1. Introduction
Flame arrestors are indispensable safety devices in the oil and gas industry, playing a pivotal role in preventing catastrophic events like explosions and fires. These devices are engineered to halt the progression of flames, ensuring the safety of equipment, personnel, and the environment. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the origins, working principles, types, applications, and standards of flame arrestors, shedding light on their paramount importance in the oil and gas sector.
Table of Contents
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
2. Brief History
Early Innovations and Developments
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| Late 19th c. | First experiments with flame control mechanisms |
| 20th Century | Advancements in materials and combustion dynamics |
| 21st Century | Specialized flame arrestors for diverse industrial needs |
The inception of flame arrestors traces back to the early days of industrialization when the oil and gas industry started facing the challenges posed by flammable gases and vapors. In the late 19th century, pioneering engineers began experimenting with various mechanisms to curb the spread of flames. These rudimentary designs paved the way for more sophisticated and efficient flame arrestors that we rely on today.
Milestones and Innovations
The evolution of flame arrestors witnessed significant milestones during the 20th century. Advancements in materials, coupled with a deeper understanding of combustion dynamics, led to the development of specialized flame arrestors for different applications. Notable innovations include the introduction of deflagration and detonation arrestors, each designed to handle specific types of combustion processes.
3. Basic Function and Working Principle
The Fundamental Purpose
At its core, a flame arrestor operates with the objective of preventing flame propagation. When flammable gases or vapors pass through the device, the flame arrestor interrupts the flame front, extinguishing it and averting a potential explosion. Understanding the underlying principles is essential to grasp the significance of these devices in the oil and gas industry.
Working Mechanism
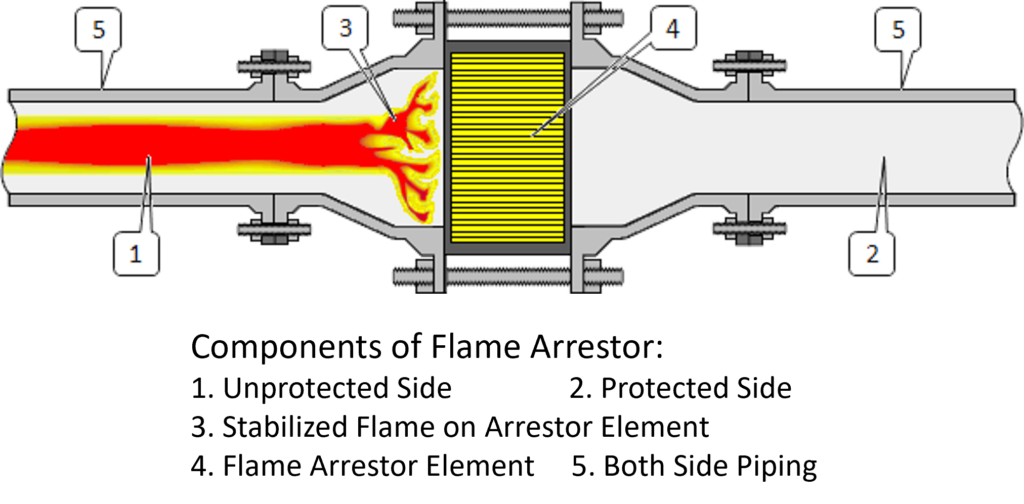
The working principle of a flame arrestor involves the careful arrangement of its components. When a flame front encounters the arrestor, the device’s elements disrupt the combustion process. Typically, this is achieved through a combination of mesh screens, perforated plates, and spiral wound elements, each meticulously designed to quench the flame without impeding the flow of gases.
4. Main Components and Their Functions
Flame Arrester Element
| Material | Function |
|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Disrupts the flame front, allowing gas passage |
| Mesh Screens | Quenches the flame, preventing further propagation |
The flame arrester element, often made of stainless steel or other high-temperature resistant materials, is the heart of the device. Its intricate design disrupts the flame front while allowing the passage of gases. Mesh screens and perforated plates are common forms of flame arrester elements, with their effectiveness depending on factors like pore size and thickness.
Housing
| Feature | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Durable Materials | Provides structural integrity and protection |
| Easy Installation | Facilitates convenient setup and maintenance for longevity |
The housing encapsulates the flame arrester element, providing structural integrity and protection. It is constructed from durable materials to withstand harsh industrial environments. The housing also incorporates features to facilitate easy installation and maintenance, ensuring the long-term functionality of the flame arrestor.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
5. Types of Flame Arrestors
Deflagration Arrestors
| Application | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Pipelines | Prevents flame propagation in subsonic combustion |
| Storage Tanks | Safeguards against accidental ignition sources |
Deflagration arrestors are designed to quench flames resulting from deflagration, a rapid combustion process with subsonic flame propagation. These arrestors are commonly used in pipelines and storage tanks where the risk of deflagration exists due to the presence of flammable gases or vapors.
Detonation Arrestors
| Application | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Refineries and Petrochemicals | Handles supersonic combustion, providing safety in high-pressure areas |
Detonation arrestors are engineered to handle the more severe threat posed by detonation, a supersonic combustion process. Detonation arrestors employ specialized designs and materials to withstand the intense pressures and shockwaves generated during detonation events. They find application in facilities where high-pressure gas discharges are anticipated.
6. Applications of Flame Arrestors in the Oil & Gas Industry
Pipelines
In oil and gas pipelines, the presence of flammable hydrocarbons necessitates the installation of flame arrestors at strategic points. These arrestors prevent flame propagation in case of accidental ignition, ensuring the safety of the entire pipeline network and nearby areas.
Storage Tanks
Storage tanks containing volatile substances are susceptible to ignition sources such as lightning strikes or static electricity. Flame arrestors installed on the tank vents mitigate the risk of explosions by extinguishing any flames that might develop within the tanks, safeguarding both the storage facility and the surrounding environment.
Refineries and Petrochemical Plants
Refineries and petrochemical plants house a myriad of processes involving flammable gases and liquids. Flame arrestors are integrated into various equipment and pipelines within these facilities, including distillation columns, reactors, and transfer lines. Their presence ensures that any accidental ignition does not escalate into a catastrophic event, preserving the integrity of the entire operation.
7. Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Flame Arrestors
- Enhanced Safety: Flame arrestors significantly enhance the safety of industrial operations by preventing explosions and fires, thereby protecting personnel and assets.
- Compliance with Regulations: Adherence to safety regulations and standards is mandatory in the oil and gas industry. Flame arrestors aid in compliance, avoiding legal complications.
- Minimal Disruption: Flame arrestors function passively, meaning they do not disrupt the normal flow of gases until an ignition event occurs. This ensures continuous operations without interruptions.
Disadvantages of Flame Arrestors
- Maintenance Requirements: Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the proper functioning of flame arrestors. Accumulated debris or corrosion can impair their effectiveness.
- Initial Cost: The upfront cost of installing flame arrestors might be relatively high, especially for specialized applications. However, this cost is often outweighed by the safety benefits they provide.
8. Codes and Standards for Flame Arrestors
International Fire Codes (IFC)
The International Fire Code (IFC) outlines specific requirements for the installation and maintenance of flame arrestors in industrial facilities. It provides guidelines on proper placement, testing procedures, and documentation, ensuring that flame arrestors meet the necessary safety standards.
American Petroleum Institute (API) Standards
API standards, such as API 2000 for venting atmospheric and low-pressure storage tanks, incorporate detailed specifications for flame arrestors. These standards cover various aspects, including sizing, materials, and performance criteria, offering comprehensive guidelines for engineers and manufacturers.
National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) Standards
NFPA standards, particularly NFPA 69 on explosion prevention systems, are essential references for flame arrestor design and implementation. These standards focus on risk assessment, vent sizing, and flame arrester selection, providing a holistic approach to safety in industrial settings.
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
9. Conclusion
Flame arrestors stand as guardians against the perilous consequences of industrial fires and explosions in the oil and gas sector. As technology advances and our understanding of combustion processes deepens, the design and efficacy of these essential safety devices continue to improve. By adhering to stringent standards and embracing innovative solutions, the industry ensures the protection of its workforce, assets, and the environment. In the ever-evolving landscape of the oil and gas industry, flame arrestors remain steadfast, exemplifying the marriage of engineering brilliance and unwavering commitment to safety.
FAQs
- Q1: What is the primary function of a flame arrestor in the oil and gas industry?A: Flame arrestors in the oil and gas industry serve as crucial safety devices designed to prevent the propagation of flames and explosions. They achieve this by interrupting the flame front, ensuring the safety of equipment, personnel, and the surrounding environment.
- Q2: Where are flame arrestors commonly used within oil and gas facilities?A: Flame arrestors find widespread applications in various areas of oil and gas facilities, including pipelines, storage tanks, refineries, and petrochemical plants. They are strategically installed to mitigate the risk of explosions and fires, particularly in locations where flammable gases and vapors are present.
- Q3: How do different types of flame arrestors, such as deflagration and detonation arrestors, differ in their functionality?A: Deflagration arrestors are designed to handle rapid combustion processes with subsonic flame propagation, while detonation arrestors are engineered to handle the more severe threat of supersonic combustion. Detonation arrestors employ specialized designs and materials to withstand intense pressures and shockwaves generated during detonation events.
- Q4: What are the maintenance requirements for flame arrestors, and how often should they be inspected?A: Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the proper functioning of flame arrestors. Inspection intervals vary based on factors such as the operating environment and the specific guidelines provided by manufacturers. Generally, flame arrestors should be inspected periodically for signs of corrosion, debris accumulation, and overall integrity to guarantee their effectiveness.
- Q5: What industry standards and regulations govern the design and installation of flame arrestors in the oil and gas sector?A: Flame arrestors must adhere to industry standards such as the International Fire Code (IFC), American Petroleum Institute (API) standards, and National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) standards. These regulations provide comprehensive guidelines on proper design, sizing, installation, and maintenance, ensuring the safety and compliance of flame arrestors in industrial settings.
Recommended courses (Published on EPCLand)
- Basics of Piping Engineering
- Piping Layout Engineering
- Piping Material Engineering
- Piping Stress Analysis
- Complete Course on Piping Engineering
- Material Requisitions
- Piping Material Specifications
- Valve Material Specifications
Don’t miss the published articles on following:
Don’t miss the Complete Course on Piping Engineering: Check Now
Enrollment Link
Attempt Quiz
Question 1:
What is the primary function of a flame arrestor in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Explanation: Flame arrestors are designed to prevent the propagation of flames and protect equipment in the Oil & Gas Industry.
Question 2:
Which of the following types of flames can a flame arrestor prevent?
Explanation: Flame arrestors can prevent both small and large flames from propagating.
Question 3:
Where are flame arrestors commonly used in the Oil & Gas Industry?
Explanation: Flame arrestors are used in various applications, including pipelines, storage tanks, and vents in the Oil & Gas Industry.
Question 4:
What is the purpose of the mesh or perforated plate in a flame arrestor?
Explanation: The mesh or perforated plate in a flame arrestor blocks flame propagation while allowing gas flow.
Question 5:
Which of the following gases/fluids are flame arrestors designed to handle?
Explanation: Flame arrestors are designed to handle various gases and liquids in the Oil & Gas Industry.
Question 6:
Which of the following is NOT a common type of flame arrestor?
Explanation: Convection flame arrestors are not a common type of flame arrestor.
Question 7:
Why is grounding important for flame arrestors?
Explanation: Grounding is important for flame arrestors to prevent static electricity buildup and potential sparks.
Question 8:
What is the purpose of the flame quenching gap in a flame arrestor?
Explanation: The flame quenching gap in a flame arrestor extinguishes the flame by cooling and disrupting the combustion process.
Question 9:
Which material is commonly used to construct flame arrestors?
Explanation: Stainless steel is commonly used to construct flame arrestors due to its resistance to high temperatures and corrosion.
Question 10:
What is the main difference between deflagration and detonation flame arrestors?
Explanation: Deflagration flame arrestors handle small flames, whereas detonation flame arrestors handle large flames and higher pressures.



