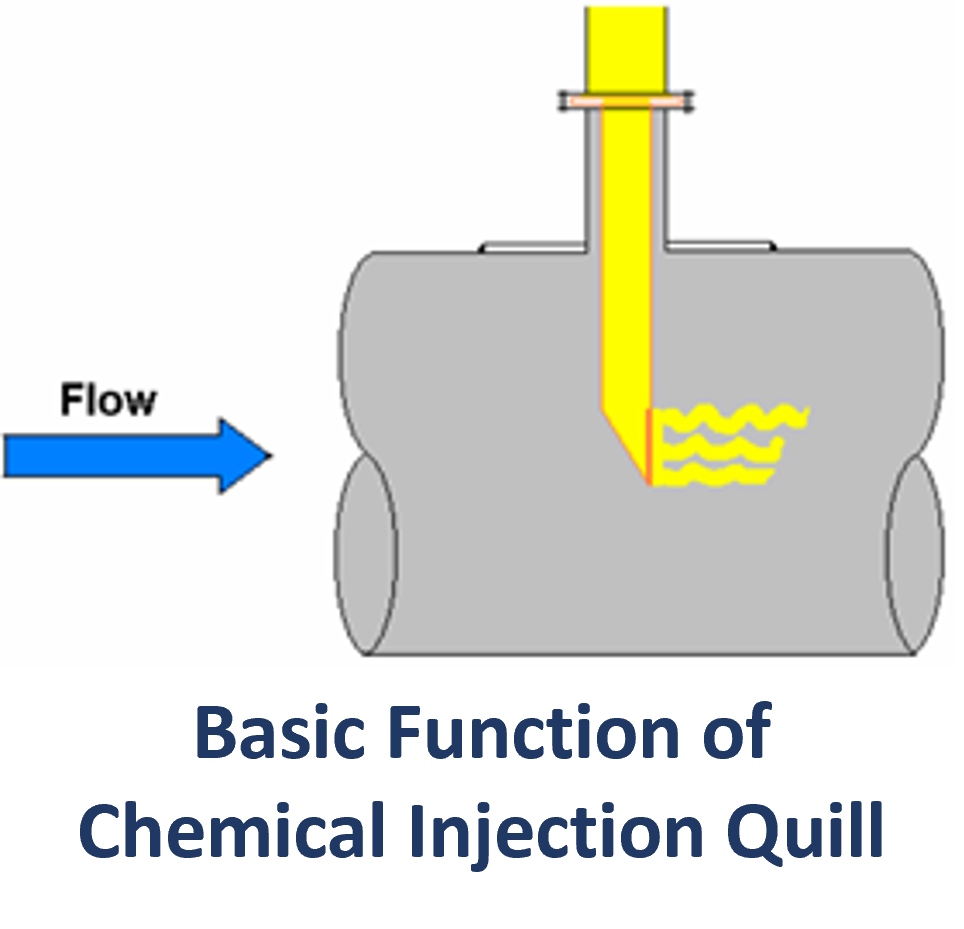
3.1 Functionality
Chemical Injection Quills are specialized devices designed to precisely introduce chemicals into a flowing fluid stream, a crucial process in the oil and gas industry. They serve several key functions:
a. Precise Chemical Injection: The primary purpose of a Chemical Injection Quill is to ensure the accurate and consistent injection of chemicals into a fluid system. This precision is essential because the effectiveness of various chemical treatments, such as corrosion inhibition, scale control, and hydrate prevention, relies on the correct dosage.
b. Chemical Dispersion: Another critical function of the quill is to disperse the injected chemicals evenly within the main fluid stream. This even distribution maximizes the chemicals’ effectiveness by ensuring that they are thoroughly mixed with the process fluid.
c. Minimization of Chemical Waste: Chemical Injection Quills are designed to minimize chemical waste. By injecting chemicals precisely where they are needed and ensuring thorough mixing, they help avoid over-injection and the unnecessary use of expensive chemicals.
d. Enhanced Safety: The controlled injection of chemicals by quills also contributes to safety. By preventing the over-concentration of certain chemicals in specific areas of the pipeline or equipment, quills help maintain the integrity of the system and reduce safety risks.
3.2 Working Principle
The working principle of a Chemical Injection Quill is relatively straightforward, yet highly effective. It involves the following components and steps:
a. Quill Design: A typical Chemical Injection Quill consists of a tube or pipe, often made of corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or plastic. At the end of this tube, there is a specialized diffuser or mixing element. The design of the diffuser plays a crucial role in achieving uniform chemical dispersion.
b. Installation: The quill is installed directly into the process pipeline or vessel. It is positioned in such a way that it intercepts a small portion of the main fluid flow. This intercepted side stream is where the chemicals will be injected and mixed.
c. Fluid Diversion: As the main fluid flows through the pipeline or vessel, a small portion of it is diverted through the quill. This diversion is achieved through the quill’s design and placement within the system. The side stream, which now contains a fraction of the main fluid, is directed into the quill.
d. Chemical Injection: Chemicals are introduced into the side stream at this point. The injection method varies depending on the quill’s design but often involves a separate chemical injection line or connection. The chemicals are precisely metered and introduced into the side stream.
e. Mixing and Dispersion: The side stream, now carrying the injected chemicals, passes through the diffuser at the end of the quill. The diffuser’s design promotes thorough mixing by creating turbulence and ensuring that the chemicals are evenly dispersed throughout the side stream.
f. Recombination: After passing through the diffuser, the chemically treated side stream recombines with the main fluid flow. This recombination ensures that the chemicals are distributed evenly within the process fluid, achieving the desired chemical treatment effect throughout the system.
IV. Main Components of a Chemical Injection Quill and Their Functions
A Chemical Injection Quill is a precision instrument designed to introduce chemicals into a flowing fluid stream in the oil and gas industry. Its effectiveness relies on several key components, each serving a crucial role in ensuring the accurate and controlled injection of chemicals. Here are the main components and their functions:
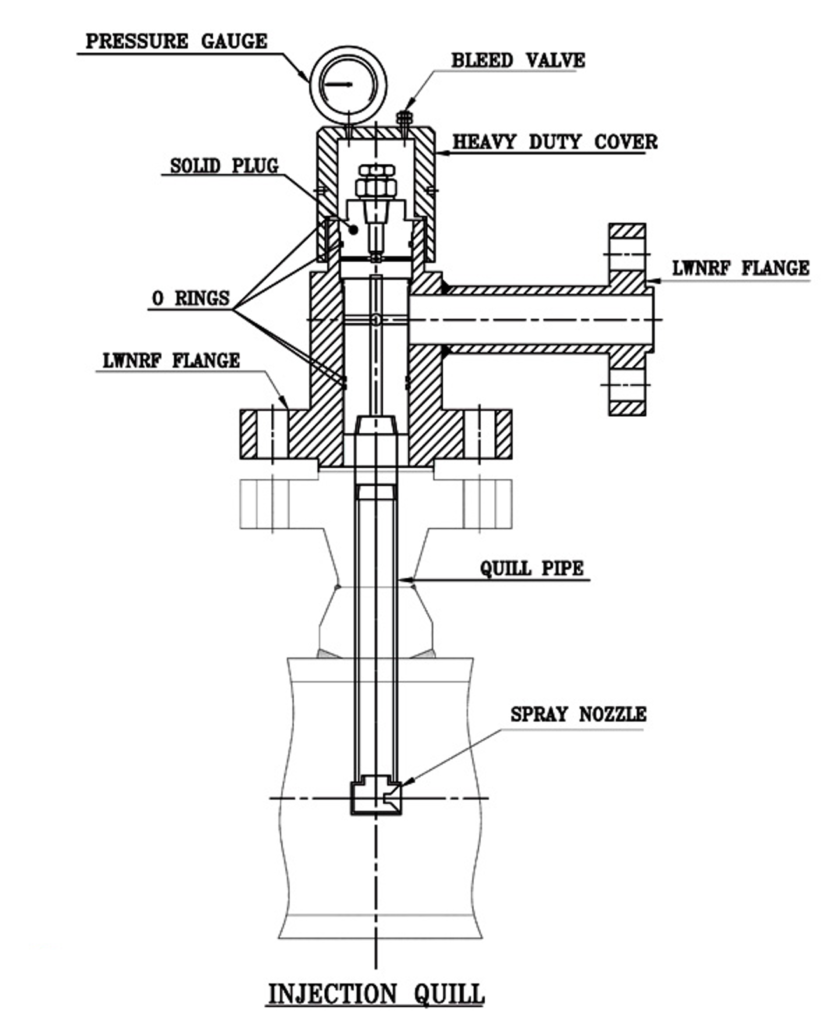
1. Quill Body or Tube
Function: The quill body or tube is the primary structure of the quill. It is typically made of corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or plastic. The quill body serves as a conduit through which the chemical is delivered into the main fluid stream.
2. Injection Nozzle or Tip
Function: The injection nozzle or tip is located at the end of the quill body and is responsible for releasing the chemical into the flowing fluid. Its design is crucial for ensuring uniform dispersion and mixing of the chemical with the main fluid. The nozzle is engineered to create a turbulent zone that promotes thorough mixing.
3. Diffuser
Function: The diffuser is a specially designed section of the quill, typically located downstream of the injection nozzle. Its primary function is to distribute the injected chemical evenly into the main fluid stream. By creating turbulence and dispersion, the diffuser ensures that the chemical is thoroughly mixed with the main fluid, preventing localized concentrations and ensuring uniform treatment.
4. Check Valve
Function: In some Chemical Injection Quill designs, a check valve is integrated into the quill body. The check valve prevents backflow of the main fluid into the quill, ensuring that the chemical only flows into the process stream and not in reverse. This feature is essential for maintaining the integrity of the chemical injection process.
5. Retractable Mechanism (for Retractable Quills)
Function: In the case of retractable quills, a retractable mechanism is a critical component. It allows the quill to be removed or retracted from the process pipeline without interrupting the overall system. This feature facilitates maintenance, replacement, or inspection of the quill without the need for a system shutdown.
6. Mounting Hardware
Function: The mounting hardware includes the fittings and connections required to secure the Chemical Injection Quill to the process pipeline or vessel. Proper mounting ensures the quill’s stability and alignment, allowing for accurate and consistent chemical injection.
7. Chemical Inlet
Function: The chemical inlet is the point at which the chemical is introduced into the quill. It is connected to a chemical supply line or container. The design of the chemical inlet must accommodate the specific requirements of the chemical being injected, such as pressure and flow rate.
8. Flow Control Devices (optional)
Function: Some Chemical Injection Quill designs incorporate flow control devices, such as valves or flow meters, to precisely control the rate at which the chemical is injected. These devices allow for fine-tuning of the injection process to meet the specific needs of the application.
9. Isolation Valve (optional)
Function: In certain applications, an isolation valve may be included upstream of the quill. This valve allows for the isolation and shutdown of the quill, ensuring that the chemical injection can be temporarily halted for maintenance or other purposes.
10. Pressure Relief Valve (optional)
Function: In situations where pressure regulation is critical, a pressure relief valve may be incorporated into the quill. This valve helps maintain a consistent pressure within the quill, preventing overpressurization and ensuring the safe and controlled injection of chemicals.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
V. Types of Chemical Injection Quills
Chemical Injection Quills come in various types and configurations, each designed to meet specific requirements and applications in the oil and gas industry. Here, we’ll explore these types in greater detail:
1. Fixed Quills
Overview: Fixed Chemical Injection Quills are permanently installed in the process pipeline or vessel. They are designed for applications where a constant and consistent injection rate is required.
Key Features:
- Stability: Fixed quills are stable and reliable, ensuring a steady injection of chemicals over time.
- Simplicity: They are relatively straightforward to install and operate, making them a common choice for many applications.
Applications:
- Corrosion Inhibition: Fixed quills are commonly used to inject corrosion inhibitors into pipelines to protect against rust and corrosion.
- Scale and Deposit Control: They are effective in introducing scale inhibitors to prevent scaling in pipelines and equipment.
2. Retractable Quills
Overview: Retractable Chemical Injection Quills are designed to be removed or retracted from the process pipeline without shutting down the entire system. They are useful when maintenance, replacement, or adjustment of the quill is necessary.
Key Features:
- Maintenance Flexibility: Retractable quills allow for easier access and maintenance, reducing downtime and operational disruptions.
- Adjustability: They offer the flexibility to change injection points or rates without extensive modifications.
Applications:
- Hydrate Inhibition: In applications where the risk of hydrate formation is high, retractable quills enable the adjustment of hydrate inhibitor injection points.
- Changing Chemicals: When switching between different chemicals, retractable quills simplify the process by allowing easy removal and replacement of the quill.
3. Direct and Indirect Quills
Overview: Chemical Injection Quills can be categorized as either direct or indirect, depending on how they introduce chemicals into the fluid stream.
Key Features:
- Direct Quills: These quills inject chemicals directly into the flowing fluid within the pipeline.
- Indirect Quills: Indirect quills introduce chemicals into a separate mixing chamber or manifold, where they are mixed with the main fluid before rejoining the process stream.
Applications:
- Direct Quills: Direct quills are commonly used when a precise injection point is required, such as injecting corrosion inhibitors directly into a high-corrosion area.
- Indirect Quills: Indirect quills are used in situations where it’s essential to thoroughly mix chemicals with the process fluid before they interact with the pipeline or equipment. This can help ensure even distribution and prevent localized reactions.
4. Adjustable Quills
Overview: Adjustable Chemical Injection Quills allow for the regulation and fine-tuning of the chemical injection rate. They provide flexibility in controlling the amount of chemical introduced into the fluid stream.
Key Features:
- Injection Rate Control: Adjustable quills can be customized to achieve precise injection rates, making them suitable for applications with varying chemical requirements.
- Flowrate Variability: They can adapt to changes in fluid flow rates, ensuring that the correct amount of chemical is injected at all times.
Applications:
- Well Treatments: In oil and gas well treatments, the flow rate of fluids may vary. Adjustable quills are useful for injecting chemicals at rates proportional to the flow.
- Batch Processes: Industries that use batch processes benefit from adjustable quills to control chemical injection during different phases of production.
5. Material-Specific Quills
Overview: Some applications in the oil and gas industry require Chemical Injection Quills made from specific materials to withstand harsh environments or corrosive fluids.
Key Features:
- Material Selection: These quills are designed using materials that are resistant to the chemicals being injected or to the environmental conditions of the process.
- Durability: Material-specific quills ensure long-term durability and performance in challenging conditions.
Applications:
- Sour Service Environments: In areas with sour gas (containing hydrogen sulfide), special material-specific quills are used to prevent corrosion and maintain safety.
- High-Temperature Applications: For processes involving high temperatures or extreme pressures, quills made from heat-resistant materials are employed.
VI. Applications of Chemical Injection Quills
Chemical Injection Quills find extensive applications in the oil and gas industry:
6.1 Corrosion Prevention
Corrosion is a pervasive issue in the oil and gas industry due to the aggressive nature of many fluids and the high-pressure, high-temperature environments in which equipment operates. Chemical Injection Quills play a crucial role in preventing corrosion by injecting specialized corrosion inhibitors into pipelines and vessels.
These inhibitors form a protective film on the inner surfaces of pipes and equipment, reducing the rate of corrosion. By introducing these inhibitors precisely and consistently, quills help extend the lifespan of critical infrastructure, such as pipelines and wellheads. Corrosion prevention is essential not only for maintaining operational efficiency but also for ensuring the safety and integrity of oil and gas facilities.
6.2 Scale and Deposit Control
Scaling and the buildup of deposits in pipelines and equipment can impede fluid flow, reduce efficiency, and increase maintenance costs. Chemical Injection Quills are employed to inject scale inhibitors into the fluid streams, mitigating scaling issues caused by minerals and other substances present in the fluids.
Scale inhibitors disrupt the formation of scale crystals, preventing them from adhering to the inner surfaces of pipelines and equipment. This process helps maintain the flow capacity of pipelines and minimizes the need for frequent maintenance and cleaning. Effective scale and deposit control are vital for preventing costly production interruptions and maintaining the efficiency of oil and gas operations.
6.3 Hydrate Inhibition
In the oil and gas industry, the formation of gas hydrates poses a significant challenge, especially in subsea and deepwater operations. Gas hydrates are ice-like compounds that can block pipelines, valves, and equipment, causing severe operational disruptions and safety hazards.
Chemical Injection Quills are used to introduce hydrate inhibitors into the flow streams. These inhibitors alter the thermodynamic conditions, preventing hydrate formation even in high-pressure, low-temperature environments. The controlled injection of hydrate inhibitors ensures uninterrupted fluid flow and safeguards against potentially catastrophic hydrate blockages.
6.4 Chemical Dosing
Beyond their specific applications in corrosion prevention, scale control, and hydrate inhibition, Chemical Injection Quills are also employed for general chemical dosing in various processes within the oil and gas industry. Some common applications include:
6.4.1 Wastewater Treatment
Oil and gas operations generate wastewater containing various contaminants, including hydrocarbons and chemicals. Chemical Injection Quills are used to introduce chemicals for treating and purifying wastewater before discharge, complying with environmental regulations.
6.4.2 Desalination
In offshore oil and gas facilities, seawater is often used for various purposes, including cooling. Chemical Injection Quills can introduce chemicals for desalination processes, ensuring the removal of salt and other impurities from seawater before it is used in industrial processes.
6.4.3 Process Control
In some cases, quills are used to introduce chemicals for process control, maintaining specific conditions within the system. For example, pH-adjusting chemicals can be precisely dosed into process streams to optimize chemical reactions or maintain required pH levels.
6.5 Enhanced Safety
The application of Chemical Injection Quills enhances safety in the oil and gas industry by ensuring the effective delivery of chemicals. Safety is paramount in this industry, and the precise injection of chemicals is critical for preventing equipment failures, operational disruptions, and potentially hazardous situations. By maintaining the integrity of pipelines and equipment through corrosion prevention, scale control, and hydrate inhibition, quills contribute significantly to overall safety.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
VII. Advantages & Disadvantages
7.1 Advantages of Chemical Injection Quills
- Precise Chemical Injection: Quills ensure accurate and consistent chemical injection rates, improving the effectiveness of chemical treatments.
- Easy Installation: Quills can be easily installed in existing pipelines or systems without extensive modifications.
- Reduced Chemical Waste: The efficient mixing provided by quills minimizes chemical waste.
- Enhanced Safety: Controlled chemical injection helps in maintaining the integrity of pipelines and equipment, reducing safety risks.
7.2 Disadvantages of Chemical Injection Quills
- Maintenance: Quills require periodic maintenance, and if not properly maintained, they can become clogged or malfunction.
- Initial Cost: The cost of purchasing and installing quills can be relatively high, especially for retractable or specialized quill designs.
- Limited Flow Rates: Quills may have limitations on the maximum flow rates they can handle.
VIiI. Associated Codes & Standards
The oil and gas industry is highly regulated, and Chemical Injection Quills must adhere to specific codes and standards to ensure safety and reliability. Some of the relevant standards include:
8.1 API RP 14J: Recommended Practice for Design and Hazards Analysis for Offshore Production Facilities
This American Petroleum Institute (API) document provides guidance on the design and analysis of hazards in offshore production facilities, including the use of chemical injection systems like quills.
8.2 ASME B31.3: Process Piping
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) B31.3 standard addresses process piping systems, including those involving chemical injection quills.
8.3 NACE MR0175/ISO 15156: Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries – Materials for Use in H2S-Containing Environments in Oil and Gas Production
This standard specifies requirements for materials used in sour service, which may include materials used in chemical injection quills for sour gas applications.
IX. Conclusion
In the oil and gas industry, precision and control are essential for maintaining safe and efficient operations. Chemical Injection Quills have emerged as vital tools for ensuring the accurate and effective introduction of chemicals into process streams. Their history, functionality, types, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and adherence to industry standards all contribute to their significance in this critical industry. As technology continues to advance, Chemical Injection Quills are expected to play an even more crucial role in optimizing oil and gas processes while ensuring safety and environmental compliance.
FAQs
1. What is a Chemical Injection Quill, and how does it work?
- A Chemical Injection Quill is a specialized device used to introduce chemicals into a flowing fluid stream in a controlled and efficient manner. It works by diverting a small portion of the fluid through the quill, where chemicals are injected and then thoroughly mixed using a diffuser. The chemically treated side stream is then reintroduced into the main fluid, ensuring even distribution of the chemicals.
2. What types of chemicals are typically injected using Chemical Injection Quills?
- Chemical Injection Quills are used to introduce a variety of chemicals into oil and gas processes, including corrosion inhibitors, scale inhibitors, hydrate inhibitors, and other treatment chemicals. The specific type of chemical depends on the application and the desired outcome, such as preventing corrosion, controlling scaling, or inhibiting hydrate formation.
3. What are the main advantages of using Chemical Injection Quills in the oil and gas industry?
- Some key advantages of using Chemical Injection Quills include:
- Precise and consistent chemical injection rates.
- Easy installation in existing pipelines or systems.
- Reduced chemical waste due to efficient mixing.
- Enhanced safety by maintaining the integrity of pipelines and equipment.
4. Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with Chemical Injection Quills?
- While Chemical Injection Quills offer numerous benefits, they also have some limitations, including:
- The need for periodic maintenance to prevent clogging or malfunction.
- Initial costs, which can be relatively high, especially for specialized or retractable quill designs.
- Limitations on maximum flow rates, which may not be suitable for all applications.
5. What industry standards and codes govern the use of Chemical Injection Quills in the oil and gas sector?
- Chemical Injection Quills in the oil and gas industry must adhere to specific codes and standards to ensure safety and reliability. Some relevant standards include API RP 14J (Recommended Practice for Design and Hazards Analysis for Offshore Production Facilities), ASME B31.3 (Process Piping), and NACE MR0175/ISO 15156 (Materials for Use in H2S-Containing Environments in Oil and Gas Production).
Recommended courses (Published on EPCLand)
- Basics of Piping Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Complete Course on Piping Engineering
- Material Requisitions
- Piping Material Specifications
- Valve Material Specifications
Don’t miss the published articles on following:
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
Attempt Quiz
Question 1:
What is the primary purpose of a Chemical Injection Quill in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Explanation: A Chemical Injection Quill is primarily used to inject chemicals into pipelines for various purposes in the Oil & Gas Industry.
Question 2:
What is the typical material of construction for Chemical Injection Quills?
Explanation: Chemical Injection Quills are commonly constructed from materials like Stainless Steel for their corrosion resistance and durability.
Question 3:
What is the purpose of a check valve in a Chemical Injection Quill?
Explanation: A check valve in a Chemical Injection Quill is used to ensure one-way chemical flow and prevent backflow into the injection line.
Question 4:
What is the typical location for installing a Chemical Injection Quill in a pipeline?
Explanation: A Chemical Injection Quill is typically installed downstream of a control valve to ensure proper mixing and dispersion of injected chemicals.
Question 5:
What is the purpose of an erosion-resistant tip on a Chemical Injection Quill?
Explanation: An erosion-resistant tip on a Chemical Injection Quill is used to prevent wear and damage from abrasive chemicals, ensuring durability and longevity.
Question 6:
Which type of chemicals are commonly injected using Chemical Injection Quills?
Explanation: Chemical Injection Quills are versatile and can be used to inject a wide range of chemicals, including corrosion inhibitors and biocides.
Question 7:
What is the main advantage of using a Chemical Injection Quill in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Explanation: The main advantage of using a Chemical Injection Quill in the Oil & Gas Industry is the ability to achieve precise and controlled chemical injection, enhancing process efficiency and safety.
Question 8:
Which industry standards are commonly followed in the design and installation of Chemical Injection Quills?
Explanation: API RP 14E is a commonly followed industry standard for the design and installation of Chemical Injection Quills in the Oil & Gas Industry.
Question 9:
What is the typical method of connecting a Chemical Injection Quill to a pipeline?
Explanation: A typical method of connecting a Chemical Injection Quill to a pipeline is through a threaded connection, ensuring a secure and leak-free attachment.
Question 10:
What is the recommended maintenance interval for Chemical Injection Quills in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Explanation: The recommended maintenance interval for Chemical Injection Quills in the Oil & Gas Industry varies but is typically based on performance and condition, requiring maintenance as needed.